(Press-News.org) CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — According to a new paper, ancient Maya reservoirs, which used aquatic plants to filter and clean the water, “can serve as archetypes for natural, sustainable water systems to address future water needs.”
The Maya built and maintained reservoirs that were in use for more than 1,000 years, wrote University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign anthropology professor Lisa Lucero in a perspective in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. These reservoirs provided potable water for thousands to tens of thousands of people in cities during the annual, five-month dry season and in periods of prolonged drought.
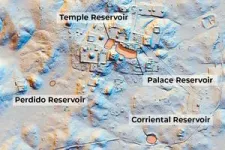
“Most major southern lowland Maya cities emerged in areas that lacked surface water but had great agricultural soils,” Lucero said. “They compensated by constructing reservoir systems that started small and grew in size and complexity.”
Over time, the Maya built canals, dams, sluices and berms to direct, store and transport water. They used quartz sand for water filtration, sometimes importing it from great distances to massive cities like Tikal in what is now northern Guatemala. A sediment core from one of Tikal’s reservoirs also found that zeolite sand had been used in its construction. Previous studies have shown that this volcanic sand can filter impurities and disease-causing microbes from water. The zeolite also would have been imported from sources about 18 miles (30 kilometers) away.
“Tikal’s reservoirs could hold more than 900,000 cubic meters of water,” Lucero wrote. Estimates suggest that up to 80,000 people lived in the city and its environs in the Late Classic period, roughly 600 to 800 C.E. The reservoirs kept people and crops hydrated during the dry season, Lucero said.
Maya royalty got much of their status from their ability to provide water to the populace.
“Clean water and political power were inextricably linked – as demonstrated by the fact that the largest reservoirs were built near palaces and temples,” Lucero wrote. The kings also performed ceremonies to gain the favor of ancestors and the rain god, Chahk.
A key challenge was to keep standing water in reservoirs from becoming stagnant and undrinkable, and for that the Maya likely relied on aquatic plants, many of which still populate Central American wetlands today, Lucero said. These include cattails, sedges, reeds and others. Some of these plants have been identified in sediment cores from Maya reservoirs.
These plants filtered the water, reducing murkiness and absorbing nitrogen and phosphorous, Lucero said.
“The Maya would have had to dredge every several years… (and) harvest and replenish aquatic plants,” she wrote. The nutrient-laden soils and plants removed from reservoirs could then be used to fertilize urban fields and gardens.
The most iconic aquatic plant associated with the ancient Maya is the water lily, Nymphaea ampla, which thrives only in clean water, Lucero said. Its pollen has been found in sediment cores from several Maya reservoirs. Water lilies symbolized “Classic Maya kingship,” Lucero wrote.
“The kings even donned headdresses adorned with the flowers and are depicted with water lilies in Maya art,” Lucero said.
“Water lilies do not tolerate acidic conditions or too much calcium such as limestone or high concentrations of certain minerals like iron and manganese,” she wrote.
To keep water lilies alive, water managers would have had to line the reservoirs with clay, Lucero said. A layer of sediment would be needed for plants’ roots. In turn, the water lilies and trees and shrubs planted near the reservoirs shaded the water, cooling it and inhibiting the growth of algae.
“The Maya generally did not build residences near reservoir edges, so contamination seeping through the karstic terrain would not have been an issue,” Lucero wrote.
The evidence gathered from several southern lowland cities indicates that, as constructed wetlands, Maya reservoirs supplied potable water to people for more than 1,000 years, failing only when the severest droughts took hold in the region between 800 and 900 C.E., Lucero said. She notes that current climate trends will require many of the same approaches the Maya employed, including the use of aquatic plants to improve and maintain water quality naturally.
“Constructed wetlands provide many advantages over conventional wastewater treatment systems,” she wrote. “They provide an economical, low technology, less expensive and high energy-saving treatment technology.”
In addition to providing clean water, constructed wetlands also support aquatic animals and can be a source of nutrients to replenish agricultural soils, she wrote.
“The next step moving forward is to combine our respective expertise and implement the lessons embodied in ancient Maya reservoirs in conjunction with what is currently known about constructed wetlands,” she wrote.
Editor’s note:
To reach Lisa Lucero, email ljlucero@illinois.edu
Once published, the paper “Ancient Maya Reservoirs, Constructed Wetlands, and Future Water Needs” is available online or from the U. of I. News Bureau.
DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2306870120
END
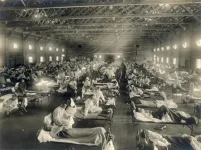
Hamilton, ON, Oct. 9, 2023 – New analysis of the remains of victims of the 1918 influenza pandemic, which killed an estimated 50 million people worldwide, contradicts the widespread belief the flu disproportionately impacted healthy young adults.
