(Press-News.org) Researchers at North Carolina State University and global collaborators have mapped the mosquito’s tree of life, a major step toward understanding important traits, such as how the insects choose their hosts, feed on blood and spread disease. The findings will help researchers make better predictions to model disease transmission and understand what makes some mosquitoes better disease carriers than others.
The research suggests that mosquito evolution over the past 200 million years mirrors the Earth’s history of shifting land masses and changing host organisms, says Dr. Brian Wiegmann, William Neal Reynolds Professor of Entomology at NC State and corresponding author of a paper describing the mosquito family tree, published in Nature Communications.
“This ongoing project builds a big-data resource that mines the academic literature with published observations of the sources of blood mosquitoes drink, from animals as diverse as fish to humans,” Wiegmann said. “It focuses explicitly on data collection to infer aspects of mosquito biology in a contextualized way. That means linking up the family, or phylogenetic, tree with the narrative of life on Earth: geologic history, climate history and organism history.”
While the researchers pored over the academic literature to capture as much published information about mosquitoes as possible, new genomic sequencing techniques also allowed them to take decades-old mosquitoes – some held in place by pins inside insect collections – and capture a great deal of information on their genetic similarities from just fragments of their genetic blueprints, or genomes.
“A lot of research goes into the important mosquitoes and there’s not much known about the incredible mosquito diversity across the globe,” Wiegmann said. “We now have the tools to sample genetic information more rapidly and very thoroughly. And so the time was right to take a big stab at putting the disease vectors and the well-known mosquitoes into the context they evolved in.”
Piecing the genetic and published information together gave the researchers a few notable findings and these can be evaluated against current patterns and distributions.
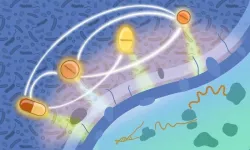
Mosquitoes are an ancient group – around 217 million years old – that probably originated in South America before it was South America, on one big land mass called Gondwana that hadn’t yet split apart.
“Major events like continental drift certainly influenced the diversification of mosquitoes,” Wiegmann said.
“The genomic data confirms that blood feeding evolved very early, before some vertebrate groups, like mammals and birds, were flourishing on Earth,” Wiegmann said. “Mosquitoes evolved right along with them with a new feeding strategy of developing hypodermic needles for mouths and feeding on blood in order for females to have plenty of protein to develop mature eggs.”
And while no mosquito gut contents exist from hundreds of millions of years ago, Wiegmann says that dinosaurs likely provided blood meals for mosquitoes.
“Before mammals became the main hosts on Earth, there had to be something else that mosquitoes fed on. Our research suggests that mosquitoes started out feeding on amphibians and then moved onto other groups – reptiles and birds – as those groups flourished during the Jurassic Era between about 200 million and 145 million years ago.”
Wiegmann said work on the mosquito family tree will continue.
“The family tree ends up being a road map for the kinds of adaptations that led to why some mosquitoes are such important vectors of disease and others are not,” Wiegmann said. “If we figure out which are the bad mosquitoes and put them in the context that led to the success of being vectors of human disease, then we can understand more about how similar pathways may be taken, or how we can predict why some mosquitoes are carriers of viruses and other are not.”
Funding for the research came from the National Science Foundation under grant DEB-17534376. John Soghigian, Charles Sither, Silvia Andrade Justi, Gen Morinaga, Brian K. Cassel, Christopher J. Vitek, Todd Livdahl, Siyang Xia, Andrea Gloria-Soria, Jeffrey R. Powell, Thomas Zavortink, Christopher M. Hardy, Nathan D. Burkett-Cadena, Lawrence E. Reeves, Richard C. Wilkerson, Robert R. Dunn, David K. Yeates, Maria Anice Sallum, Brian D. Byrd, Michelle D. Trautwein, Yvonne-Marie Linton and Michael H. Reiskind co-authored the paper.
- kulikowski -
Note to editors: An abstract of the paper follows.
“Phylogenomics reveals the history of host use in mosquitoes”
Authors: John Soghigian, Charles Sither, Brian K. Cassel, Robert R. Dunn, Michael H. Reiskind and Brian M. Wiegmann, North Carolina State University, et al
Published: Oct. 6, online in Nature Communications
DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-41764-y
Abstract: Mosquitoes have profoundly affected human history and continue to threaten human health through the transmission of a diverse array of pathogens. The phylogeny of mosquitoes has remained poorly characterized due to difficulty in taxonomic sampling and limited availability of genomic data beyond the most important vector species. Here, we used phylogenomic analysis of 709 single copy ortholog groups from 256 mosquito species to produce a strongly supported phylogeny that resolves the position of the major disease vector species and the major mosquito lineages. Our analyses support an origin of mosquitoes in the early Triassic (217 MYA [highest posterior density region: 188–250 MYA]), considerably older than previous estimates. Moreover, we utilize an extensive database of host associations for mosquitoes to show that mosquitoes have shifted to feeding upon the blood of mammals numerous times, and that mosquito diversification and host-use patterns within major lineages appear to coincide in earth history both with major continental drift events and with the diversification of vertebrate classes.
