Surprising discovery shows electron beam radiation can repair nanostructures
Self-healing crystals could improve materials used in today’s electronics
2023-10-12
(Press-News.org)
MINNEAPOLIS / ST. PAUL (10/12/2023)—In a surprising new study, researchers at the University of Minnesota Twin Cities have found that the electron beam radiation that they previously thought degraded crystals can actually repair cracks in these nanostructures.
The groundbreaking discovery provides a new pathway to create more perfect crystal nanostructures, a process that is critical to improving the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of materials that are used in virtually all electronic devices we use every day.
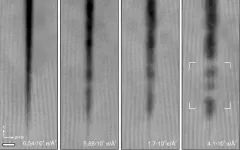
“For a long time, researchers studying nanostructures were thinking that when we put the crystals under electron beam radiation to study them that they would degrade,” said Andre Mkhoyan, a University of Minnesota chemical engineering and materials science professor and lead researcher in the study. “What we showed in this study is that when we took a crystal of titanium dioxide and irradiate it with an electron beam, the naturally occurring narrow cracks actually filled in and healed themselves.”
The researchers accidentally stumbled upon the discovery when using the University of Minnesota’s state-of-the-art electron microscope to study the crystals for a completely different reason.
“I was studying the cracks in the crystals under the electron microscope and these cracks kept filling in,” said Silu Guo, a University of Minnesota chemical engineering and materials science Ph.D. student. “This was unexpected, and our team realized that maybe there was something even bigger that we should be studying.”
In the self-healing process, several atoms of the crystal moved together in tandem and met in the middle and formed a sort of bridge that filled the crack. For the first time, the researchers showed that the electron beams could be used constructively to engineer novel nanostructures atom-by-atom.
"Whether it's atomically sharp cracks or other types of defects in a crystal, I believe it's inherent in the materials we've grown, but it's truly astonishing to see how Professor Mkhoyan's group can mend these cracks using an electron beam," said University of Minnesota Chemical Engineering and Materials Science Professor Bharat Jalan, a collaborator on the research.
The researchers say the next step is to introduce new factors like changing the electron beam conditions or changing the temperature of crystal to find a way to improve or speed up the process.
“First we discovered, now we want to find more ways to engineer the process,” Mkhoyan said.
In addition to Mkhoyan, Guo, and Jalan, the research team included University of Minnesota Chemical Engineering and Materials Science Ph.D. student Sreejith Nair, and former graduate student Hwanhui Yun.
This work was supported primarily by the National Science Foundation (NSF). Parts of this work were carried out at the UMN Characterization Facility. Computational resources were provided by the Minnesota Supercomputing Institute (MSI) and film growth was supported by the Department of Energy (DOE).
To read the entire research paper entitled “Mending cracks atom-by-atom in rutile TiO2 with electron beam radiolysis,” visit the Nature Communications website.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-10-12
Zachary Tonzetich, an associate professor in the UTSA College of Sciences’ chemistry department, is part of a duo that has been awarded a one-year, $100,000 grant from The Welch Foundation for a project that could remove carbon emissions from the atmosphere.
Tonzetich and his research collaborator Anthony Cozzolino, an associate professor in Texas Tech University’s chemistry department, were the recipients of a WelchX pilot grant this past August. The WelchX program brings together leading chemistry researchers from across Texas to address challenging issues that are ...
2023-10-12
Buy your ticket on a Tuesday. Search in your browser’s incognito mode. Use a VPN to pretend you live in Suriname.
“There are so many hacks out there for finding cheaper airline tickets,” says Olivia Natan, an assistant professor of marketing at the Haas School of Business. “But our data shows many of these beliefs are wrong.”
With four colleagues—Ali Hortaçsu and Timothy Schwieg from the University of Chicago, Kevin Williams from Yale, and Hayden Parsley from the University of Texas at Austin—Natan looked deeply into the structure and processes behind how ...
2023-10-12
A new paper in the journal Function, published by Oxford Univetrsity Press, finds that a widely prescribed drug for treating hypertension, amlodipine, is not dangerous for patients, despite recent concerns from researchers and clinicians that taking amlodipine may have risks.
