(Press-News.org) DNA analysis of mummified poop reveals two pre-Columbian Caribbean cultures ate a wide variety of plants, like maize, sweet potato, and peanuts—and tobacco and cotton traces were detected too, according to a study published October 11, 2023 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Jelissa Reynoso-García from the University of Puerto Rico, Puerto Rico, and colleagues.
Mummified poop, or coprolites, can reveal clues to diet and lifestyle. In this study, Reynoso-García and colleagues analyzed plant DNA isolated from coprolites sampled from archeological sites of two pre-Columbian cultures (Huecoid and Saladoid) to see what these peoples ate and drank.
The authors carefully extracted and analyzed plant DNA from ten coprolite samples at the La Hueca archaeological site in Puerto Rico. They compared the extracted plant DNA against a database of diverse coprolite samples and contemporary plant DNA sequences.
The results suggest that Huecoid and Saladoid people enjoyed a diverse and sophisticated food system, with sweet potato, wild and domesticated peanut, chili peppers, a domesticated strain of tomatoes, papaya and maize all detected. The analysis also detected tobacco, possibly due to the use of chewing tobacco, pulverized tobacco inhalation, or tobacco as a food additive for medicinal and/or hallucinogenic purposes. Also surprisingly, cotton was detected—perhaps due to the use of ground cotton seeds for oil, or because women wet the cotton strands with their saliva leaving strands in the mouth while weaving. The authors did not find evidence of cassava/manioc/yucca (Manihot esculenta) consumption, though this plant was often reported as a staple food in the pre-Columbian Caribbean by chroniclers. The authors note that the elaborate grating and drying cassava preparation techniques reported in these accounts might have degraded the plant DNA, or that this might have been a seasonal staple food.
Due to food preparation techniques, the fact that each coprolite sample is only a snapshot of what one specific person had been recently eating, and the limitation that the authors were only able to identify plants also in current DNA sequence databases (not capturing any now-extinct, rare, or non-commercial crops) it’s likely that the Huecoid and Saladoid people ate other plants or fungi not noted here. Nevertheless, the authors hope this analysis gives further insight into the lives of pre-Columbian people of the Americas.
Dr. Toranzos adds: "Who would have thought that something that we avoid even looking at would contain so much information? It’s especially incredible that this is so even after thousands of years."
#####
In your coverage please use this URL to provide access to the freely available article in PLOS ONE: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0292077
Citation: Reynoso-García J, Santiago-Rodriguez TM, Narganes-Storde Y, Cano RJ, Toranzos GA (2023) Edible flora in pre-Columbian Caribbean coprolites: Expected and unexpected data. PLoS ONE 18(10): e0292077. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0292077
Author Countries: Puerto Rico, USA
Funding: (JRG) This study was partially supported by the National Institute of Health (NIH) Research Initiative for Scientific Enhancement (RISE) Program (Grant No. 5R25GM061151) https://brtc.uprrp.edu/rise/. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript. This study was also supported by an Institutional Development Award (IDeA) INBRE Grant Number P20GM103475 from the National Institute of General Medical Science (NIGMS), a component of the National Institutes of Health (NIH), and the Bioinformatics Research Core of the INBRE. Its contents are solely the responsibility of the authors and do not necessarily represent the official view of NIGMS or NIH. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
END
Mummified poop reveals pre-Columbian cultures of the Caribbean consumed a diversity of plants, with peanuts, papaya, maize, and even cotton and tobacco detected
2023-10-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Risk factors for dementia vary by ethnicity, study finds
2023-10-11
Modifiable risk factors—including hypertension, obesity, diabetes, low HDL cholesterol and sleep disorders—confer a higher risk of dementia for people in some minority ethnic groups compared to White people, according to a new study published this week in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Naaheed Mukadam of University College London, UK, and colleagues.
The number of people with dementia is on the rise around the world. There has been increasing interest in potentially modifiable risk factors, ...
Study links selfies to higher ratings of slimness
2023-10-11
In a new study, participants tended to rate women’s bodies as slimmer when viewed in selfie photographs than in photographs taken from other angles. Ruth Knight of York St John University, UK, and Catherine Preston of the University of York, UK, present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on October 11.
Popular on social media, selfies are portraits taken by the photo’s subject, who positions the camera away from their body but pointed back at themself. Prior research has suggested that viewing selfies might affect viewers’ judgments of the photo subjects’ attractiveness and could, in some cases, lead to ...
