(Press-News.org) Embargoed for release until 5:00 p.m. ET on Monday 9 October 2023
Annals of Internal Medicine Tip Sheet
@Annalsofim
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not only on their own behalf, but also on behalf of the organization they represent.
----------------------------
1. History of parental infertility associated with small increased risk for birth defects among children conceived through fertility treatment
Experts urge informed decision-making when choosing a reproductive technology
Abstract: https://www.acpjournals.org/doi/10.7326/M23-0872
URL goes live when the embargo lifts
A study of more than 850,000 children born in Australia found that parental infertility may be a factor for a small increased risk of birth defects in children conceived through fertility treatment. The authors also found that the use of intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) was associated with an increased risk for major genitourinary abnormalities. However, the authors caution that the overall increase in the relative risks is small. The study is published in Annals of Internal Medicine.
Many children are conceived through assisted reproductive technology (ART) cycles each year. Previous research has shown that children born from ART have a 25% to 50% increased risk for congenital abnormalities, particularly cardiac and genitourinary anomalies. However, it is unclear how much of this risk can be attributed to parental infertility problems compared to ART treatment.
Researchers from University of New South Wales, Sydney, Australia, conducted propensity score–weighted population-based cohort study of 851,984 infants born between 2009 and 2017 in New South Wales, Australia. The authors found that there were approximately 40 additional cases of any major congenital abnormality per 10,000 singleton ART births compared to singletons conceived naturally to parents without prior infertility problems. This risk became insignificant when ART-conceived children were compared to children conceived naturally to parents with a history of infertility. The authors say that these findings suggest that parental infertility may partly explain the increase in risk seen in ART-conceived children. The authors also found that ICSI treatment was a risk factor for genitourinary anomalies, even in couples without male infertility. They note that these findings strongly suggest that ICSI represents an independent risk factor for congenital abnormalities and should be reserved for patients with male infertility.
Media contacts: For an embargoed PDF, please contact Angela Collom at acollom@acponline.org. To speak with the corresponding author Georgina M. Chambers, Ph.D., please contact g.chambers@unsw.edu.au.
----------------------------
2. Researchers describe horrific effects of new drug threat, xylazine, or "tranq"
An animal sedative approved by the FDA, xylazine has now made its way to the illicitly manufacture fentanyl supply, creating new challenges for physicians caring for its victims
Abstract: https://www.acpjournals.org/doi/10.7326/M23-2001
Editorial: https://www.acpjournals.org/doi/10.7326/M23-2299
URL goes live when the embargo lifts
Xylazine, an animal sedative that is approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for veterinary use only, has made its way into the illicitly manufactured fentanyl (IMF) supply and has significantly increased in prevalence in recent years, likely due to its low cost, easy availability, and presumed enhanced "high." Researchers reviewed pertinent xylazine research and pulled from their own clinical experience to offer new guidance on the care of patients exposed to this dangerous drug. Their review is published in Annals of Internal Medicine.
The authors provide several critical recommendations for health care institutions and agencies to help combat the threat of xylazine and improve awareness among providers. They suggest educating providers in many settings (emergency departments, primary care, low-barrier clinics, opioid treatment
programs, office-based opioid treatment programs) on the alterations in recognition, acknowledgment, prophylaxis, and treatment in the presence of chronic xylazine use; conducting animal and human research to further investigate xylazine–fentanyl pharmacology, toxicology, adverse effects, withdrawal syndrome, and treatment strategies; expanding screening to include xylazine on standard urine drug testing; further define the test characteristics to understand the parameters and timing of testing; harm-reduction efforts including increased surveillance of the drug supply and xylazine test strip distribution; expanding access to low-barrier treatment settings with collocated substance use disorder and wound care treatment; and expanding access to inpatient and residential settings where both wound care and substance use disorder treatment are offered.
An accompanying editorial by authors from New York University and University of Florida College of Medicine emphasizes the importance of comprehensive surveillance of xylazine use and poisonings. The authors note that most data on xylazine use comes from decedents and an increasing number of studies monitoring hospitalization, very little is known about the more common outcome—use that does not lead to hospitalization or death. The authors suggest several courses of action that can be taken to increase understanding of xylazine use and risk, including monitoring drug-using persons who are not currently at risk; including xylazine in drug testing efforts; and educating users, clinicians, and researchers about exposure.
