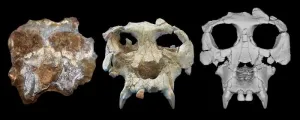
(Press-News.org) A new study led by scientists at the American Museum of Natural History, Brooklyn College, and the Catalan Institute of Paleontology Miquel Crusafont has reconstructed the well-preserved but damaged skull of a great ape species that lived about 12 million years ago. The species, Pierolapithecus catalaunicus, may be crucial to understanding great ape and human evolution. The researchers describe their findings today in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Pierolapithecus catalaunicus, a species from northeastern Spain first described in 2004, was one of a diverse group of now-extinct ape species that lived in Europe around 15 to 7 million years ago. The species is key to understanding the mosaic nature of hominid (great ape and human) evolution because it is known from a cranium and partial skeleton of the same individual—a rarity in the fossil record.
“Features of the skull and teeth are extremely important in resolving the evolutionary relationships of fossil species, and when we find this material in association with bones of the rest of the skeleton, it gives us the opportunity to not only accurately place the species on the hominid family tree, but also to learn more about the biology of the animal in terms of, for example, how it was moving around its environment,” said lead author Kelsey Pugh, a research associate in the Museum’s Division of Anthropology and a lecturer at Brooklyn College.
Previous work on Pierolapithecus suggests that an upright body plan preceded adaptations that allowed hominids to hang from tree branches and move among them. However, debate persists about the species’ evolutionary place, partly due to damage to the cranium.
“One of the persistent issues in studies of ape and human evolution is that the fossil record is fragmentary, and many specimens are incompletely preserved and distorted,” said co-author Ashley Hammond, associate curator and chair of the Museum’s Division of Anthropology. “This makes it difficult to reach a consensus on the evolutionary relationships of key fossil apes that are essential to understanding ape and human evolution.”
In an effort to bring clarity to these questions, the researchers used CT scans to virtually reconstruct the cranium of Pierolapithecus, compare it to other primate species, and model the evolution of key features of ape facial structure. They found that Pierolapithecus shares similarities in overall face shape and size with both fossilized and living great apes, but it also has distinct facial features not found in other Middle Miocene apes. The results are consistent with the idea that this species represents one of the earliest members of the great apes and human family.
“An interesting output of the evolutionary modeling in the study is that that the cranium of Pierolapithecus is closer in shape and size to the ancestor from which living great apes and humans evolved. On the other hand, gibbons and siamangs (the ‘lesser apes’) seem to be secondarily derived in relation to size reduction,” said co-author Sergio Almécija, a senior research scientist in the Museum’s Division of Anthropology.
Other authors on this study include Santiago Catalano, from the Fundación Miguel Lillo (Argentina); Miriam Pérez de los Ríos, from the Universidad Complutense de Madrid; Josep Fortuny, from the Catalan Institute of Paleontology Miquel Crusafont (ICP); Brian Shearer, from New York University; Alessandra Vecino Gazabón, from the American Museum of Natural History; Salvador Moyà-Solà, from the ICP and ICREA; and David Alba, from the ICP.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2218778120
ABOUT THE AMERICAN MUSEUM OF NATURAL HISTORY (AMNH)
The American Museum of Natural History, founded in 1869 with a dual mission of scientific research and science education, is one of the world’s preeminent scientific, educational, and cultural institutions. The Museum encompasses more than 40 permanent exhibition halls, galleries for temporary exhibitions, the Rose Center for Earth and Space including the Hayden Planetarium, and the Richard Gilder Center for Science, Education, and Innovation. The Museum’s scientists draw on a world-class permanent collection of more than 34 million specimens and artifacts, some of which are billions of years old, and on one of the largest natural history libraries in the world. Through its Richard Gilder Graduate School, the Museum offers two of the only free-standing, degree-granting programs of their kind at any museum in the U.S.: the Ph.D. program in Comparative Biology and the Master of Arts in Teaching (MAT) Earth Science residency program. Visit amnh.org for more information.
END
Extinct ape gets a facelift, 12 million years later
New study reconstructs the face of Pierolapithecus catalaunicus, a key fossil in the story of great ape and human evolution
2023-10-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Signatures of the Space Age: Spacecraft metals left in the wake of humanity’s path to the stars
2023-10-16
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. – The Space Age is leaving fingerprints on one of the most remote parts of the planet — the stratosphere — which has potential implications for climate, the ozone layer and the continued habitability of Earth.
Using tools hitched to the nose cone of their research planes and sampling more than 11 miles above the planet’s surface, researchers have discovered significant amounts of metals in aerosols in the atmosphere, likely from increasingly frequent launches and returns of spacecraft and satellites. That mass of metal is changing atmospheric chemistry in ways that ...
Stress levels worse in women who have heart attacks with blockages, study finds
2023-10-16
Stress and depression are known to increase risk of heart attack, especially among women. They’ve also been linked to worse recovery. But does stress and depression contribute more to women with heart attacks with open arteries or blocked arteries? That’s what a new study published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology aimed to find out.
Researchers found stress and depression were indeed common among women at the time of heart attack and for two months after. But they also found that women with heart attacks due to blockages (MI-CAD) in their coronary arteries had higher ...
The new robot is taking its first intuitive steps
2023-10-16
When walking on the sidewalk, a person is able to avoid puddles, other walkers, and cracks in the pavement. It may seem intuitive – and that's because it is.
There’s actually a biological component that allows humans and other mammals to navigate our complex environments. Central Pattern Generators (CPG) are neural networks that produce rhythmic patterns of control signals for limbs using simple environmental cues. When we quickly step away to avoid something blocking our path, that’s ...