Groundbreaking achievement as bionic hand merges with user’s nervous and skeletal systems, remaining functional after years of daily use
2023-10-11
Karin's life took a dramatic turn when a farming accident claimed her right arm over 20 years ago. Since then, she endured excruciating phantom limb pain. “It felt like I constantly had my hand in a meat grinder, which created a high level of stress and I had to take high doses of various painkillers.” In addition to her intractable pain, she found that conventional prostheses were uncomfortable and unreliable, and thus of little help in daily life. All this changed when she received groundbreaking bionic technology that allowed her to wear a much more functional ...
Drug-filled nanocapsule helps make immunotherapy more effective in mice
2023-10-11
UCLA researchers have developed a new treatment method using a tiny nanocapsule to help boost the immune response, making it easier for the immune system to fight and kill solid tumors.
The investigators found the approach, described in the journal Science Translational Medicine, increased the number and activity of immune cells that attack the cancer, making cancer immunotherapies work better.
“Cancer immunotherapy has reshaped the landscape of cancer treatment,” said senior author of the ...
Trial results indicate potential for organ transplantation without long-term immunosuppression
2023-10-11
Giving living donor liver transplant recipients an infusion of immune cells derived from their donor a week before transplantation is feasible, safe – and may lead to recipients being successfully weaned off immunosuppressant medications without rejecting the transplanted organ.
The early-stage clinical trial results by University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine scientists, reported today in Science Translational Medicine, point to a path that may spare organ transplant recipients from the serious side effects of long-term immunosuppressant use, which can include cancer, diabetes, kidney failure and susceptibility to infections.
“These trial results are very encouraging,” ...
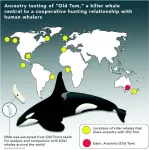
Evolutionary secrets of ‘Old Tom’ and the killer whales of Eden revealed by genetic study
2023-10-11
Evolutionary biologists have for the first time decoded the genetic lineage of a famous killer whale and a pod that once worked alongside whale hunters off the coast of New South Wales.
In the Australian tradition of claiming New Zealand’s celebrities as its own, Old Tom, the leader of a pod of killer whales that famously helped whalers hunt baleen whales in the 20th century, has ancestral links to modern-day killer whales in New Zealand, according to new DNA research.
Old Tom also shared a common ancestor with killer whales from Australasia, the North Pacific, and North Atlantic Oceans, but is most similar to modern New Zealand killer whales. However, most of Tom’s ...
Fruit fly serenade: Princeton neuroscientists decode their tiny mating song
2023-10-11
Love songs are at least as popular in the animal kingdom as on the radio. The importance of musically serenading your true love has driven plotlines from Twelfth Night to The Trumpet of the Swan to Happy Feet.
The latest exploration of music in the natural world is taking place in Mala Murthy’s lab at the Princeton Neuroscience Institute, where Murthy and her research group have used neural imaging, optogenetics, motion capture, modeling and artificial intelligence to pinpoint precisely where and how a fruit fly’s brain toggles between its standard solo and its mating serenade. Their research ...
Experiencing record-breaking heat days affects perception of weather trends
2023-10-11
PHILADELPHIA -- New research published by a team at the Annenberg Public Policy Center of the University of Pennsylvania finds that experiencing days in which the temperature exceeds previous highs for that time of year affects people’s perception of weather trends.
Published in Scientific Reports, the study “Record-breaking Heat Days Disproportionately Influence Heat Perceptions” finds that living in an area with record-breaking heat effectively increases perceptions that the weather is getting hotter. The research was co-authored by economist Timothy Hyde, a postdoctoral fellow in APPC’s Science of Science Communication Division, and psychologist and communication ...
Aston University researcher named in Photonics top 100
2023-10-11
Aston University professor named in international Top 100 of Photonics
Professor Igor Meglinski’s research overlaps engineering and health sciences
He applies his photonics knowledge to develop methods to detect diseases such as dementia and cancer.
An Aston University professor has been named in an international Top 100 of Photonics key players.
Igor Meglinski, professor in quantum bio-photonics and biomedical engineering was elected by fellow experts as one of the Top 100 in the field of photonics – the science and technology of light.
Although he is based in the College ...
Novel biomaterial delivers medication directly to fish gut
2023-10-11
A novel biomaterial developed at the Federal University of São Paulo (UNIFESP) in Brazil can help solve two problems at once. As a bioparticle, it can act as a drug carrier, delivering medication directly to the gastrointestinal tract of fish in order to circumvent resistance to conventional antibiotics, for example. In addition, it is administered orally in powder form and is highly palatable to fish, increasing the probability of effective treatment while at the same time reducing the waste ...