(Press-News.org) Researchers from Texas Christian University, University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, and University of Georgia published a new Journal of Marketing article that examines the consumer trend towards minimalist packaging in consumable products.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing, is titled “Symbolically Simple: How Simple Packaging Design Influences Willingness to Pay for Consumable Products” and is authored by Lan Anh N. Ton, Rosanna K. Smith, and Julio Sevilla.
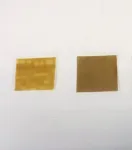
Designing products is both an art and a science. Companies have found that bringing together many visual elements in product design—with multiple colors, text, and illustrations incorporated in the packaging—can lead to enhanced brand engagement. However, in the last few years, consumers have increasingly desired more minimalist aesthetics.
The new Journal of Marketing study examines this consumer trend toward minimalist packaging in consumable products. The research team theorizes that consumers tend to assume that the simplicity of the product package suggests that the product contains few ingredients, which in turn increases perceived product purity, defined as the belief that the essential ingredients of the product are undiluted. With customers increasingly seeking product purity, there is an increase in a willingness to pay for consumable products with simple packaging.
The study defines simple packaging design as the extent to which a product package contains few design elements, which lack detail, are similar to one another, and are arranged in regular ways. Complex packaging design refers to the extent to which a product package contains many design elements that are highly detailed, different from one another, and arranged in irregular ways. The researchers examined over 1,000 consumable product packages from the largest supermarket chain in the U.S. and find that the simplicity of the packaging design is positively associated with price. As Ton explains, “in a series of experiments, we show that the visual design of a product can hold symbolic meanings to consumers. Specifically, although there is no information about the product’s composition on the package, we find that consumers assume that the simplicity of the product package signals that there are few ingredients within, which enhances perceived product purity.”
However, simple packaging does not always enhance consumers’ willingness to pay. Smith says, “we find that store-brand products are not likely to experience the same benefits of simple packaging as non-store brand products. This is likely because the simplicity of the product package aligns with consumers’ default assumption that store brands invest less in product quality. Thus, the simplicity of store brand packaging likely signals a lack of investment in the product rather than few ingredients and product purity.”
Sevilla adds that “we also find the preference for simple packaging depends on consumers’ goals. When consumers have a health goal, they are more likely to pay for a product with simple packaging. This is because simple packaging conveys that the product contains few ingredients and high product purity, attributes that tend to be associated with healthy products. By contrast, when consumers seek to indulge, they are less willing to pay for products with simple packaging. This is because complex packaging signals many ingredients and low product purity, attributes that tend to be associated with unhealthy and, by extension, tasty products.”
This research extends the understanding of consumer interest in minimalist aesthetics by showing conditions under which design simplicity can be less desirable. Visual simplicity often conveys the idea of “less is more,” but there are situations when it can simply signal “less is less.” It also broadens the understanding of the concept of purity in the context of consumer research. While explicit illustrations, such as a drawing of a mountain spring, can enhance consumer judgments of product purity, product purity can be inferred from more subtle visual cues (or even the lack of visual design elements). Relatedly, the study digs into the concept of product purity, which can hold a variety of meanings, and differentiates purity from its related construct of naturalness, which typically refers to products that are not man-made.
This research provides several insights for chief marketing officers:
Simplifying package design can be an effective way for brands to visually (and nonverbally) communicate key product information to consumers. Simple packaging can lead consumers to infer that the product has fewer ingredients and is purer—thereby enhancing their willingness to pay.
Aligning the visual design of the product package with ingredient information is essential to make a positive impact on consumers.
Managers may consider the specific brand when using simple packaging because positive inferences are less likely to occur for store-brand products.
When managers want to signal that their products are indulgent, opting for more complex designs could be more effective.
This work could be extended to durable goods such as technology products. For instance, Apple products are well-known for their simple packaging and are often seen as easier to use than their competitors. It may be fruitful to explore how inferences derived from simple packaging of technology products align or differ from those of consumable goods.
Full article and author contact information available at: https://doi.org/10.1177/00222429231192049
About the Journal of Marketing
The Journal of Marketing develops and disseminates knowledge about real-world marketing questions useful to scholars, educators, managers, policy makers, consumers, and other societal stakeholders around the world. Published by the American Marketing Association since its founding in 1936, JM has played a significant role in shaping the content and boundaries of the marketing discipline. Shrihari (Hari) Sridhar (Joe Foster ’56 Chair in Business Leadership, Professor of Marketing at Mays Business School, Texas A&M University) serves as the current Editor in Chief.
https://www.ama.org/jm
About the American Marketing Association (AMA)
As the largest chapter-based marketing association in the world, the AMA is trusted by marketing and sales professionals to help them discover what is coming next in the industry. The AMA has a community of local chapters in more than 70 cities and 350 college campuses throughout North America. The AMA is home to award-winning content, PCM® professional certification, premiere academic journals, and industry-leading training events and conferences.
https://www.ama.org
END
Is less more? Or is less sometimes less? Examining the consumer trend toward minimalist packaging in consumable products
News from the Journal of Marketing
2023-10-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Killer whales’ diet more important than location for pollutant exposure, study says
2023-10-11
Both elegant and fierce, killer whales are some of the oceans’ top predators, but even they can be exposed to environmental pollution. Now, in the largest study to date on North Atlantic killer whales, researchers in ACS’ Environmental Science & Technology report the levels of legacy and emerging pollutants in 162 individuals’ blubber. The animals’ diet, rather than location, greatly impacted contaminant levels and potential health risks — information that’s helpful to conservation efforts.
