(Press-News.org) A phase 3 clinical trial evaluating the injectable prescription medication tirzepatide, showed an additional 21.1% weight loss after intensive lifestyle intervention in adults with obesity or who were overweight with weight-related comorbidities, excluding Type 2 diabetes.
The findings of the SURMOUNT-3 study, sponsored by pharmaceutical company Eli Lilly, were simultaneously published this week in the journal Nature Medicine and presented at a national conference of obesity researchers.
Tirzepatide, marketed as a treatment of Type 2 diabetes under the brand name Mounjaro, mimics the actions of two hormones, glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP). These hormones work together to stimulate insulin secretion and slow stomach emptying extending the sensation of fullness following a meal. This helps regulate blood sugar levels and cause weight loss.
Gitanjali Srivastava, MD, associate professor of Medicine in the Division of Diabetes, Endocrinology and Metabolism and medical director of Obesity Medicine at Vanderbilt University Medical Center, served as a site investigator for the 72-week randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled trial evaluating the efficacy of tirzepatide.
“We are excited about the results of the SURMOUNT-3 trial,” said Srivastava. “This medication has already proven to be highly effective as a treatment for persons with Type 2 diabetes. This research provides solid evidence that it is also extremely effective as a tool to achieve significant, life-changing weight loss, in conjunction with a low-calorie diet, exercise and frequent nutrition and behavioral counseling.”
The trial enrolled 806 participants across the United States, including Puerto Rico, and Argentina and Brazil. Before taking tirzepatide or a placebo, participants took part in a 12-week intensive lifestyle intervention.
Participants who had at least a 5% body weight reduction by the end of the 12-week lead-in period were randomized to receive either a placebo or tirzepatide. The starting dose of 2.5 mg of tirzepatide was increased by 2.5 mg every four weeks until a maximum tolerated dose of 10 mg or 15 mg once weekly was achieved.
At the beginning of the study, the mean body weight was 241.4 lbs. (109.5 kg). At the end of the 12-week lead-in period, participants achieved 6.9% (7.6 kg or 16.8 lbs.) mean weight loss.
In a co-primary endpoint, following the lead-in period, participants taking tirzepatide achieved an additional 21.1% mean weight loss. From study entry to 84 weeks, participants achieved a total mean weight loss of 26.6% (29.2 kg or 64.4 lbs.).
Participants taking the placebo achieved a total mean weight loss of 3.8% (4.1 kg or 9.0 lbs.) from study entry over 84 weeks.
The most common side effects from tirzepatide were gastrointestinal, such as nausea, diarrhea and constipation, which were generally mild to moderate in severity.
“Tirzepatide, following on the heels of semaglutide 2.4 mg once weekly for adults with overweight or obesity, brings a new era of incretin-based therapies that can achieve beyond just the clinically meaningful 5% weight loss,” said Srivastava. “These novel therapies are changing the landscape of obesity treatment rapidly, and still more are in development. For persons with obesity, there is now hope coupled with scientific evidence.”
END
WASHINGTON, DC – Applications are currently being accepted for the Summer 2024 term of two undergraduate internship programs offered by the Department of Energy (DOE) Office of Science: the Science Undergraduate Laboratory Internships (SULI) program and the Community College Internships (CCI) program. The application deadline is January 9, 2024, at 5:00 p.m. EST.
Through SULI and CCI, undergraduate students and recent graduates discover science and technology careers at the DOE national laboratories and gain the experience needed to transition ...
WASHINGTON, DC – Applications are currently being accepted for the Summer 2024 term of the DOE Office of Science’s Visiting Faculty Program (VFP). The application deadline is January 9, 2024, at 5:00 p.m. ET.
Two application assistance workshops will be held for all faculty interested in applying to VFP:
November 17, 2023, at 12:00 p.m. ET (register here)
December 1, 2023, at 12:00 p.m. ET (register here)
In addition, prospective VFP applicants can engage with recruiters and scientists from the DOE national laboratories at a summer internship fair sponsored by the Office of Workforce ...