Media contacts: For an embargoed PDF, please contact Angela Collom at acollom@acponline.org. To speak with the corresponding author Joseph D’Orazio, M.D., please contact Joseph D’Orazio at dorazio-joseph@cooperhealth.edu
----------------------------
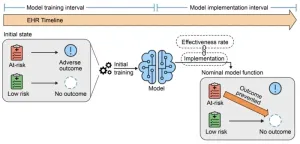
3. AI predictive models shown to be unreliable over time in clinical settings
Abstract: https://www.acpjournals.org/doi/10.7326/M23-0949
Editorial https://www.acpjournals.org/doi/10.7326/M23-2345
URL goes live when the embargo lifts
A simulation study of artificial intelligence (AI) predictive models using electronic health record (EHR) data in the ICU setting found that the successful use of such models may impair the function of other models – present and future, as well as themselves. This impaired function will manifest as unnecessary investigations and procedures. The authors also report that retraining these models did not significantly reduce these errors. The study is published in Annals of Internal Medicine.
Researchers from Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai Health System and the University of Michigan School of Medicine simulated 3 common scenarios of model implementation and associated changes in model performance using data from 130,000 critical care admissions. The scenarios each consider deployment of models to predict the risk for death or acute kidney injury (AKI) in the first 5 days after admission to the ICU. Scenario 1 considers the result of implementing and retraining a mortality prediction model, scenario 2 considers the implementation of an AKI model followed by the creation of a new mortality prediction model, and scenario 3 considers the simultaneous implementation of both an AKI and mortality prediction model. The authors found that the model in scenario 1 lost 9 to 39% specificity after retraining once. The mortality model in scenario 2 lost 8% to 15% specificity when created after the AKI model had been in use. In scenario 3, models for AKI and mortality prediction implemented simultaneously, each led to reduced effective accuracy of the other by 1% to 28%. The authors report that in each scenario, performance for models trained on data from populations that benefit from interventions afforded by model prediction is inferior to performance of the original model.
Based on their findings, rather than adopting a universal strategy, model developers should simulate each model’s updating strategy at each site where a model is to be implemented. They also recommend measures to track how and when predictions influence clinical decision making, because most suggested mitigation strategies rely on this information being available, and EHR data may be rendered unsuitable for training models otherwise.
An accompanying editorial by authors from Johns Hopkins University provides important context to these findings. They note that the drift observed in the models included in this study appear in AI in other contexts, including popular large language models like Chat GPT. The authors highlight that these models collapse if recursively trained on their own output, and this “noise” introduced to other clinical models may further degrade clinical predictions in the future. The editorial authors also suggest that fixing model drift starting with inspection, rather than immediate correction, may help. They suggest that, as with other interventions, clinical trials may be required to evaluate the effect of AI models on relevant clinical outcomes.
Media contacts: For an embargoed PDF, please contact Angela Collom at acollom@acponline.org. To speak with the corresponding authors Akhil Vaid, M.D., and Girish N. Nadkarni, M.D. please contact Karin Eskenazi at karin.eskenazi@mssm.edu.
----------------------------
4. Physicians debate best screening tools and practices for patients with potential dementia and cognitive impairment
‘Beyond the Guidelines’ features are based on the Department of Medicine Grand Rounds at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center
Abstract: https://www.acpjournals.org/doi/10.7326/M23-1808
URL goes live when the embargo lifts
In a new Annals ‘Beyond the Guideline’s feature, two experts review the available evidence about cognitive impairment to determine effective screening tools, interventions to improve patient outcomes, and the circumstances under which they would recommend screening for cognitive impairment (CI). All ‘Beyond the Guidelines’ features are based on the Department of Medicine Grand Rounds at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC) in Boston and include print, video, and educational components published in Annals of Internal Medicine.