As the largest member of the dolphin family, killer whales, also known as orcas, are ...
Metal-organic frameworks could someday deliver antibacterial nitric oxide
2023-10-11
Because metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) — highly porous metal complexes — are so structurally and chemically diverse, they could be used for many applications, such as drug delivery and environmental clean-up. But researchers still need to get a better understanding of how they function, especially when embedded in polymers. Reporting in ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, researchers have now developed and characterized nitric oxide (NO)-storing MOFs embedded in a thin film with novel antibacterial potential.
Studying ...
Significant development in mild cognitive impairment treatment revealed in Australia
2023-10-11
AUSTRALIA, Sydney – October 11, 2023 – Western Sydney University’s NICM Health Research Institute has led a world-first clinical trial in Australia that offers new hope in the treatment of mild cognitive impairment (MCI) among older people. The trial’s results, published in Alzheimer's and Dementia: Diagnosis, Assessment and Disease Monitoring, a journal of the Alzheimer’s Association, signal the efficacy and safety of Sailuotong (SLT), a novel herbal extract, as a potential treatment for MCI.
Trial ...
Rivers may not recover from drought for years
2023-10-11
Lack of rainfall is not the only measure of drought. New UC Riverside research shows that despite a series of storms, the impact of drought can persist in streams and rivers for up to 3.5 years.
There are two measures of drought in streams. One measure is the total water level, which is impacted by snowmelt and rainfall. Many researchers examine this measurement. Another measure is baseflow, which is the portion of streamflow fed by groundwater.
Fewer researchers examine baseflow droughts, and there was not previously an accurate way to measure them. Because baseflow is strongly tied to groundwater, and because the ...
Chronic kidney disease may be linked to sudden cardiac arrest in Hispanic/Latino adults
2023-10-11
Research Highlights:
Chronic kidney disease was strongly associated with an increased risk of sudden cardiac arrest among Hispanic/Latino adults, in a new study.
Early identification and management of kidney disease may reduce risk of sudden cardiac arrest among Hispanic/Latino people, researchers suggest.
Embargoed until 4 a.m. CT/5 a.m. ET Wednesday, Oct. 11, 2023
DALLAS, October 11, 2023 — Chronic kidney disease may increase risk and predict sudden cardiac arrest among Hispanic/Latino adults, according to new research published today in the Journal of the American Heart Association, an open access, peer-reviewed journal of the American ...
Cardiac arrest: Hispanics, Latinos with kidney disease at high risk
2023-10-11
Hispanics and Latinos with chronic kidney disease are at significant risk for suffering from sudden cardiac arrest, according to a new study from the Smidt Heart Institute at Cedars-Sinai.
During sudden cardiac arrest, the heart unexpectedly stops beating.
“Because people who experience sudden cardiac arrest have a survival rate of less than 10%, prevention is extremely important,” said Kyndaron Reinier, Ph.D., associate director of Epidemiology in the Center for Cardiac Arrest Prevention at the Smidt Heart Institute and lead author of the study published in the Journal of the American Heart Association.
“This study highlights the importance for Hispanic ...
Tens of thousands of endangered sharks and rays caught off Congo
2023-10-11
Tens of thousands of endangered sharks and rays are caught by small-scale fisheries off the Republic of the Congo each year, new research shows.
Scientists surveyed fish brought ashore at Songolo, which is home to more than 60% of the country's “artisanal” fishers (small boats, small engines, hand-hauled lines and nets).
In three years, the team – led by the University of Exeter in partnership with the Wildlife Conservation Society (WCS) Congo Program and the Republic of the Congo’s fisheries department – recorded more than 73,000 sharks and rays landed.
Most were juveniles, and 98% of individuals were of species listed as vulnerable, ...
Bouldering in south-central Madagascar: a new “rock-climbing” gecko species of the genus Paroedura
2023-10-11
Named after its habitat preference, Paroedura manongavato, from the Malagasy words “manonga” (to climb) and “vato” (rock), is a bouldering expert. Part of its “home range” is also very well-known to rock climbers for its massive granitic domes. “Its description represents another step into the crux (in climbing jargon, the most difficult section of a bouldering problem) of resolving the taxonomy of the recently revised P. bastardi group, where the new species belongs, and reaching a total of 25 described species in this genus, ...
Peregrine falcons set off false alarms to make prey easier to catch
2023-10-11
Predators must eat to survive — and to survive, prey must avoid being eaten. One theory, the Wolf-Mangel model, suggests predators could use false attacks to tire prey out or force them to take bigger risks, but this has been hard to show in practice. Now, scientists observing peregrine falcons have found evidence that they deliberately exhaust their prey to improve later hunting success.
“Although predators are imagined as clever in novels and movies, like the velociraptors in Jurassic Park, empirical biologists are generally not inclined to give much credence to such ideas,” ...
Make diagnosing serious geriatric diseases as easy as measuring blood sugar
2023-10-11
In 2023, life expectancy in Korea will be 83.6 years, the third highest among OECD countries, and it is steadily increasing every year. As the proportion of the elderly population increases, the social cost of treating various geriatric diseases is also increasing rapidly, and there is a growing interest in early diagnosis of diseases. Among the various diagnostic methods, researchers are actively conducting research on measuring glutamine as an indicator of geriatric diseases by finding that the concentration of glutamine in the cells and blood of patients with serious diseases such as cancer, diabetes, and dementia is significantly changed compared to normal people.
Dr. Seo, Moon-Hyeong ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] Is less more? Or is less sometimes less? Examining the consumer trend toward minimalist packaging in consumable productsNews from the Journal of Marketing