(Press-News.org) Even highly mobile, large, and long-lived species are sensitive to dynamic and changing conditions as the Arctic warms. A new study reports that population swings in eastern North Pacific grey whales – some of which have resulted in recent mass mortality events – are driven by changing prey biomass and ice cover in the Arctic. Climate change is driving rapid change in Arctic ecosystems, including the highly productive shallow basins of the Pacific Arctic, which are critical marine areas that support seasonal foraging opportunities for various migratory marine species. While climate impacts affect lower-trophic level and short-lived species most directly, it is less clear how long-lived migratory species will respond to rapid polar warming. Eastern North Pacific grey whales travel great distances across the Pacific to summer in these areas in the Pacific Arctic, where they feed on highly abundant benthic crustacean prey. Populations of these whales – a species hunted to near extinction by the early 1900s through commercial whaling – have shown great success in rebounding to estimated pre-whaling levels. However, several unexpected major mortality events over the past 35 years have each led to large declines in grey whale abundance, casting concern on the status and stability of the whale’s population.
It’s been proposed that variable and changing Arctic conditions may be drivers of grey whale population dynamics. Joshua Stewart and colleagues combined more than 50 years of data on grey whale abundance, calving, body condition, and strandings with a population dynamics model to better understand the factors underlying the carrying capacity for the population. Stewart et al. discovered boom-and-bust cycles in abundance driven by large and rapid changes in their Arctic food supply – and access to it. When low prey biomass coincided with high ice cover, grey whales experienced pronounced mortality events, each reducing the population by ~15 to 20%. According to the findings, in the last 35 years alone, grey whales have experienced three significant population “busts.” Moreover, Stewart et al. suggest that, given current trends, future climate conditions in the Arctic will not be favorable for the whales’ vital prey species,. “If Stewart et al. are correct, then species with a narrow dietary niche composed of low-trophic-level prey species should be expected to exhibit considerable variation in their demography as environmental conditions change,” writes Andrew Read in a related Perspective.
END
Boom-and-bust cycles in grey whale population associated with changing Arctic ecosystem
2023-10-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
About 2 million years ago, Homo Erectus lived at high altitudes and produced both Oldowan and Acheulean tools
2023-10-12
Two million years ago, Homo erectus had expanded beyond the lowland savanna environments of East Africa and into the high-altitude regions of the Ethiopian highlands, where they produced both Oldowan and Acheulean tools, according to a new study. It presents a reanalysis of an early hominin fossil first discovered in 1981. The findings provide novel insights into the evolution, migration and adaptive capacities of early human ancestors. In Africa, the limited number of hominin fossils found in direct association with stone tools has hindered attempts to link Homo habilis and Homo erectus with ...
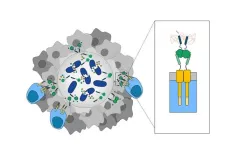
Engineered bacteria guide CAR-T cells to poorly infiltrated solid tumors
2023-10-12
A new probiotic-guided chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T platform uses engineered bacteria to infiltrate and produce synthetic antigen targets, enabling CAR-T cells to find, identify, and destroy tumor cells in situ, according to a new study. The combined cell therapy platform expands the scope of CAR-T cell therapy to include difficult-to-target solid tumors. Immunotherapies using CAR-T cells have proven successful in treating some types of blood cancers. However, their efficacy against solid tumors remains elusive. A key challenge facing tumor-antigen targeting immunotherapies like CAR-T is the identification of suitable ...
An electrical switch to control chemical reactions
2023-10-12
New pharmaceuticals, cleaner fuels, biodegradable plastics: in order to meet society’s needs, chemists have to develop new synthesis methods to obtain new products that do not exist in their natural state. A research group at the University of Geneva (UNIGE), in collaboration with Cardiff University, has discovered how to use an external electric field to control and accelerate a chemical reaction, like a ‘‘switch’’. This work, to be read in Science Advances, could have a considerable impact on the development of new molecules, enabling not only more environmentally friendly synthesis, but also very simple external control of a chemical reaction.
