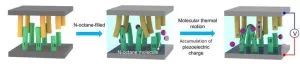
(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON, Oct. 17, 2023 – Wave energy technology is a proven source of power generation, but there is power inherent in every molecule of liquid on earth, even when the liquid is at rest. At the molecular scale, atoms and ions are always moving. If this nanoscale movement can be harvested, it could be a big source of energy.
“There are vast amounts of air and liquid on the earth, and their successful harvesting could produce a gigantic amount of energy for society,” author Yucheng Luan said.
In an article published this week in APL Materials, by AIP Publishing, Luan and his collaborators tested a molecular energy harvesting device that captures the energy from the natural motion of molecules in a liquid. Their work showed molecular motion can be used to generate a stable electric current.
To create the device, the researchers submerged nanoarrays of piezoelectric material in liquid, allowing the movement of the liquid to move the strands like seaweed waving in the ocean, except in this case the movement is on the invisible, molecular scale, and the strands are made of zinc oxide. The zinc oxide material was chosen for its piezoelectric properties, which means that when it waves, bends, or deforms under motion, it generates electric potential.
“As a well-studied piezoelectric material, zinc oxide can be easily synthesized into various nanostructures, including nanowhiskers,” Luan said. “A nanowhisker is a neat and orderly structure of many nanowires, similar to the bristles on a toothbrush.”
Their energy harvesters could be used to power nanotechnologies like implantable medical devices, or they could be scaled to full-size generators and kilowatt-scale energy production. One key design feature of the device is that it doesn’t rely on any external forces, which increases its potential as a game-changing clean energy source.
“Molecular thermal motion harvester devices do not need any external stimulation, which is a big advantage compared with other energy harvesters,” Luan said. “At present, electrical energy is mainly obtained by external energy, such as wind energy, hydroelectric energy, solar energy, and others. This work opens up the possibility of generating electrical energy through the molecular thermal motion of liquids, from the internal energy of the physical system that is essentially different from ordinary mechanical motion.”
The authors are already working on the next phase of their design to improve the energy density of the device by testing different liquids, high-performing piezoelectric materials, and new device architectures and by enlarging the device.
“We believe this novel kind of system will become an indispensable way for human beings to obtain electrical energy in the near future.”
###
The article “Molecular thermal motion harvester for electricity conversion” is authored by Yucheng Luan, Fengwei Huo, Mengshi Lu, Wei Li, and Tonghao Wu. It will appear in APL Materials on Oct. 17, 2023 (DOI: 10.1063/5.0169055). After that date, it can be accessed at https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0169055.
ABOUT THE JOURNAL
APL Materials is an open access journal that features original research on significant topical issues within all areas of materials science. See https://pubs.aip.org/aip/apm.
###
END
Harnessing molecular power: electricity generation on the nanoscale
There is power in numbers when generating electricity from the movement of molecules
2023-10-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study reveals our European ancestors ate seaweed and freshwater plants
2023-10-17
For many people seaweed holds a reputation as a superfood, heralded for its health benefits and sustainability, but it appears our European ancestors were ahead of the game and were consuming the nutrient-rich plant for thousands of years.
Researchers say they have found “definitive” archaeological evidence that seaweeds and other local freshwater plants were eaten in the mesolithic, through the Neolithic transition to farming and into the Early Middle Ages, suggesting that these resources, now rarely eaten in Europe, only ...
Effects of the million hearts model on heart attacks, strokes, and Medicare spending
2023-10-17
About The Study: The Million Hearts Model, which encouraged and paid health care organizations to assess and reduce cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk, reduced first-time heart attacks and strokes. The results support guidelines to use risk scores for CVD primary prevention.
Authors: Laura Blue, Ph.D., of Mathematica in Washington, D.C., is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2023.19597)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional ...
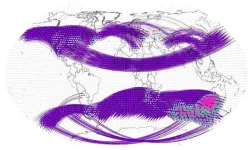
Climate network analysis helps pinpoint regions at higher risk of extreme weather
2023-10-17
WASHINGTON, Oct. 17, 2023 – Climate change and the rapid increase in frequency of extreme weather events around the globe – such as wildfires and floods – reinforces the reality that these events are not only not random but, rather, interconnected. Interlinked climate behavior, or teleconnections, isn’t a well understood field but will be necessary to fully comprehend how our climate system works.
In Chaos, from AIP Publishing, a team of researchers affiliated with Beijing Normal University and Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications in China and the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research in Germany describes a climate network analysis method to explore ...
Race and ethnicity and prehospital use of opioid or ketamine analgesia in acute traumatic injury
2023-10-17
About The Study: The results of this study of over 4.7 million patient encounters across the U.S. during a 3-year period suggest that patients from racial and ethnic minority groups with acute traumatic injuries do not have their pain treated equitably in the prehospital setting.
Authors: Eli Carrillo, M.D., of the Stanford University School of Medicine in Stanford, California, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.38070)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional ...
Adult attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and the risk of dementia
2023-10-17
About The Study: In this study of 109,000 individuals born between 1933 and 1952 and followed up in old age, adult attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) was associated with an increased risk of dementia. Policy makers, caregivers, patients, and clinicians may wish to monitor reliably for ADHD in old age.
Authors: Stephen Z. Levine, Ph.D., of the University of Haifa in Haifa, Israel, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.38088)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including ...