Dementia, according to the American Psychiatric Association’s Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, is defined by a significant decline in 1 or more cognitive domains that interferes with a person’s independence in daily activities. Mild cognitive impairment differs from dementia in that the impairment is not sufficient to interfere with independence. A variety of screening tests are available for Cognitive Impairment. A positive screening test does not diagnose CI; rather it should lead to additional testing to confirm the diagnosis. Upon review of the evidence, the United States Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) concluded in 2020 that the evidence was insufficient to assess the balance of benefits and harms of screening for cognitive impairment in older adults (“I statement”). The USPSTF did clarify that although there is insufficient evidence, there may be important reasons to identify CI.
BIDMC Grand Rounds discussants, Michael Barry, M.D., Chair of the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force and a Professor of Medicine at Harvard Medical School, and Deborah Blacker, M.D., ScD, member of the Department of Psychiatry and the Alzheimer's Disease Research Center at Massachusetts General Hospital and Professor of Psychiatry at Harvard Medical School recently debated the case of Ms. B., a 75-year-old woman who, along with her primary care physician, were wondering whether she should be screened for memory loss given multiple risk factors and her desire to be proactive about her medical care.
Dr. Barry explained the rationale for the “I” statement and the lack of sufficient evidence from either the direct or indirect evidence pathway to recommend for or against screening. Dr. Blacker agrees that the available screening tests have issues with reliability, especially in certain patient populations. Both discussants also agree that the established agents have limited efficacy and have not been observed to change the course of the disease. Dr. Blacker reviewed that the newer antiamyloid agents may change the course of the disease, but any cognitive benefits are modest and carry the risk for significant adverse effects. Dr. Barry reviewed that although the USPSTF found that there is insufficient evidence to recommend for or against screening, there may be important reasons to identify CI, as early detection may allow for identification and treatment of reversible causes, help clinicians be aware of patients who might have difficulty understanding and adhering to medical treatment plans, and provide useful information for patients and families as they begin advance care planning. Dr. Blacker concurs and adds that these potential benefits add to the importance of developing a system that conducts and supports screening in primary care. In summary, Dr. Barry would leave the informed decision to screen our patient, Ms. B, to her and her clinician. Dr. Blacker would grant Ms. B's request for screening, as she thinks Ms. B's request may reflect greater difficultie than are otherwise apparent and that, given her family responsibilities and complex medical regimen, the prompt recognition of CI is of particular importance.
A complete list of ‘Beyond the Guidelines’ topics is available at www.annals.org/grandrounds.
Media contacts: For an embargoed PDF, please contact Angela Collom at acollom@acponline.org. For an interview with the discussants, please contact Kendra McKinnon at kmckinn1@bidmc.harvard.edu.
END
History of parental infertility associated with small increased risk for birth defects among children conceived through fertility treatment
2023-10-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
What is the impact of predictive AI in the health care setting?
2023-10-09
Models built on machine learning in health care can be victims of their own success, according to researchers at the Icahn School of Medicine and the University of Michigan. Their study assessed the impact of implementing predictive models on the subsequent performance of those and other models. Their findings—that using the models to adjust how care is delivered can alter the baseline assumptions that the models were “trained” on, often for worse—were detailed in the October 9 online issue of Annals of Internal Medicine: https://www.acpjournals.org/doi/10.7326/M23-0949.
“We wanted to explore ...
Space weather disrupts nocturnal bird migration, study finds
2023-10-09
Graphics
It's well-known that birds and other animals rely on Earth's magnetic field for long-distance navigation during seasonal migrations.
But how do periodic disruptions of the planet's magnetic field, caused by solar flares and other energetic outbursts, affect the reliability of those biological navigation systems?
University of Michigan researchers and their colleagues used massive, long-term datasets from networks of U.S. Doppler weather radar stations and ground-based magnetometers—devices that measure the ...
Long-term lizard study challenges the rules of evolutionary biology
2023-10-09
Charles Darwin said that evolution was constantly happening, causing animals to adapt for survival. But many of his contemporaries disagreed. If evolution is always causing things to change, they asked, then how is it that two fossils from the same species, found in the same location, can look identical despite being 50 million years apart in age?
