(Press-News.org) Proton exchange membrane hydrogen fuel cells (PEMFCs) used in hydrogen vehicles use expensive platinum catalysts to facilitate the oxygen reduction reaction at the anode. There are a vast number of elemental combinations and compositions that need to be explored to develop more efficient and cost-effective catalyst materials than platinum, and researchers are still doing a lot of trial and error in the lab.
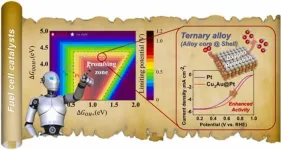
The Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST, President Seok Jin Yoon) announced that Dr. Donghun Kim and Dr. Sang Soo Han of the Computational Science Research Center, Dr. Jong Min Kim of the Materials Architecturing Research Center, and Prof. Hyuck Mo Lee of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST, President Kwang Hyung Lee) have presented a new artificial intelligence-based catalyst screening methodology and succeeded in developing a new catalytic material based on a ternary element-based alloy (Cu-Au-Pt) that is cheaper and performs more than twice as well as pure platinum catalysts.
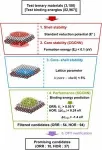
The team developed Slab Graph Convolutional Neural Network (SGCNN) artificial intelligence model to accurately predict the binding energy of adsorbates on the catalyst surface. This is not the first application of AI to materials discovery. The SGCNN model was developed by evolving the CGCNN model, which is specialized in predicting bulk properties of solid materials, to predict surface properties of catalytic materials.
However, there is a big difference between predicting bulk properties and surface properties. When you can quickly and accurately predict the surface properties of a catalyst, you can more efficiently screen for catalysts that meet the triple bottom line of material stability, performance, and cost. In fact, when developing fuel cell anode reaction catalysts using this methodology, we were able to explore the potential of nearly 3,200 ternary candidate materials in just one day, a scale that would have taken years using the density functional theory (DFT) adsorption energy simulation calculations traditionally used to predict catalyst properties.
The researchers developed a novel ternary (Cu-Au-Pt) alloy catalyst through experimental validation of 10 catalysts with the potential to outperform platinum catalysts out of approximately 3,200 candidate materials. The catalyst uses only 37% of the element platinum compared to pure platinum catalysts, but the kinetic current density is more than twice as high as that of pure platinum catalysts. The catalyst also exhibits excellent durability, with little degradation after 5,000 stability tests.
"In the future, we plan to continue to build high-quality adsorption energy data and perform more sophisticated AI modeling, which will further improve the success rate of catalytic material development," said Dr. Kim of KIST. The new methodology has the advantage of being immediately applicable not only to catalysts for hydrogen fuel cells, but also to various catalytic reactions such as water electrolysis-based hydrogen production, which is essential for the realization of the hydrogen economy. The team plans to further reduce the unit cost and improve the performance of the developed catalysts through material and system optimization.
###
KIST was established in 1966 as the first government-funded research institute in Korea. KIST now strives to solve national and social challenges and secure growth engines through leading and innovative research. For more information, please visit KIST’s website at https://eng.kist.re.kr/
The research was supported by the Samsung Future Technology Fostering Project (SRFC-MA1801-03) of Samsung Electronics (CEO Kye-hyun Kyung) and the Materials Research Data Platform Project of the Ministry of Science and ICT (Minister Jong-ho Lee), and was published in the international journal Applied Catalysis B: Environmental.
END
Using AI to develop hydrogen fuel cell catalysts more efficiently and economically
Development of a new ternary alloy (Cu-Au-Pt) catalyst that is cheaper and more efficient than traditional platinum (Pt) catalysts
2023-10-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Enhancing the safety and efficacy of drone flights in polar regions
2023-10-18
Collecting accurate weather data in remote and challenging environments like the polar regions and mountains can be extremely difficult. These areas often lack the infrastructure and resources needed for traditional weather stations, and the harsh weather conditions can make it dangerous for humans to access and maintain these stations.
Drones can navigate these challenging terrains, gather data, and transmit it to researchers, making them an indispensable tool for addressing these data gaps. Unfortunately, in-cloud flights still pose a challenge, with icing from supercooled cloud droplets that can damage vital drone components, ...
Is it ok to press the snooze button?
2023-10-18
Snoozing, or using intermittent alarms to get in a few more minutes of sleep in the morning, may have benefits for some people, according to research published in the Journal of Sleep Research.
In a study of 1,732 adults who described their waking habits, 69% of participants reported using the snooze function or setting multiple alarms at least “sometimes.” In those who snoozed, the average time spent snoozing per morning was 22 minutes, ranging from 1 to 180 minutes. Snoozers tended to be younger than non-snoozers and were more likely to be evening types. Morning drowsiness and shorter sleep were also more common in those who snoozed.
