(Press-News.org) A landmark scientific article on the workplace as a major determinant of health is published today (Thursday, 12 October) in The Lancet, and reveals a global picture of the work-related causes of mental health conditions.
Carried by University College Cork (UCC) researchers for the Lancet Series on work and health, the paper illustrates that major progress in population health can be made by an increased focus on improving people’s work environments.
The paper, ‘Work-related causes of mental health conditions and interventions for their improvement in workplaces’, presents sound epidemiological evidence based on large-scale international cohort studies that adverse working conditions contribute to an increased risk of onset of depressive disorders and outlines critical interventions to improve mental health conditions in workplaces.
Dr Birgit Greiner and Professor Ella Arensman, UCC School of Public Health, co-authored the article with academics from universities in Europe, Japan and Australia. Dr Birgit Greiner will present the findings at the World Health Summit in Berlin on Sunday, 15 October.
Mental health problems and mental disorders are common
The report finds that mental health problems and mental disorders are common in the working population. Researchers cite that 15% of adults of working age experience mental health disorders, with depression, anxiety and substance abuse being the most common.
Workers with mental health disorders are at increased risk of sickness absence, unemployment, permanent exit from employment, and lower lifetime income, which in turn can exacerbate mental disorders. Mental disorders incur substantial costs for workers, employers and the whole of society.
The article finds that most interventions focus on the individual level only and recommends that more proactive interventions need to be developed to protect and promote workers’ mental health and wellbeing.
Ahead of her address at the World Health Summit, Dr Birgit Greiner said: “We know mental health problems and disorders are common in our working population. Workplaces have huge potential to influence mental health by promoting the positive aspects of work and providing safe, non-discriminatory support for those showing signs of mental health problems. Modifying psychosocial working conditions is key. Workplace mental health should be made a collective concern at all levels of an organisation.”
Professor Ella Arensman, Head of School of Public Health UCC and Chief Scientist, National Suicide Research Foundation, said: “Work-related mental health is an issue of society and public health importance. We know burnout and distress are common particularly within the healthcare sector, leading to difficulties in attracting new workers, their retention and turnover. Interventions must include the prevention of mental health problems along with helping affected individuals regardless of cause. They must also include the pro-active promotion of positive mental health, wellbeing and recovery.”
Key recommendations
The report outlines recommendations for decision-makers to support healthy and safe work for diverse populations. Key recommendations include:
Governments need to ensure that the workplace is an integral part of their mental health strategies.
Policymakers at local, national and international levels need to regulate and control working environments—evidence suggests an increased risk of mental health problems and mental disorders in adverse conditions.
Policymakers should develop and improve policy on mentally healthy work, with a particular focus on the work environments of low-wage or marginalised workers.
Policymakers need to develop guidance on how to create and maintain mentally healthy work at all levels of an organisation—this includes promoting training programmes.
Governments should improve support and workplace conditions to enable individuals with mental health problems and disorders to be part of the workforce.
Healthcare providers should routinely include information on working conditions in the clinical assessment, diagnosis and management of mental health problems and mental disorders.
Professor Ella Arensman said: “Workplace mental health promotion practice and policy gained a lot of traction in many sectors during the past few years. Several large organisations implemented Employee Assistance Programmes and Peer support systems to offer support for those with mental health problems. Organisations now need to take a second step and augment these programmes with proactive initiatives to improve work organisations and working conditions. This is not just a moral imperative but necessary for employers to meet legal and ethical mandates on psychologically safe work environments.”
The above-mentioned recommendations are currently being investigated in the ongoing EU Horizon 2020 MENTUPP project: Mental Health Promotion and Intervention in Occupational Settings and the new EU Horizon Europe PROSPERH project: Promoting Positive Mental and Physical Health at Work in a Changing Environment – A Multi-level Approach, led by the UCC School of Public Health and the National Suicide Research Foundation.
ENDS
END
Landmark publication calls for increased attention to workplace mental health
2023-10-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
DNA methylation: The hidden mechanism enabling plants to adapt in a warmer world
2023-10-13
As global warming continues to redefine ecosystems, plants are increasingly tasked with swift adaptation to ensure their survival. One primary mechanism facilitating such rapid adaptation is epigenetic memory, specifically DNA methylation. DNA methylation, a form of epigenetic modification, involves the addition of a methyl group to the cytosine bases of the DNA, altering its accessibility in chromatin and modulating gene expression. In the context of a warming climate, changes in DNA methylation can be triggered by environmental factors like increased temperature. Such epigenetic adaptations ...
Unlocking the secrets of cold tolerance: a deep dive into tomato plants' molecular responses to chilling stress
2023-10-13
Cold sensitivity poses a significant challenge for certain essential crops. While there's an indication that these plants may possess cold acclimation capabilities, the molecular dynamics, particularly involving the CRT binding factor (CBF) family, are not fully explored. One primary concern has been the disparity in cold tolerance between temperate plants and tropical species such as the tomato. Additionally, the accumulation of small metabolites, termed cryoprotectants, plays a crucial role in enabling plants to resist damage from low temperatures. Adding ...
