(Press-News.org) A new study published by CHEST Science Journal shows that high-performance intensive care units (ICUs) might also have better patient outcomes during health crises. The study used as a benchmark the mortality rate observed in Brazilian ICUs before and during the COVID-19 pandemic, and analyzed data from over 380,000 patients of private hospital ICUs across 10 Brazilian states. The research was coordinated by the D'Or Institute for Research and Education (IDOR) and concluded that the mortality rate during the pandemic was significantly reduced in ICUs that exhibited high efficiency before the pandemic.
The COVID-19 pandemic, which peaked just a few years ago, has left an indelible mark on the global population and, unfortunately, we may face similar pandemics in the future. Nevertheless, the lessons learned from COVID-19 can be our greatest resource to prevent extreme outcomes in future health crises.
In an effort to understand how ICU efficiency during regular times would impact treatment outcomes during a pandemic, the study conducted a retrospective analysis of data from 33 private hospitals in the country. This analysis considered adult patients admitted to their ICUs between January 2018 and December 2021. The data was collected through a software developed by the company Epimed Solutions, which prospectively gathers standardized information from all participating ICUs.
Using the database, the performance of ICUs was assessed before and during the pandemic through two different metrics. One metric considered patient mortality rates, while the other evaluated resource management in the intensive care centers. ICUs that performed well in both aspects were considered high-efficiency centers. These metrics were also adjusted for disease severity, age, sex, and comorbidities of the patients, as these factors would impact the clinical outcome of COVID-19.
Of the 386,528 patients included in the analysis, 35,619 were admitted to ICUs with a COVID-19 diagnosis during the pandemic. The median profile of patients with the disease ranged from 53 to 70 years of age, with the majority being male, and 64.7% of those admitted had one or more comorbidities.
During the pandemic, the study observed the ICUs displayed a striking range in mortality rates for COVID-19 patients, ranging from 3.6% to 63.2%. These mortality rates also showed variability within ICUs over time, reflecting the dynamics of the pandemic.
The study's results indicate that ICUs with better performance before the pandemic also achieved more favorable outcomes during the health crisis. This included a lower risk and less variation in mortality rates, as well as a faster recovery after the peak of cases, and this stability was held even when considering patient comorbidities and disease severity.
The research highlights that the effective management of patients outside of a pandemic context not only improves overall outcomes but also serves as preparation for addressing a global health crisis. Proper preparation, continuous improvement of efficiency, and the resilience of ICUs in times of stress and high demand for healthcare are essential for providing high-quality care and saving lives.
Dr. Jorge Salluh, a critical care researcher at IDOR and the study's coordinator, commented that the study's results are relevant not only for addressing future pandemics but also for establishing a standard of operation for ICUs. "Regardless of pandemics, ICUs routinely face periods of high stress and occupancy. Efficient management is a constant benefit for healthcare professionals and their patients. While the risk of death is partly related to the severity of the disease and patient fragility, our study reveals that ICUs management has a direct impact on clinical outcomes. This information is the most relevant because it's something we can actually control within the hospital environment."
This study, in addition to serving as a warning for future health adversities, provides an extremely valuable contribution to the functionality of healthcare systems, emphasizing that optimizing ICU efficiency is a crucial strategy for both regular critical care and future challenges similar to the COVID-19 pandemic.
END
High-performance ICUs reduce mortality rates during pandemics and other health crises
New study reveals that mortality rates in Brazilian ICUs ranged from 3% to 63% during the COVID-19 pandemic
2023-10-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Information about abortion care largely omitted or buried on 80% of health systems’ patient-facing websites
2023-10-16
Embargoed for release until 5:00 p.m. ET on Monday 16 October 2023
Annals of Internal Medicine Tip Sheet
@Annalsofim
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not only on their own behalf, but also on behalf of the organization they represent.
----------------------------
1. Information ...
Andrea Califano receives Alfred G. Knudson award from NCI
2023-10-16
Andrea Califano, Dr, has been honored with the 26th Alfred G. Knudson Award in Cancer Genetics by the National Cancer Institute (NCI) for his exceptional contributions to the field of cancer research. Califano, a pioneer in the field of cancer genetics, is the Clyde and Helen Wu Professor of Chemical and Systems Biology at Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons and a member of the Herbert Irving Comprehensive Cancer Center.
The award is named in honor of geneticist and cancer researcher Alfred G. Knudson, MD, a 1947 graduate of the Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons, who helped uncover several major genetic mysteries behind ...
Learning more about how cancer affects stroke risk
2023-10-16
Patients with a previous or current cancer diagnosis are more likely to have a stroke than the general population, but how are specific cancers and treatments associated with stroke risk?
A collaborative team led by University of Cincinnati, University of North Carolina (UNC) and Duke University researchers is seeking to answer that question.
Soma Sengupta, MD, PhD, now division chief of neuro-oncology at UNC, had the idea to study the prevalence of stroke in patients with different cancer types while a faculty member at UC. She recruited a team that included stroke experts Stacie Demel, DO, PhD, of UC and Wuwei Feng of Duke to put together a retrospective pilot study.
“This ...
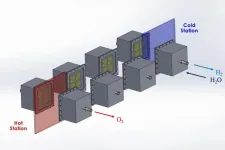
MIT design would harness 40% of the sun’s heat to produce clean hydrogen fuel
2023-10-16
MIT engineers aim to produce totally green, carbon-free hydrogen fuel with a new, train-like system of reactors that is driven solely by the sun.