Neutrons see stress in 3D-printed parts, advancing additive manufacturing
2023-10-16
Using neutrons to see the additive manufacturing process at the atomic level, scientists have shown that they can measure strain in a material as it evolves and track how atoms move in response to stress.
The automotive, aerospace, clean energy and tool-and-die industries — any industry that needs complex and high-performance parts — could use additive manufacturing,” said Alex Plotkowski, materials scientist in ORNL’s Materials Science and Technology Division and the lead scientist of the experiment. Plotkowski and his ...
How to tell if your boss is a ‘corporate psychopath’
2023-10-16
Findings from research to help the business world identify destructive ‘corporate psychopaths’ will be presented at the Chelmsford Science Festival on Monday, 23 October.
Dr Clive Boddy of Anglia Ruskin University, a pioneer in the field of corporate psychopathy, will discuss his research, published in the International Journal of Market Research, looking at how the financial industry can identify, manage and, if necessary, remove these individuals.
Around 1% of the adult population are ...
Ochsner Health Recipient of the 2023-24 WebMD Choice Awards
2023-10-16
NEW ORLEANS, La. - Ochsner Health was named among the “Best Hospitals According to Patients & Health Care Providers” by WebMD, an online publication for health news and information.
The 2023 WebMD Choice Awards recognized a select group of 167 health systems with Elite Choice Awards, WebMD Patient Choice Awards, and Medscape Physician Choice Awards. Results were gathered via a survey of a national audience encompassing thousands of patients and healthcare clinicians to determine which hospitals they believe deliver the best quality and treatments. The awards program identifies the “best in class” ...
Carnegie Mellon University's Synergy Lab releases three papers on ubiquitous sensing
2023-10-16
Researchers from Carnegie Mellon's Systems, Networking, and Energy Efficiency (Synergy) Lab will present several multi-year studies on their work around ubiquitous sensing at this week's ACM International Joint Conference on Pervasive and Ubiquitous Computing (UbiComp).
The works unveil several innovative systems and explain how the collected data can be converted to offer useful insights, all while ensuring the privacy of the individuals being monitored.
Led by School of Computer Science Associate Professor Yuvraj Agarwal, ...
Insilico Medicine presents data on AI-designed cancer drugs at 3 major cancer conferences
2023-10-16
Clinical stage artificial intelligence (AI) drug discovery company Insilico Medicine (“Insilico”) has been invited to present scientific data on its novel anti-cancer assets at three major upcoming cancer conferences -- the European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) conference in Madrid Oct. 20-24, 2023; the Society of Immunotherapy of Cancer (SITC) conference Nov. 1-5, 2023 in San Diego; and the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium (SABCS) Dec. 5-9, 2023.
Small molecule oncology ...
American Society of Anesthesiologists recognizes Philip G. Morgan, M.D., and Margaret M. Sedensky, M.D., with its Excellence in Research Award
2023-10-16
SAN FRANCISCO — The American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) today presented Philip G. Morgan, M.D., and Margaret M. Sedensky, M.D., with its 2023 Excellence in Research Award in recognition of their extensive research focused on understanding how anesthetics work and whether certain anesthetics are safe for children with mitochondrial disease. The award is presented annually for outstanding achievement in research that has had, or is likely to have, an important impact on the practice of anesthesiology.
Drs. Morgan and Sedensky are professors in the Department of Anesthesiology ...
Study reveals areas of Brazilian Amazon where no ecological research has been done
2023-10-16
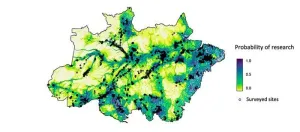
Many parts of the Brazilian Amazon are neglected in ecological research, for several reasons, according to an article published in the journal Current Biology. Authored by Joice Ferreira of the Federal University of Pará (UFP) and colleagues from many countries who also belong to the Synergize Consortium, the article identifies the areas missing from ecological research and the factors that have determined these gaps, pinpointing opportunities for the planning of new investments in research ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Carsten Bönnemann, MD, joins St. Jude to expand research on pediatric catastrophic neurological disorders
Women use professional and social networks to push past the glass ceiling
Trial finds vitamin D supplements don’t reduce covid severity but could reduce long COVID risk
Personalized support program improves smoking cessation for cervical cancer survivors
Adverse childhood experiences and treatment-resistant depression
Psilocybin trends in states that decriminalized use
New data signals high demand in aesthetic surgery in southern, rural U.S. despite access issues
$3.4 million grant to improve weight-management programs
Higher burnout rates among physicians who treat sickle cell disease
Wetlands in Brazil’s Cerrado are carbon-storage powerhouses
Brain diseases: certain neurons are especially susceptible to ALS and FTD
Father’s tobacco use may raise children’s diabetes risk
Structured exercise programs may help combat “chemo brain” according to new study in JNCCN
The ‘croak’ conundrum: Parasites complicate love signals in frogs
Global trends in the integration of traditional and modern medicine: challenges and opportunities
Medicinal plants with anti-entamoeba histolytica activity: phytochemistry, efficacy, and clinical potential
What a releaf: Tomatoes, carrots and lettuce store pharmaceutical byproducts in their leaves
Evaluating the effects of hypnotics for insomnia in obstructive sleep apnea
A new reagent makes living brains transparent for deeper, non-invasive imaging
Smaller insects more likely to escape fish mouths
Failed experiment by Cambridge scientists leads to surprise drug development breakthrough
Salad packs a healthy punch to meet a growing Vitamin B12 need
Capsule technology opens new window into individual cells
We are not alone: Our Sun escaped together with stellar “twins” from galaxy center
Scientists find new way of measuring activity of cell editors that fuel cancer
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
[Press-News.org] Extinct ape gets a facelift, 12 million years laterNew study reconstructs the face of Pierolapithecus catalaunicus, a key fossil in the story of great ape and human evolution