Approximately 700,000 Americans die from hypertension each year and researchers believe some 116 million Americans (and one in five adults worldwide) have the disease, which is responsible for 7.6 million deaths per year. If untreated, hypertension significantly increases ...
2023-10-12
Physical activity has positive effects on mental health and yet, activity rates are declining. This is particularly worrying because the mental well-being of teenagers continues to deteriorate. In the US, one in six school children is diagnosed with some type of mental disorder.
Riding bikes is a promising approach to introduce school-aged children to physical activity. Now, researchers in the US have investigated how adolescents’ psychosocial well-being changed after participating in a school-based cycling program.
“Participation in a school cycling education program during the Covid-19 pandemic was associated with improved psychosocial well-being amongst middle schoolers in the ...
2023-10-12
Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in daily products such as paints, adhesives, furniture, cosmetics, and deodorants make our lives easier. However, constant exposure can cause serious health problems such as respiratory illness, headaches, dermatitis, and cancer. Natural ventilation is the most effective way to reduce VOCs in indoor air, but recently, air purifiers have become a common method to maintain indoor air quality due to the frequent extreme outdoor condition (e.g. high concentration of fine dust, heat waves, and extreme cold). Generally, air purifiers remove ...
2023-10-12
Osaka, Japan – As you watch Morpho butterflies wobble in flight, shimmering in vivid blue color, you’re witnessing an uncommon form of structural color that researchers are only beginning to use in lighting technologies such as optical diffusers. Furthermore, imparting a self-cleaning capability to such diffusers would minimize soiling and staining and maximize practical utility.
Now, in a study recently published in Advanced Optical Materials, researchers at Osaka University have developed a water-repelling ...
2023-10-12
WASHINGTON (Oct. 12, 2023) – Patients and oncologists are supportive of complementary therapies, such as nutrition counseling, exercise, massage, and mediation, for cancer treatment, according to a new survey conducted on behalf of the Healing Works Foundation. However, a disconnect exists between this growing interest and oncologists’ perceptions of patient support. One-third of oncologists said their patients lack interest in these therapies, but only 13% of cancer patients cite lack of interest when asked ...
2023-10-12
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Farmers are used to growing crops and producing other goods, but a new study led by Penn State researchers suggests the social media platform TikTok may help them cultivate something new: empathy around the issue of climate change.
The researchers published their work in the Journal of Rural Studies.
The team, who analyzed responses to climate change TikToks posted by farmers, found that many people responded to the videos with warmth and compassion, signaling emotional empathy.
However, the researchers also found that the videos were not as successful at triggering cognitive empathy ...
2023-10-12
EX-Fusion Inc. (CEO: Kazuki Matsuo, hereinafter referred to as "EX-Fusion") has established a Collaborative Research Cluster focused on advancing liquid metal devices (Terminology 1) for the realization of commercial laser fusion reactors (Figure1, Terminology 2) in collaboration with Tokyo Institute of Technology (President: Kazuya Masu, hereinafter referred to as "Tokyo Tech"). The signing ceremony to formalize this partnership was held on October 11, marking the official commencement of their joint efforts.
The ‘EX-Fusion Liquid Metal Collaborative Research Cluster’ has been established with the support of the Tokyo Tech's Open Innovation Platform. ...
2023-10-12
The massive 2015 flooding of the Sagavanirktok River in northern Alaska had immediate impacts, including closure of the Dalton Highway for several days, but it also contributed to longer-term ground subsidence in the permafrost-rich region.
That’s the finding by assistant professor Simon Zwieback at the University of Alaska Fairbanks Geophysical Institute in a study published Sept. 27 by the journal Permafrost and Periglacial Processes.
Zwieback is the paper’s lead author. UAF scientists Mikhail Kanevskiy, Donald Walker, Vladimir ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Surprising discovery shows electron beam radiation can repair nanostructures
Self-healing crystals could improve materials used in today’s electronics