Big Tech’s race into augmented reality (AR) grows more competitive by the day. This month, Meta released the latest iteration of its headset, the Quest 3. Early next year, Apple plans to drop its first headset, the Vision Pro. The announcements for each platform emphasize games and entertainment that merge the virtual and physical worlds: a digital board game imposed on a coffee table, a movie screen projected above airplane seats.
Some researchers, though, are more curious about other uses for AR. The University of Washington’s Makeability Lab is applying these budding technologies to assist people with disabilities. This month, ...
AUSTIN, Texas -- A rule to limit trading based on nonpublic stock information has limited effectiveness, according to a recent study by Texas McCombs Finance Professor Robert Parrino.
Issued in 2000 by the Securities & Exchange Commission, Rule 10b5–1 requires corporate insiders to schedule the purchase or sale of a predetermined number of shares through a third-party broker up to two years in advance. Because the trades under these “plan” sales are scheduled in advance of their execution, insiders are presumed less likely to be acting on inside information.
But ...
A special brain-wave cap can diagnose stroke in the ambulance, allowing the patient to receive appropriate treatment faster. Jonathan Coutinho, neurologist at Amsterdam UMC, is one of the inventors the swimming cap: "Our research shows that the brain-wave cap can recognize patients with large ischemic stroke with great accuracy. This is very good news, because the cap can ultimately save lives by routing these patients directly to the right hospital." The research is published today in Neurology.
Every year, millions of people worldwide suffer an ischemic stroke, the most common type of stroke. An ischemic stroke occurs ...
Aspergillus fumigatus is the major airborne fungus present indoors and outdoors that causes various diseases, the severity of which are dependent on an individual’s immune status.
Researchers in the College of Pharmacy at the University of Tennessee Health Science Center have received a $423,500 grant from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) of the National Institutes of Health for research aimed at reducing disease and mortality rates associated with Aspergillus infections ...
Lugano, Switzerland, 17 October 2023 – Women living and working in places with higher levels of fine particle air pollution are more likely to get breast cancer than those living and working in less polluted areas. Results of the first study to take account of the effects of both residential and workplace exposure to air pollution on breast cancer risk are presented at the ESMO Congress 2023 in Madrid, Spain (1).
“Our data showed a statistically significant association between long term exposure to fine particle air pollution, at home and at work, and risk of breast cancer. This contrasts with previous research which looked only at fine particle exposure ...
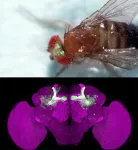
Thermosensation is critical for the survival of animals, but the mechanisms by which this is modulated by nutritional status remain unclear; here, behavioral and live brain imaging studies reveal why food-sated fruit flies prefer to stay at relatively higher temperatures compared to hungry flies.
#####
In your coverage, please use this URL to provide access to the freely available paper in PLOS Biology: http://journals.plos.org/plosbiology/article?id=10.1371/journal.pbio.3002332
Article Title: Independent insulin signaling modulators govern hot avoidance ...
Different strains of E.coli can outcompete one another to take over the gut, a new study reveals.
Publishing their findings today in PLOS Biology, scientists reveal that a particular strain, known as MDR ST131, can readily colonise new hosts, even if those hosts are already have E.coli in their healthy gut.
The international team, led by experts at the University of Birmingham, used a mouse model to help understand why strains of E.coli that live in a healthy gut are rapidly overtaken of when challenged with a multi-drug resistant strain.
Lead author Professor Alan McNally, from ...
Sleeping patterns and stress hormones could be the key to understanding how and when people with epilepsy are likely to experience seizures, a new study reveals.
Researchers used mathematical modelling to understand the impact of different physiological processes, such as sleep and changes in concentration of the stress-hormone cortisol, on key signatures of epilepsy – known as epileptiform discharges (ED).
Epilepsy is a serious neurological disorder characterised by a tendency to have recurrent, spontaneous seizures. Classically, seizures were assumed to occur at random, until the discovery of ED activity with timescales that vary from hours and days through to months.
The scientists ...