In a study appearing today in Solar Energy Journal, the engineers lay out the conceptual design for a system that can efficiently produce “solar thermochemical hydrogen.” The system harnesses the sun’s heat to directly split water and generate hydrogen — a clean fuel that can power long-distance trucks, ships, and planes, while in the process emitting no greenhouse gas emissions.
Today, hydrogen is largely produced through processes that involve natural gas and other fossil fuels, ...
Fungal infection in the brain produces changes like those seen in Alzheimer’s disease
2023-10-16
Previous research has implicated fungi in chronic neurodegenerative conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease, but there is limited understanding of how these common microbes could be involved in the development of these conditions.
Working with animal models, researchers at Baylor College of Medicine and collaborating institutions discovered how the fungus Candida albicans enters the brain, activates two separate mechanisms in brain cells that promote its clearance, and, important for the understanding of Alzheimer’s disease development, generates amyloid beta (Ab)-like peptides, toxic protein ...
Jefferson Lab to lead $300+ million high performance data facility hub
2023-10-16
NEWPORT NEWS, VA – The U.S. Department of Energy has just announced the selection of Thomas Jefferson National Accelerator Facility as the lead for its new High Performance Data Facility Hub. Jefferson Lab will partner with DOE’s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory to form a joint project team led by Jefferson Lab. The HPDF will be a $300-500 million computing and data infrastructure resource that will provide transformational capabilities for data analysis, networking and storage for the nation’s research enterprise. ...
VA study provides new insights into COVID-19 pandemic death rates
2023-10-16
A multi-institutional team of researchers led by the White River Junction VA, and including the West Haven and Palo Alto VA, analyzed electronic health record data from more than 5.9 million Veterans―spanning both pre-pandemic (March 2018 - February 2020) and pandemic (March 2020 - February 2022) periods―to discover nuanced insights from COVID-19’s impact on mortality rates.
While former studies have primarily relied on aggregate data, this research―published in the October 2023 issue of the International Journal of Epidemiology―offered a unique perspective ...
Leading scientists, philosophers identify nature’s missing evolutionary law
2023-10-16
A paper in the prestigious Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences today describes “a missing law of nature,” recognizing for the first time an important norm within the natural world’s workings.
In essence, the new law states that complex natural systems evolve to states of greater patterning, diversity, and complexity. In other words, evolution is not limited to life on Earth, it also occurs in other massively complex systems, from planets and stars to atoms, minerals, and more.
Authored by a nine-member team — leading scientists from the Carnegie Institution for ...
Study shows long-term health impacts after exposure to environmental disaster
2023-10-16
Exposure to a large-scale disaster, such as a tsunami, impacts population health over a decade later. A new study by an inter-disciplinary team of researchers in the United States and Indonesia has found that women who lived along the coast of Aceh, Indonesia when it was hit by waves from the 2004 tsunami have lower cortisol levels 14 years later than women who lived in other, nearby coastal communities that were not directly affected.
Cortisol is a stress hormone produced by the adrenal glands. Cortisol levels rise in response to stress as part of the fight or flight response, but consistently elevated ...
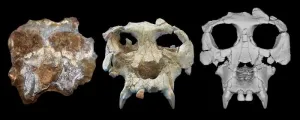
Extinct ape gets a facelift, 12 million years later
2023-10-16
A new study led by scientists at the American Museum of Natural History, Brooklyn College, and the Catalan Institute of Paleontology Miquel Crusafont has reconstructed the well-preserved but damaged skull of a great ape species that lived about 12 million years ago. The species, Pierolapithecus catalaunicus, may be crucial to understanding great ape and human evolution. The researchers describe their findings today in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Pierolapithecus catalaunicus, a species from northeastern Spain first described in 2004, was one of a diverse group of now-extinct ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Mount Sinai, Uniformed Services University join forces to predict and prevent diseases before they start
Science of fitting in: Do best friends or popular peers shape teen behavior?
USF study: Gag grouper are overfished in the Gulf; this new tool could help
New study from Jeonbuk National University finds current climate pledges may miss Paris targets
Theoretical principles of band structure manipulation in strongly correlated insulators with spin and charge perturbations
A CNIC study shows that the heart can be protected during chemotherapy without reducing antitumor efficacy
Mayo Clinic study finds single dose of non-prescribed Adderall raises blood pressure and heart rate in healthy young adults
Engineered immune cells show promise against brain metastases in preclinical study
Improved EV battery technology will outmatch degradation from climate change
AI cancer tools risk “shortcut learning” rather than detecting true biology
Painless skin patch offers new way to monitor immune health
Children with poor oral health more often develop cardiovascular disease as adults
GLP-1 drugs associated with reduced need for emergency care for migraine
New knowledge on heritability paves the way for better treatment of people with chronic inflammatory bowel disease
Under the Lens: Microbiologists Nicola Holden and Gil Domingue weigh in on the raw milk debate
Science reveals why you can’t resist a snack – even when you’re full
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
[Press-News.org] High-performance ICUs reduce mortality rates during pandemics and other health crisesNew study reveals that mortality rates in Brazilian ICUs ranged from 3% to 63% during the COVID-19 pandemic