(Press-News.org) Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in daily products such as paints, adhesives, furniture, cosmetics, and deodorants make our lives easier. However, constant exposure can cause serious health problems such as respiratory illness, headaches, dermatitis, and cancer. Natural ventilation is the most effective way to reduce VOCs in indoor air, but recently, air purifiers have become a common method to maintain indoor air quality due to the frequent extreme outdoor condition (e.g. high concentration of fine dust, heat waves, and extreme cold). Generally, air purifiers remove VOCs by adsorption using activated carbon, which has a non-polar carbon surface and a large specific surface area. This activated carbon can effectively remove non-polar substances such as toluene and benzene, but cannot remove polar substances such as ketones and aldehydes.
The Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST, President Seok Jin Yoon) announced that Dr. Jiwon Lee and Dr. Youngtak Oh from the Center for Sustainable Environment Research have developed a new adsorbent technology that can efficiently adsorb amphiphilic VOCs, which have both hydrophilic and hydrophobic properties and are difficult to remove with existing activated carbon technology.
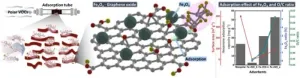
The KIST research team synthesized a graphene-iron oxide heterostructure by precisely controlling the surface oxidation of graphite and iron, resulting in a high adsorption capacity for amphiphilic VOCs due to the increase of oxygen functional groups and iron oxide on the surface. This unique adsorbent showed up to 15 times better adsorption efficiency for amphiphilic VOCs than conventional activated carbon adsorbents.
They also found that precise oxygen functional groups and iron oxides control of the adsorbent can offer flexible surface optimization freedom for a desirable nature of the pollutant. By testing four different ketones that are difficult to control with activated carbon adsorbents, the researchers found the correlation between the length of carbon chains and the adsorption efficiency; by optimizing the content of oxygen functional groups and iron oxides in the adsorbent, they were able to bring the maximum removal efficiency for the ketones. The researchers also analyzed the sub-nanometer electron transfer phenomenon between the adsorbent and VOC molecules; they found a link between the geometric shape of the pollutant and its adsorption trend for the first time. This is expected to enable the development of customized detection and control technologies for various air pollutants in our environment.
"Unlike previous studies that focused on mere improvement of the adsorption performance and regeneration efficiency of adsorbents, we succeeded in developing a breakthrough material that exceeds the limits of existing adsorbents using accessible materials such as graphite and iron, which have high commercialization potential," said Dr. Jiwon Lee.
###
KIST was established in 1966 as the first government-funded research institute in Korea. KIST now strives to solve national and social challenges and secure growth engines through leading and innovative research. For more information, please visit KIST’s website at https://eng.kist.re.kr/
The research, which was conducted as a major project of KIST (Air Environment Research Program) with support from the Ministry of Science and ICT (Minister Jong-ho Lee), was published on October 1 in the Chemical Engineering Journal.
END
New technology for customized air purification of toxic gases
KIST's iron oxide-graphene oxide heterostructure improves removal efficiency of harmful volatile organic compounds by up to 15 times
2023-10-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Enlightening insects: Morpho butterfly nanostructure inspires technology for bright, balanced lighting
2023-10-12
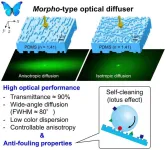
Osaka, Japan – As you watch Morpho butterflies wobble in flight, shimmering in vivid blue color, you’re witnessing an uncommon form of structural color that researchers are only beginning to use in lighting technologies such as optical diffusers. Furthermore, imparting a self-cleaning capability to such diffusers would minimize soiling and staining and maximize practical utility.
Now, in a study recently published in Advanced Optical Materials, researchers at Osaka University have developed a water-repelling ...
Majority of cancer patients interested in complementary therapies for treatment
2023-10-12
WASHINGTON (Oct. 12, 2023) – Patients and oncologists are supportive of complementary therapies, such as nutrition counseling, exercise, massage, and mediation, for cancer treatment, according to a new survey conducted on behalf of the Healing Works Foundation. However, a disconnect exists between this growing interest and oncologists’ perceptions of patient support. One-third of oncologists said their patients lack interest in these therapies, but only 13% of cancer patients cite lack of interest when asked ...
TikTok may help farmers cultivate empathy around climate change
2023-10-12
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Farmers are used to growing crops and producing other goods, but a new study led by Penn State researchers suggests the social media platform TikTok may help them cultivate something new: empathy around the issue of climate change.