In a second ...
Prenatal exposure to environmental chemicals linked to childhood growth changes
2023-10-18
A new study led by researchers from the Barcelona Institute for Global Health (ISGlobal), a centre supported by the ”la Caixa Foundation” has shed light on the influence that Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals (EDCs) can have on children's growth during their early years. The results, published in Environmental Health Perspectives, show that prenatal exposure to some of these environmental chemicals and their mixtures is linked to accelerated Body Mass Index (BMI) gain from birth to nine years ...
Nearly half of oncology drugs approved since 1998 are precision therapies
2023-10-18
Bottom Line: Of the 198 new oncology drugs approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) between 1998 and 2022, approximately 43% were precision oncology therapies, the use of which is guided by biomarker testing.
Journal in Which the Study was Published: Cancer Discovery, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR).
Authors: Debyani Chakravarty, PhD, assistant attending molecular geneticist in the Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine and lead scientist of the precision oncology knowledge base OncoKB at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSK), was the senior author of the study. Sarah P. ...
Ocean Sciences Meeting 2024 press registration now open
2023-10-18
WASHINGTON — Press registration is now open for the 2024 Ocean Sciences Meeting, co-sponsored by the American Geophysical Union (AGU), the Association for the Sciences of Limnology and Oceanography (ASLO), and The Oceanography Society (TOS), in New Orleans, Louisiana 18 to 23 February 2024. The biennial Ocean Sciences Meeting brings together 5,000 scientists, students, policymakers and educators to discuss breaking research across the ocean sciences and critical issues affecting a sustainable future for our oceans.
PRESS: REGISTER and BOOK HOTELS
Staff, freelance and student journalists are eligible to apply for complimentary press registration through the end of the conference. ...
Founder personality could predict start-up success: study
2023-10-18
The stats don’t lie – the overwhelming majority of start-up companies fail. So, what makes the seemingly lucky few not only survive, but thrive?
While good fortune and circumstances can play a part, new research reveals that when it comes to start-up success, a founder’s personality – or the combined personalities of the founding team - is paramount. The study, published today in Scientific Reports, shows founders of successful start-ups have personality traits that differ significantly from the rest of the population – and that these traits are more important for success than many other ...
Advances in gynaecological cancer research could change the treatment landscape
2023-10-18
Lugano, Switzerland, 17 October 2023 – Results from highly anticipated phase 3 clinical trials in gynaecological cancers with, among others, new data that cover the entire spectrum of managing patients with cervical cancer, will be presented at the ESMO Congress 2023 in Madrid, Spain. The late-breaking studies will be featured in Presidential and Proffered Paper Sessions, and could change the treatment landscape for women with these cancers. The new therapies tested delayed the time to relapse and, in some cases, lengthened survival.
“These ...
Physicists create new form of antenna for radio waves
2023-10-18
University of Otago physicists have used a small glass bulb containing an atomic vapor to demonstrate a new form of antenna for radio waves. The bulb was “wired up” with laser beams and could therefore be placed far from any receiver electronics.
Dr Susi Otto, from the Dodd-Walls Centre for Photonic and Quantum Technologies, led the field testing of the portable atomic radio frequency sensor.
Such sensors, that are enabled by atoms in a so-called Rydberg state, can provide superior performance over current antenna ...
UCLA-led team finds a stem-cell derived mechanism that could lead to regenerative therapies for heart damage
2023-10-18
UCLA-led team finds a stem-cell derived mechanism that could lead to regenerative therapies for heart damage
A UCLA-led team has identified an essential internal control mechanism that can promote the maturation of human stem cell-derived heart muscle cells, offering a deeper understanding of how heart muscle cells develop from their immature fetal stage to their mature adult form.
The findings, published in the peer-reviewed journal Circulation, could lead to new therapies for heart disease and cardiac damage.
The collaborative effort with Duke-NUS Medical School in Singapore and other institutions identified an RNA splicing ...
Lung cancer treatment research enters a new era
2023-10-18
Advances in lung cancer treatment highlight importance of tumour testing at diagnosis
Research presented at the ESMO Congress 2023 sets potential major changes in first-line treatment for patients with NSCLC with targetable tumour cell mutations
Lugano, Switzerland, 17 October 2023 – More people with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) are likely to benefit from new drugs that target molecular alterations in tumour cells, with less need for chemotherapy, following results of multiple landmark clinical trials reported for the first time in late-breaking presentations at the ESMO Congress 2023 (1-7). Better outcomes were achieved with combinations ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
[Press-News.org] Using AI to develop hydrogen fuel cell catalysts more efficiently and economicallyDevelopment of a new ternary alloy (Cu-Au-Pt) catalyst that is cheaper and more efficient than traditional platinum (Pt) catalysts