In ...
Gray whales experience major population swings as a result of Arctic conditions, research shows
2023-10-12
NEWPORT, Ore. – Dynamic and changing Arctic Ocean conditions likely caused three major mortality events in the eastern North Pacific gray whale population since the 1980s, a new study has found.
During each of these die-offs, including one that began in 2019 and is ongoing, the gray whale population was reduced by up to 25% over just a few years, said Joshua Stewart, an assistant professor with Oregon State University’s Marine Mammal Institute and the study’s lead author.
“These are extreme population swings that we did not expect to see in a large, long-lived species like gray whales,” Stewart said. “When the availability ...
Cell atlases of the human brain presented in Science
2023-10-12
In two parallel projects, researchers at Karolinska Institutet have been involved in creating the most comprehensive atlases of human brain cells to date. The two studies, which are published in Science, provide clues on different brain diseases and give hope for medical advancements in the future, such as new cancer drugs.
Knowing what cells constitute the healthy brain, where different cell types are located and how the brain develops from the embryo stage is fundamental to the ability to compare and better understand how diseases arise. There are at present advanced atlases of the ...
Coffee and cocoa plants at risk from pollinator loss
2023-10-12
Tropical crops such as coffee, cocoa, watermelon and mango may be at risk due to the loss of insect pollinators, finds a new study led by UCL and Natural History Museum researchers.
Published in Science Advances, the study explores the intricate interplay between climate change, land use change, and their impact on pollinator biodiversity, ultimately revealing significant implications for global crop pollination.
The study, which compiled data from 1,507 crop growing sites around the world and catalogued 3,080 insect pollinator species, exposes a concerning trend – the combined pressures ...
Scientists unveil detailed cell maps of the human brain and the nonhuman primate brain
2023-10-12
A group of international scientists have mapped the genetic, cellular, and structural makeup of the human brain and the nonhuman primate brain. This understanding of brain structure, achieved by funding through the National Institutes of Health’s Brain Research Through Advancing Innovative Neurotechnologies® Initiative, or The BRAIN Initiative®, allows for a deeper knowledge of the cellular basis of brain function and dysfunction, helping pave the way for a new generation of precision therapeutics for people with mental disorders and other disorders of the brain. The findings appear in a compendium of ...
Engineered bacteria paint targets on tumors for cancer-killing T cells to see
2023-10-12
New York, NY—October 12, 2023—For several years, researchers have been successfully using chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells to target specific antigens found on blood cells as a cure for patients with leukemia and lymphoma. But solid tumors, like breast and colon cancers, have proven to be more difficult to home in on. Solid tumors contain a mix of cells that display different antigens on their surface-often shared with healthy cells in the body. Thus, identifying a consistent and safe target has impeded the success of most CAR-T cell therapy for solid tumors at the first phase ...
How do tax proposals affect cancer health of tobacco users based on income, education?
2023-10-12
Tobacco is the leading cause of preventable death in the United States, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and cigarette smoking causes three in 10 of all cancer deaths. Smoking also accounts for more than 30 percent of the difference in life expectancy among different socioeconomic groups.
Roberta Freitas-Lemos, research assistant professor at the Fralin Biomedical Research Institute at VTC, recently received a career development award to explore the ways in which nicotine tax policies can influence health disparities. The award of more than $680,000 over five years from the National Cancer Institute of the National Institutes of Health is designed ...
NIH awards Mount Sinai researchers $12 million to personalize sickle cell treatment
2023-10-12
New York, NY (October 12, 2023) - The Mount Sinai Health System has received a $12,180,625 grant from the National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute to compare new treatment options for sickle cell disease and determine which work best for specific patients.
“Sickle cell traditionally has been a neglected disease, but it benefited from a flurry of innovation over the last decade and there are now three new medications approved for the disease,” says Jeffrey Glassberg, MD, Director of the Mount Sinai Sickle Cell Program.
“While this is welcome news, clinicians now have a new challenge. ...