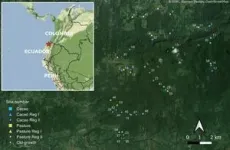
AI models identify biodiversity from animal sounds in tropical rainforests
2023-10-17
Tropical forests are among the most important habitats on our planet. They are characterised by extremely high species diversity and play an eminent role in the global carbon cycle and the world climate. However, many tropical forest areas have been deforested and overexploitation continues day by day.
Reforested areas in the tropics are therefore becoming increasingly important for the climate and biodiversity. How well biodiversity develops on such areas can be monitored very well with an automated analysis of animal sounds. This was reported by researchers in the journal Nature Communications.
Recordings on Former Cocoa Plantations and Pastures
As part of the DFG research group ...
Recognizing clinical signs of hyperthyroidism leads to appropriate treatments, reduces adverse impact on health
2023-10-17
(Boston)—Untreated hyperthyroidism, conditions where there is excess thyroid hormone present, can adversely affect health, leading to increased risks for abnormal heart rhythms, heart failure, osteoporosis, adverse pregnancy outcomes, metabolic abnormalities and increased mortality risk. Hyperthyroidism can occur due to several different etiologies, including Graves’ disease, toxic (overactive) thyroid nodules, and thyroiditis. It is important to recognize, correctly diagnose, and appropriately treat the underlying cause of hyperthyroidism to minimize its impacts on health.
In a new review article in the Journal ...
Adults with ADHD are at increased risk for developing dementia
2023-10-17
Adults with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) are nearly three times more likely to develop dementia than adults without ADHD, according to a Rutgers study.
The study, coauthored by Michal Schnaider Beeri, director of the Herbert and Jacqueline Krieger Klein Alzheimer’s Research Center at Rutgers Brain Health Institute (BHI) was published in JAMA Network Open. It followed more than 100,000 older adults in Israel over 17 years to examine if adults with ADHD are at increased risk for dementia, including Alzheimer’s disease.
Although more than 3 percent of the adult population in the United States has ADHD, there is limited research ...
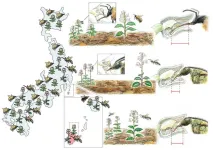
Orchid without bumblebee on island finds wasp, loses self
2023-10-17
Because the bumblebee that an orchid relies on for pollination does not exist on a remote island, the plant gets pollinated by an island wasp. Kobe University researchers found that this came at the cost of being hybridized with another orchid species adapted to being pollinated by the wasp. The finding showcases how plants in ecological relationships adapt to changing circumstances.
Remote islands have been exciting study grounds for biologists since at least the days of Darwin. When studying ecological relationships between different species, the differences between mainland and island ...
Ocean circulation, ice melt and increasing tourism could all be contributing to Arctic microplastics
2023-10-17
Scientists measured microplastic concentrations in the highly productive Barents Sea and suggest that ocean circulation, ice melt, tourism, inadequate waste management, shipping and fishing are all likely contributors.
Numerous studies have shown that global microplastic quantities in the marine environment are increasing, even in remote locations such as the Arctic.
The Barents Sea, which adjoins the Arctic Ocean, is one of the most productive oceanic areas in the world and home to an enormous diversity of organisms.
It is also a key route for Atlantic ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New strategies boost effectiveness of CAR-NK therapy against cancer
Study: Adolescent cannabis use linked to doubling risk of psychotic and bipolar disorders
Invisible harms: drug-related deaths spike after hurricanes and tropical storms
Adolescent cannabis use and risk of psychotic, bipolar, depressive, and anxiety disorders
Anxiety, depression, and care barriers in adults with intellectual and developmental disabilities
Study: Anxiety, gloom often accompany intellectual deficits
Massage Therapy Foundation awards $300,000 research grant to the University of Denver
Gastrointestinal toxicity linked to targeted cancer therapies in the United States
Countdown to the Bial Award in Biomedicine 2025
Blood marker from dementia research could help track aging across the animal world
Birds change altitude to survive epic journeys across deserts and seas
Here's why you need a backup for the map on your phone
ACS Central Science | Researchers from Insilico Medicine and Lilly publish foundational vision for fully autonomous “Prompt-to-Drug” pharmaceutical R&D
Increasing the number of coronary interventions in patients with acute myocardial infarction does not appear to reduce death rates
Tackling uplift resistance in tall infrastructures sustainably
Novel wireless origami-inspired smart cushioning device for safer logistics
Hidden genetic mismatch, which triples the risk of a life-threatening immune attack after cord blood transplantation
Physical function is a crucial predictor of survival after heart failure
Striking genomic architecture discovered in embryonic reproductive cells before they start developing into sperm and eggs
Screening improves early detection of colorectal cancer
New data on spontaneous coronary artery dissection (SCAD) – a common cause of heart attacks in younger women
How root growth is stimulated by nitrate: Researchers decipher signalling chain
Scientists reveal our best- and worst-case scenarios for a warming Antarctica
Cleaner fish show intelligence typical of mammals
AABNet and partners launch landmark guide on the conservation of African livestock genetic resources and sustainable breeding strategies
Produce hydrogen and oxygen simultaneously from a single atom! Achieve carbon neutrality with an 'All-in-one' single-atom water electrolysis catalyst
Sleep loss linked to higher atrial fibrillation risk in working-age adults
Visible light-driven deracemization of α-aryl ketones synergistically catalyzed by thiophenols and chiral phosphoric acid
Most AI bots lack basic safety disclosures, study finds
How competitive gaming on discord fosters social connections
[Press-News.org] Harnessing molecular power: electricity generation on the nanoscaleThere is power in numbers when generating electricity from the movement of molecules