Everything changed in the past 40 years, when an explosion of evolutionary studies proved that evolution can and does occur rapidly — even from one generation to the next. Evolutionary biologists were thrilled, but the findings reinforced the same paradox: If evolution can happen so fast, then why do most species on Earth continue to ...
No lizard is an island
2023-10-09
Many species experience little to no change over long periods of time. Biologists often fall back on the same explanation for why this is true: that natural selection favors individuals with more moderate characteristics. Individuals with more extreme features — longer limbs, for example — have a disadvantage, while more moderate or average individuals are more likely to survive and reproduce, passing on their common features.
But new research from Washington University in St. Louis and the Georgia ...
Nature is inventive - the same substance is produced differently by plants
2023-10-09
Maize plants form special compounds derived from indole, the so-called benzoxazinoids. They are considered ecologically important because they act against a wide range of herbivores and reduce their feeding. Benzoxazinoids also exhibit antimicrobial properties and are thought to be involved in mediating plant-plant interactions. Their biosynthesis in maize has been known since the 1990s. Meanwhile, their biosynthetic pathway has been described in several grasses, but benzoxazinoids have also been found in other plant species. Their distribution is peculiar: While specialized metabolites often occur in specific evolutionary related plant species, benzoxazinoids ...
AI language models could help diagnose schizophrenia
2023-10-09
Scientists at the UCL Institute for Neurology have developed new tools, based on AI language models, that can characterise subtle signatures in the speech of patients diagnosed with schizophrenia.
The research, published in PNAS, aims to understand how the automated analysis of language could help doctors and scientists diagnose and assess psychiatric conditions.
Currently, psychiatric diagnosis is based almost entirely on talking with patients and those close to them, with only a minimal role for tests such as blood tests and brain scans.
However, ...
Ancient Maya reservoirs offer lessons for today’s water crises
2023-10-09
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — According to a new paper, ancient Maya reservoirs, which used aquatic plants to filter and clean the water, “can serve as archetypes for natural, sustainable water systems to address future water needs.”
The Maya built and maintained reservoirs that were in use for more than 1,000 years, wrote University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign anthropology professor Lisa Lucero in a perspective in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. These reservoirs provided potable water for thousands to tens of thousands of people in cities during the annual, five-month dry season and in periods of prolonged ...
Evidence from the remains of 1918 flu pandemic victims contradicts long-held belief that healthy young adults were particularly vulnerable
2023-10-09
Hamilton, ON, Oct. 9, 2023 – New analysis of the remains of victims of the 1918 influenza pandemic, which killed an estimated 50 million people worldwide, contradicts the widespread belief the flu disproportionately impacted healthy young adults.
Because so many people fell ill so quickly, physicians at the time believed the healthy were as likely to die from the flu as those who had already been sick or frail. Despite numerous historical accounts, though, it turns out there is no concrete scientific evidence to support that belief.
Researchers at McMaster University and the University of Colorado Boulder ...
Could a specialized diet alleviate long COVID?
2023-10-09
LOS ANGELES — Approximately 7% of Americans have had long COVID, a range of ongoing health problems experienced after infection and recovery from COVID-19. Symptoms can include fatigue, brain fog, headaches, chest pain, heart palpitations and more.
To date, there is no proven treatment for the syndrome, and the mechanisms that cause it are not fully understood.
Now, a new clinical trial from Keck Medicine of USC is investigating if a diet designed to lower inflammation may play a role in easing this often debilitating condition.
The premise of ...
Miriam Merad, M.D., Ph.D., elected to the National Academy of Medicine for seminal work in immunology and cell biology
2023-10-09
Miriam Merad, M.D., Ph.D., an esteemed immunologist at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, has been elected to the National Academy of Medicine (NAM) in recognition of her pioneering contributions to the fields of immunology and cell biology.
Dr. Merad was elected for her transformational discoveries, establishing for the first time that tissue-resident macrophages have distinct origins, maintain their lineage separately from adult hematopoiesis, and possess unique functions that enhance tissue health, repair, infection defense, and impact tumor outcomes.
She is the Mount Sinai Professor ...