(Press-News.org) The future of human-machine interfaces is on the cusp of a revolution with the unveiling of a groundbreaking technology - a stretchable high-resolution multicolor synesthesia display that generates synchronized sound and light as input/output sources. A research team, led by Professor Moon Kee Choi in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at UNIST, has succeeded in developing this cutting-edge display using transfer-printing techniques, propelling the field of multifunctional displays into new realms of possibility.
Traditionally, multifunctional displays have been confined to visualizing mechanical and electrical signals in light. However, this pioneering stretchable synesthesia display shatters preconceived boundaries by offering unparalleled optical performance and precise sound pressure levels. Its inherent stretchability ensures seamless operation under both static and dynamic deformation, preserving the integrity of the sound relative to the input waveform.
A key advantage of this groundbreaking technology is its potential to revolutionize wearable devices, mobile devices, and the Internet of Things (IoT) as the next generation of displays. By seamlessly generating sound and light simultaneously, the stretchable display delivers a distinctive user experience and unlocks untapped potential for advanced encryption and authentication.
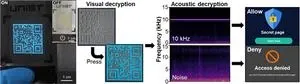
To demonstrate the capabilities of this synesthesia display, the research team presented two innovative applications. Firstly, they showcased visual-acoustic encryption, an advanced encryption method that combines visual and auditory cues. This breakthrough sets the stage for reinforced authentication systems that leverage the power of both sight and sound, elevating security to new heights.
Secondly, the team introduced a multiplex quick response code that bridges multiple domains with a single device. This remarkable technology empowers users to interact with the display, ushering in a new era of seamless integration and user-friendly experiences.
Professor Choi enthused, “The demand for next-generation displays is skyrocketing, and this stretchable high-resolution display that generates sound and light simultaneously overcomes the limitations of previous light-emitting devices. Our novel light-emission layer transfer technology, achieved through surface energy control, enables us to achieve remarkable patterns and maintain stability even under deformation.”
The manufactured device boasts exceptional brightness and sound characteristics, with a circular shape maintained at a remarkable rate of over 95% in more than 5,000 deformation experiments. This unparalleled durability and versatility render the stretchable display ideal for a wide range of applications, including wearable speakers, double encryption devices, and multi-quick response code implementations.
According to the research team, this remarkable advancement in display technology propels us one step closer to a future where multifunctional displays seamlessly integrate with our daily lives. As the demand for advanced human-machine interfaces continues to surge, the stretchable high-resolution multicolor synesthesia display offers a tantalizing glimpse into the limitless possibilities of tomorrow.
The research findings were published in the online version of the esteemed journal, Advanced Functional Materials, on August 14, 2023. This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant, funded by the Korean Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT).
Journal Reference
Jisu Yoo, Subin Ha, Gwang Heon Lee, et al., “Stretchable High-Resolution User-Interactive Synesthesia Displays for Visual–Acoustic Encryption,” Adv. Funct. Mater., (2023).
END
New study unveils stretchable high-resolution user-interactive synesthesia displays for visual–acoustic encryption
2023-10-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
The advantage of digital-native brands setting up physical brand stores—and the challenge of preventing sales losses in existing channels
2023-10-12
Researchers from Erasmus School of Economics at Erasmus University Rotterdam, KU Leuven, Universität zu Lübeck, Christian-Albrechts-Universität zu Kiel, and FoodLabs published a new Journal of Marketing article that investigates the multichannel impact of brand stores by digital-native FMCG brands.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing, is titled “Assessing the Multichannel Impact of Brand Store Entry by a Digital-Native Grocery Brand” and is authored ...
Extreme habitats: Microbial life in Old Faithful Geyser
2023-10-12
Contributed by Arianna Soldati, GSA Science Communication Fellow
Pittsburgh, Pa., USA: An eruption of Old Faithful Geyser in Yellowstone National Park is a sight to behold. Indeed, millions of tourists flock to the park each year to see it. Hot water and steam are ejected in the air to a height of 100–180 feet approximately every 90 minutes. Many adjectives come to mind to describe it: powerful, mesmerizing, unique, otherworldly . . . homey? Not so much. Yet new research by Lisa M. Keller, published on PNAS Nexus earlier this year and to be presented on Sunday at the Geological Society of America’s GSA Connects 2023 meeting, shows that for ...
Inferring wildfire intensity from quartz luminescence
2023-10-12
Pittsburgh, Pa., USA: On 8 June 2020, the Mangum Fire ignited 16 miles north of the North Rim of Grand Canyon National Park. By the time it was mostly contained, about a month later, the fire had burned over 70,000 acres of land.
