Commonly prescribed hypertension drug, amlodipine, not actually dangerous
2023-10-12
(Press-News.org)
A new paper in the journal Function, published by Oxford Univetrsity Press, finds that a widely prescribed drug for treating hypertension, amlodipine, is not dangerous for patients, despite recent concerns from researchers and clinicians that taking amlodipine may have risks.
Approximately 700,000 Americans die from hypertension each year and researchers believe some 116 million Americans (and one in five adults worldwide) have the disease, which is responsible for 7.6 million deaths per year. If untreated, hypertension significantly increases the risk of premature death through heart attack, stroke, or kidney disease.
One widely prescribed drug for treating hypertension is amlodipine, now taken regularly in pill form by over 70 million Americans. Amlodipine inhibits a type of calcium channel that is found on blood vessels. When the calcium channel opens, calcium enters the muscle and causes it to constrict, increasing blood pressure. Amlodipine prevents calcium from coming in, leading to vessel relaxation and a decrease in blood pressure.
Recently some researchers have questioned the benefit of amlodipine for treating hypertension. Studies suggested that amlodipine may activate a different type of calcium channel, resulting in changes to blood vessels and an increase in heart failure in patients. Removing amlodipine as a prescribed anti-hypertensive medication carries significant health implications, since hypertension is such a common health condition.
A new study by research teams from National Institutes of Health and Glasgow University finds that taking amlodipine is unlikely to result in an increase in heart failure in patients. The researchers found that amlodipine appears to have unique chemical properties that caused the drug to mimic the calcium channel activation, without in fact opening the channels as clinicians worried. When the study’s authors controlled for these chemical properties, they found that amlodipine did not activate calcium channels. A meta-analysis combining clinical trials and a prospective real-world analysis both showed that amlodipine was not associated with increased heart failure or other cardiovascular problems.
“Removal of amlodipine as a front-line therapy would most likely increase deaths from hypertension dramatically,” said Anant Parekh, one of the study’s authors. “The study recommends that amlodipine remain a first-line treatment for high blood pressure.”
The paper, “A reappraisal of the effects of L-type Ca2+ channel blockers on store-operated Ca2+ entry and heart failure,” is available (at midnight on October 12th) at: https://doi.org/10.1093/function/zqad047.
Direct correspondence to:
Anant B. Parekh
Chief of the Signal Transduction Laboratory
National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences,
The National Institutes of Health
Research Triangle Park, NC 27709
anant.parekh@nih.gov
To request a copy of the study, please contact:
Daniel Luzer
daniel.luzer@oup.com
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-10-12
Physical activity has positive effects on mental health and yet, activity rates are declining. This is particularly worrying because the mental well-being of teenagers continues to deteriorate. In the US, one in six school children is diagnosed with some type of mental disorder.
Riding bikes is a promising approach to introduce school-aged children to physical activity. Now, researchers in the US have investigated how adolescents’ psychosocial well-being changed after participating in a school-based cycling program.
“Participation in a school cycling education program during the Covid-19 pandemic was associated with improved psychosocial well-being amongst middle schoolers in the ...
2023-10-12
Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in daily products such as paints, adhesives, furniture, cosmetics, and deodorants make our lives easier. However, constant exposure can cause serious health problems such as respiratory illness, headaches, dermatitis, and cancer. Natural ventilation is the most effective way to reduce VOCs in indoor air, but recently, air purifiers have become a common method to maintain indoor air quality due to the frequent extreme outdoor condition (e.g. high concentration of fine dust, heat waves, and extreme cold). Generally, air purifiers remove ...
2023-10-12
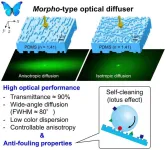
Osaka, Japan – As you watch Morpho butterflies wobble in flight, shimmering in vivid blue color, you’re witnessing an uncommon form of structural color that researchers are only beginning to use in lighting technologies such as optical diffusers. Furthermore, imparting a self-cleaning capability to such diffusers would minimize soiling and staining and maximize practical utility.
Now, in a study recently published in Advanced Optical Materials, researchers at Osaka University have developed a water-repelling ...
2023-10-12
WASHINGTON (Oct. 12, 2023) – Patients and oncologists are supportive of complementary therapies, such as nutrition counseling, exercise, massage, and mediation, for cancer treatment, according to a new survey conducted on behalf of the Healing Works Foundation. However, a disconnect exists between this growing interest and oncologists’ perceptions of patient support. One-third of oncologists said their patients lack interest in these therapies, but only 13% of cancer patients cite lack of interest when asked ...
2023-10-12
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Farmers are used to growing crops and producing other goods, but a new study led by Penn State researchers suggests the social media platform TikTok may help them cultivate something new: empathy around the issue of climate change.
The researchers published their work in the Journal of Rural Studies.
The team, who analyzed responses to climate change TikToks posted by farmers, found that many people responded to the videos with warmth and compassion, signaling emotional empathy.
However, the researchers also found that the videos were not as successful at triggering cognitive empathy ...
2023-10-12
EX-Fusion Inc. (CEO: Kazuki Matsuo, hereinafter referred to as "EX-Fusion") has established a Collaborative Research Cluster focused on advancing liquid metal devices (Terminology 1) for the realization of commercial laser fusion reactors (Figure1, Terminology 2) in collaboration with Tokyo Institute of Technology (President: Kazuya Masu, hereinafter referred to as "Tokyo Tech"). The signing ceremony to formalize this partnership was held on October 11, marking the official commencement of their joint efforts.
The ‘EX-Fusion Liquid Metal Collaborative Research Cluster’ has been established with the support of the Tokyo Tech's Open Innovation Platform. ...
2023-10-12
The massive 2015 flooding of the Sagavanirktok River in northern Alaska had immediate impacts, including closure of the Dalton Highway for several days, but it also contributed to longer-term ground subsidence in the permafrost-rich region.
That’s the finding by assistant professor Simon Zwieback at the University of Alaska Fairbanks Geophysical Institute in a study published Sept. 27 by the journal Permafrost and Periglacial Processes.
Zwieback is the paper’s lead author. UAF scientists Mikhail Kanevskiy, Donald Walker, Vladimir ...
2023-10-12
A new study, jointly conducted by the University of Adelaide and University of Essex, has found that renting, rather than owning, a private-sector home leads to faster biological ageing.
The negative health impacts of renting were shown to be greater than those of experiencing unemployment or being a former smoker.
“Our findings demonstrate that housing circumstances have a significant impact on biological ageing, even more so than other important social determinants, such as unemployment, for example, and therefore health impacts should be an important consideration shaping housing policies,” ...
2023-10-12
Scientists at Stanford University School of Medicine and Sanford Burnham Prebys have demonstrated a new way to accelerate recovery from peripheral nerve injury by targeting an enzyme that was thought to be responsible for muscle wasting with aging.
Damage to the peripheral nervous system (the nerves that form the communications network between the brain, spinal cord and body) is debilitating; the effectiveness of physiotherapy as treatment is limited. Whether from trauma, disease or aging, nerve function declines and/or is lost, resulting in diminished strength and even paralysis.
In ...
2023-10-12
Australian researchers have designed an algorithm that can intercept a man-in-the-middle (MitM) cyberattack on an unmanned military robot and shut it down in seconds.
In an experiment using deep learning neural networks to simulate the behaviour of the human brain, artificial intelligence experts from Charles Sturt University and the University of South Australia (UniSA) trained the robot’s operating system to learn the signature of a MitM eavesdropping cyberattack. This is where attackers ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Commonly prescribed hypertension drug, amlodipine, not actually dangerous