END
Antimicrobial resistance – occurring when pathogens can survive antibiotic treatment – is one of the most rapidly emerging global public health threats today. According to a 2022 study, nearly five million deaths were associated with antibiotic-resistant bacteria in 2019, with over a million deaths per year directly attributable to antimicrobial resistance.
In a new study, researchers from the Typas Group at EMBL Heidelberg have systematically profiled over 10,000 drug combinations for their effectiveness against common multidrug-resistant bacteria.
“Previously, ...
GRAND RAPIDS, Mich. (Oct. 18, 2023) — A new model developed by Van Andel Institute, Lund University and University of Florence scientists will enable researchers to better understand how Alzheimer’s disease progresses in the brain.
Like other neurodegenerative diseases, Alzheimer’s is challenging to study. It is immensely complex, develops over a long period of time and varies from person to person. Critically, scientists also lack non-invasive techniques to monitor disease progression in the human brain. Instead, they often rely on models that mimic the disease, allowing them to ...
About The Study: There was an increased likelihood of live birth among assisted reproductive technology cycles with a gestational carrier versus those without a gestational carrier in this analysis of 2014 to 2020 national surveillance data. Gestational carrier use was a risk factor for twins, even after adjusting for the number of embryos transferred. More than one-quarter of embryo transfers to gestational carriers involved two or more embryos despite national recommendations of single embryo transfer.
Authors: Lisa M. Shandley, M.D, M.Sc., of the Emory University School of Medicine in Atlanta, is the corresponding author.
To access ...
New York, NY | October 18, 2023 – Two grants from the National Institute of Allergies and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), a four-year $3.2 million award and a 12-month $550,000 administrative supplement, will support innovative research to advance the understanding of how climate change and extreme weather influence HIV-related health outcomes around the world.
A multidisciplinary team of researchers from the CUNY Institute for Implementation Science in Population Health (CUNY ISPH) at the CUNY Graduate School of ...
Recently published in the scientific journal Critical Care Medicine, a review led by the D’Or Institute for Research and Education (IDOR) shed light on the importance of clinical quality registries (CQRs) for the healthcare sector. Also known as electronic medical records, CQRs are systems for collecting and storing health information related to patients and their treatments. The publication includes the collaboration of 15 countries' institutions and shows how the qualified collection of clinical and administrative information has been relevant for optimizing healthcare and management in intensive care units ...
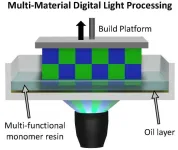
AMES, Iowa – The U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) is looking for materials that “revolutionize and engineer our future.”
Researchers at Iowa State University and the University of California, Santa Barbara think they can do just that by fundamentally changing Digital Light Processing – a type of 3D printing that users light rather than heat to quickly cure and harden liquid resin into plastic layers – to enable multi-material printing.
“We want to produce two material properties ...
A newly launched, first-of-its-kind institute aims to address a glaring gap in the medical system by working to integrate food-based nutrition interventions into health care to treat disease and advance health equity.
The Food is Medicine Institute at the Friedman School of Nutrition Science and Policy at Tufts University, launched today, establishes a university-wide initiative aimed at transforming health care through scalable food-based interventions such as: medically tailored meals and prescriptions for produce; nutrition education for doctors; and clinical care, electronic health record, and reimbursement pathways for nutrition-based tools to help treat or prevent ...
By Benjamin Boettner
(BOSTON) — The Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority (BARDA), part of the Administration for Strategic Preparedness and Response (ASPR) at the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), partnered with the Wyss Institute at Harvard University to support the Institute in advancing its human Organ Chip platform and drug discovery capabilities to better understand the illness and injuries that result from a broad range of health security threats, including high doses of radiation, as well as predicting and evaluating ...
Quantum mechanics is full of weird phenomena, but perhaps none as weird as the role measurement plays in the theory. Since a measurement tends to destroy the “quantumness” of a system, it seems to be the mysterious link between the quantum and classical world. And in a large system of quantum bits of information, known as “qubits,” the effect of measurements can induce dramatically new behavior, even driving the emergence of entirely new phases of quantum information.
This happens when two competing effects come to a head: interactions and measurement. In a quantum system, when the qubits interact ...
Investigators from the Smidt Heart Institute at Cedars-Sinai found that an artificial intelligence (AI) algorithm can detect an abnormal heart rhythm in people not yet showing symptoms.
The algorithm, which identified hidden signals in common medical diagnostic testing, may help doctors better prevent strokes and other cardiovascular complications in people with atrial fibrillation—the most common type of heart rhythm disorder.
Previously developed algorithms have been primarily used in white ...