April Phinney, a M.Sc. candidate at Utah State University, immediately started drafting a burn intensity map based on remote sensing data. Six months later, she set boots on the burned ground and started collecting soil samples, hoping they would contain quartz grains. This research ...
Cancer Prevention and Research Institute of Texas awards grants to four TTUHSC Researchers
2023-10-12
The Cancer Prevention and Research Institute of Texas (CPRIT) recently awarded grants to four researchers from the Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center (TTUHSC). Combined, the grants will provide nearly $2.3 million that TTUHSC will use to conduct a pair of two-year pilot studies, acquire a state-of-the-art piece of laboratory equipment known as a cell sorter, and administer a colorectal cancer screening and prevention program.
Three of the recipients are from the TTUHSC School of Medicine, including Hongjun (Henry) Liang, Ph.D., a professor in the Department of Cell Physiology and Molecular Biophysics; Min Kang, Pharm.D., a professor ...
Proof-of-concept method advances bioprocess engineering for a smoother transition to biofuels
2023-10-12
One of the primary goals of bioprocess engineering is to increase the yield of the desired material while maintaining high production rates and low raw material utilization. This optimization is usually accomplished by controlling the behavior of microorganisms used in the process and ensuring that their biological capabilities are fully utilized. This control may be computerized (in silico feedforward) or autonomous (in-cell feedback) which predicts the optimization based on inputs received. However, a process-model mismatch (PMM) occurs when there is a discrepancy between the predicted and actual production processes.
A recent paper published in Scientific Reports demonstrates a ...
Revolutionizing energy storage: Metal nanoclusters for stable lithium–sulfur batteries
2023-10-12
The demand for efficient energy storage systems is ever increasing, especially due to the recent emergence of intermittent renewable energy and the adoption of electric vehicles. In this regard, lithium–sulfur batteries (LSBs), which can store three to five times more energy than traditional lithium-ion batteries, have emerged as a promising solution.
LSBs use lithium as the anode and sulfur as the cathode, but this combination poses challenges. One significant issue is the “shuttle effect,” in which intermediate lithium polysulfide ...
Toward a global scientific consensus: identifying vulnerable marine ecosystems through imagery
2023-10-12
The scientific community is taking a significant step towards establishing a consensus on the designation of Vulnerable Marine Ecosystems (VMEs) from imagery data, as highlighted in the new article titled "Towards a scientific community consensus on designating Vulnerable Marine Ecosystems from imagery," authored by Dr. Amy R. Baco and colleagues, and published in PeerJ Life & Environment.
“Many scientists around the world were working independently on a similar question: Given the UN Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) regulations for deep-sea Vulnerable Marine Ecosystems ...
Surprising discovery shows electron beam radiation can repair nanostructures
2023-10-12
MINNEAPOLIS / ST. PAUL (10/12/2023)—In a surprising new study, researchers at the University of Minnesota Twin Cities have found that the electron beam radiation that they previously thought degraded crystals can actually repair cracks in these nanostructures.
The groundbreaking discovery provides a new pathway to create more perfect crystal nanostructures, a process that is critical to improving the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of materials that are used in virtually all electronic devices we use every day.
“For ...
UTSA study could remove carbon emissions from atmosphere
2023-10-12
Zachary Tonzetich, an associate professor in the UTSA College of Sciences’ chemistry department, is part of a duo that has been awarded a one-year, $100,000 grant from The Welch Foundation for a project that could remove carbon emissions from the atmosphere.
Tonzetich and his research collaborator Anthony Cozzolino, an associate professor in Texas Tech University’s chemistry department, were the recipients of a WelchX pilot grant this past August. The WelchX program brings together leading chemistry researchers from across Texas to address challenging issues that are ...
New research shows why hunting for the cheapest plane ticket is a waste of your time
2023-10-12
Buy your ticket on a Tuesday. Search in your browser’s incognito mode. Use a VPN to pretend you live in Suriname.
“There are so many hacks out there for finding cheaper airline tickets,” says Olivia Natan, an assistant professor of marketing at the Haas School of Business. “But our data shows many of these beliefs are wrong.”
With four colleagues—Ali Hortaçsu and Timothy Schwieg from the University of Chicago, Kevin Williams from Yale, and Hayden Parsley from the University of Texas at Austin—Natan looked deeply into the structure and processes behind how ...