Because so many people fell ill so quickly, physicians at the time believed the healthy were as likely to die from the flu as those who had already been sick or frail. Despite numerous historical accounts, though, it turns out there is no concrete scientific evidence to support that belief.
Researchers at McMaster University and the University of Colorado Boulder ...
LOS ANGELES — Approximately 7% of Americans have had long COVID, a range of ongoing health problems experienced after infection and recovery from COVID-19. Symptoms can include fatigue, brain fog, headaches, chest pain, heart palpitations and more.
To date, there is no proven treatment for the syndrome, and the mechanisms that cause it are not fully understood.
Now, a new clinical trial from Keck Medicine of USC is investigating if a diet designed to lower inflammation may play a role in easing this often debilitating condition.
The premise of ...
Miriam Merad, M.D., Ph.D., an esteemed immunologist at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, has been elected to the National Academy of Medicine (NAM) in recognition of her pioneering contributions to the fields of immunology and cell biology.
Dr. Merad was elected for her transformational discoveries, establishing for the first time that tissue-resident macrophages have distinct origins, maintain their lineage separately from adult hematopoiesis, and possess unique functions that enhance tissue health, repair, infection defense, and impact tumor outcomes.
She is the Mount Sinai Professor ...
In cases where standard therapies fail, a medication called XEN1101 reduces seizure frequency by more than 50% in some patients and sometimes eliminates them altogether, a new study shows. Unlike several treatments that must be started at low doses and slowly ramped up, the new drug can safety be taken at its most effective dose from the start, the authors say.
Focal seizures, the most common type seen in epilepsy, occur when nerve cells in a particular brain region send out a sudden, excessive burst of electrical signals. Along with seizures, this uncontrolled activity can lead to abnormal behavior, periods of lost awareness, and mood changes. ...
*EMBARGOED UNTIL 11 A.M. MONDAY, OCT. 9*
Liquid biopsies are blood tests that can serially measure circulating tumor DNA (cell-free DNA that is shed into the bloodstream by dying cancer cells). When used in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer undergoing immunotherapy, they may identify patients who could benefit from treatment with additional drugs, according to a phase 2 clinical trial in the U.S. and Canada. The trial is led by investigators at the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center and its Bloomberg~Kimmel ...
In the game of soccer (association football), goalkeepers have a unique role. To do the job well, they must be ready to make split-second decisions based on incomplete information to stop their opponents from scoring a goal. Now researchers reporting in Current Biology on October 9 have some of the first solid scientific evidence that goalkeepers show fundamental differences in the way they perceive the world and process multi-sensory information.
“Unlike other football players, goalkeepers are required to make thousands of very fast decisions based on limited or incomplete sensory information,” says Michael Quinn, the study’s ...
About The Study: This study of 23,000 individuals found a higher risk of all-cause, cardiovascular disease, and ischemic heart disease mortality among adults with moderate to severe depressive symptoms compared to those without depressive symptoms. Public health efforts to improve awareness and treatment of depression and associated risk factors could support a comprehensive, nationwide strategy to reduce the burden of depression.
Authors: Zefeng Zhang, M.D., Ph.D., of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in Atlanta, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: ...
About The Study: During the first full calendar year of the pandemic, approximately 1 in 5 adolescents had major depressive disorder, and less than half of adolescents who needed treatment had any mental health treatment, according to this analysis of nationally representative survey data of 10,000 U.S. adolescents. Adolescents in racial and ethnic minority groups, particularly Latinx, experienced the lowest treatment rates.
Authors: Michael William Flores, Ph.D., M.P.H., of the Cambridge Health Alliance in Cambridge, Massachusetts, is the corresponding author.
To access ...
A new, bio-inspired drug restores the effectiveness of immune cells in fighting cancer, a team led by researchers at The University of Texas at Austin has found. In mouse models of melanoma, bladder cancer, leukemia and colon cancer, the drug slows the growth of tumors, extends lifespan and boosts the efficacy of immunotherapy. The research is published in the journal Cancer Cell and could be a game changer for many cancer patients.
Many cancers delete a stretch of DNA called 9p21, which is the most common deletion across all cancers, occurring in 25%-50% of certain cancers such as melanoma, bladder ...
A new combination of treatments safely decreased growth of pancreatic cancer in mice by preventing cancer cells from scavenging for fuel, a new study finds.
Led by researchers at NYU Grossman School of Medicine, its Department of Radiation Oncology, and the Perlmutter Cancer Center, the work builds on prior discoveries at NYU Langone that revealed how pancreatic cancer cells, to avert starvation and keep growing, find alternate fuel sources. Normally supplied by the bloodstream, oxygen, blood sugar, and other resources become scarce as the increasing density of fast-growing pancreatic tumors cuts off their own blood supply. ...