The researchers published their work in the Journal of Rural Studies.
The team, who analyzed responses to climate change TikToks posted by farmers, found that many people responded to the videos with warmth and compassion, signaling emotional empathy.
However, the researchers also found that the videos were not as successful at triggering cognitive empathy ...
Japan’s technology progress pushes laser fusion energy closer to commercialization Ex-Fusion and Tokyo Tech establish collaborative research cluster
2023-10-12
EX-Fusion Inc. (CEO: Kazuki Matsuo, hereinafter referred to as "EX-Fusion") has established a Collaborative Research Cluster focused on advancing liquid metal devices (Terminology 1) for the realization of commercial laser fusion reactors (Figure1, Terminology 2) in collaboration with Tokyo Institute of Technology (President: Kazuya Masu, hereinafter referred to as "Tokyo Tech"). The signing ceremony to formalize this partnership was held on October 11, marking the official commencement of their joint efforts.
The ‘EX-Fusion Liquid Metal Collaborative Research Cluster’ has been established with the support of the Tokyo Tech's Open Innovation Platform. ...
Flooding that closed Alaska's Dalton Highway also caused widespread ground sinking
2023-10-12
The massive 2015 flooding of the Sagavanirktok River in northern Alaska had immediate impacts, including closure of the Dalton Highway for several days, but it also contributed to longer-term ground subsidence in the permafrost-rich region.
That’s the finding by assistant professor Simon Zwieback at the University of Alaska Fairbanks Geophysical Institute in a study published Sept. 27 by the journal Permafrost and Periglacial Processes.
Zwieback is the paper’s lead author. UAF scientists Mikhail Kanevskiy, Donald Walker, Vladimir ...
Private renting is making you age faster
2023-10-12
A new study, jointly conducted by the University of Adelaide and University of Essex, has found that renting, rather than owning, a private-sector home leads to faster biological ageing.
The negative health impacts of renting were shown to be greater than those of experiencing unemployment or being a former smoker.
“Our findings demonstrate that housing circumstances have a significant impact on biological ageing, even more so than other important social determinants, such as unemployment, for example, and therefore health impacts should be an important consideration shaping housing policies,” ...
Inhibiting an enzyme associated with aging could help damaged nerves regrow and restore strength
2023-10-12
Scientists at Stanford University School of Medicine and Sanford Burnham Prebys have demonstrated a new way to accelerate recovery from peripheral nerve injury by targeting an enzyme that was thought to be responsible for muscle wasting with aging.
Damage to the peripheral nervous system (the nerves that form the communications network between the brain, spinal cord and body) is debilitating; the effectiveness of physiotherapy as treatment is limited. Whether from trauma, disease or aging, nerve function declines and/or is lost, resulting in diminished strength and even paralysis.
In ...
New cyber algorithm shuts down malicious robotic attack
2023-10-12
Australian researchers have designed an algorithm that can intercept a man-in-the-middle (MitM) cyberattack on an unmanned military robot and shut it down in seconds.
In an experiment using deep learning neural networks to simulate the behaviour of the human brain, artificial intelligence experts from Charles Sturt University and the University of South Australia (UniSA) trained the robot’s operating system to learn the signature of a MitM eavesdropping cyberattack. This is where attackers ...
A better ‘map’ of the lights you see when you close your eyes can improve ‘bionic eye’ outcomes
2023-10-12
Researchers at Monash University have identified a new way of mapping ‘phosphenes’ – the visual perception of the bright flashes we see when no light is entering the eye – to improve the outcome of surgery for patients receiving a cortical visual prosthesis (‘bionic eye’).
Cortical visual prostheses are devices implanted onto the brain with the aim of restoring sight by directly stimulating the area responsible for vision, the visual cortex, bypassing damage to the retina of ...
Civics test policy fails to increase youth voter turnout, researchers find
2023-10-12
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — A civics test policy mandated in 18 states that focuses on rote memorization and testing of political knowledge did not improve youth voter turnout as intended, according to Penn State College of Education researchers. As an alternative, they recommend a thorough integration of practical information on the voter registration process within social studies curricula.
“Providing students opportunities to really engage with what leadership means, having discussions and debates with leaders and politicians, mock elections… ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
[Press-News.org] New technology for customized air purification of toxic gasesKIST's iron oxide-graphene oxide heterostructure improves removal efficiency of harmful volatile organic compounds by up to 15 times