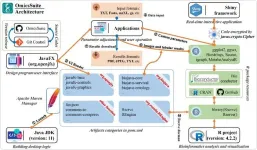
OmicsSuite: A customized and pipelined suite for analysis and visualization of multi-omics big data
2023-10-13
Abstract:
With the advancements in high-throughput sequencing technologies such as Illumina, PacBio, and 10X Genomics platforms, and gas/liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry, large volumes of biological data in multiple formats can now be obtained through multi-omics analysis. Bioinformatics is constantly evolving and seeking breakthroughs to solve multi-omics problems, however it is challenging for most experimental biologists to analyze data using command-line interfaces, coding, and scripting. Based on experience with multi-omics, we have developed OmicsSuite, a desktop suite that comprehensively integrates statistics and multi-omics analysis and visualization. The suite ...
Stress wrecks male big brown bat fertility during breeding season
2023-10-13
Even on a good day the environment can be wildly unpredictable, from unexpected gusts of wind to food scarcity, and as humans continue to edge out the natural world, the stress on wild populations is increasing. ‘Bats are critical for the maintenance and stability of many terrestrial ecosystems’, say Mattina Alonge [University of California, Berkeley (UCB), USA] and Lucas Greville (McMaster University, Canada) and the animals are known to be particularly sensitive when under strain. But little was known about the impact that stress might have on their ability to reproduce. Concerned about the effect of stress on already vulnerable bat populations, Alonge and her colleagues ...
Almost half of patients with skin disease suffer from sleep disturbances, global study finds
2023-10-13
(Friday, 13 October 2023, Berlin, Germany) Almost half (42%) of patients with skin disease experience sleep disturbances, a major study presented today at the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology (EADV) Congress 2023 has revealed.1
The ALL PROJECT, a comprehensive international research initiative, analysed over 50,000 adults across 20 countries to assess the impact of skin diseases.2
Notably, these sleep disturbances were found to have broader implications on patients' quality of life. Nearly half (49%) of patients with skin disease reported reduced productivity at work, in contrast with just one in five (19%) participants without a skin disease.1
The ...
Kraft Family Blood Donor Center expands eligibility for donors
2023-10-12
Boston – The Kraft Family Blood Donor Center, which provides lifesaving blood products to patients at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute and Brigham and Women’s Hospital, announced today that it has finished implementing a more inclusive blood donation process, in alignment with updated guidelines issued by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) that will allow many gay and bisexual men to donate blood and platelets.
On May 11, 2023, the FDA changed its policy to reflect that deferring prospective blood donors based on sexual orientation is no longer supported by data. ...
200-year-old DNA helps map tiny fly’s genetic course to new lands, modern times
2023-10-12
Back when the biggest fly enthusiasts of 19th century Sweden — Carl Fredrik Fallén, for one, and later Johan Wilhelm Zetterstedt — were collecting insects for what would become Lund University’s entomological collections, they wondered exactly what was that buzzing coming from their can of raisins.
Skip forward 200 years, and the humble fruit fly, known better to geneticists as Drosophila melanogaster, is one of the most thoroughly studied animals on the planet. And DNA from Fallén and Zetterstedt’s centuries-old curiosities are still revealing new insights into the fly’s evolution as it spread alongside ...
Study highlights concerns and preferences of residents regarding police involvement in mental health crisis response
2023-10-12
PHILADELPHIA (October 11, 2023) – Police officers often respond to incidents that do not involve crime or immediate threats to public safety but instead deal with community members facing unmet mental health needs. In response to this, many cities are experimenting with co-deploying police officers alongside health professionals or deploying teams entirely composed of civilian health professionals.
Recently, researchers from the University of Pennsylvania School of Nursing (Penn Nursing) explored the perspectives and preferences about these programs among residents in structurally disadvantaged areas where mental health distress is ...
More Aggressive treatment doesn’t impact quality of life for metastatic colorectal cancer patients, according to new study in JNCCN
2023-10-12
PLYMOUTH MEETING, PA [October 12, 2023] — New research in the October 2023 issue of JNCCN—Journal of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network finds that intensive local-regional treatment to remove as much tumor as possible (known as “debulking”), in addition to standard systemic therapy, does not impact overall quality of life significantly for people with metastatic colorectal cancer.
The researchers examined the ongoing ORCHESTRA trial (NCT01792934) to compare patients treated with standard palliative chemotherapy alone to those who received palliative chemotherapy plus either surgery, ablative therapy, and/or radiotherapy ...
Honey bees may inherit altruistic behavior from their mothers
2023-10-12
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — True altruism is rare behavior in animals, but a new study by Penn State researchers has found that honey bees display this trait. Additionally, they found that an evolutionary battle of genetics may determine the parent they inherit it from.
For the study, published in the journal Molecular Ecology, the researchers examined the genetics behind “retinue” behavior in worker honey bees, who are always female. After the worker bees are exposed to the queen bee’s pheromone, they deactivate their own ovaries, help spread the pheromone to the other worker bees, and tend to the queen ...