(Press-News.org) A “two-for-one” cancer immunotherapy is potentially more effective and at least as safe as standard immunotherapies, physician-scientists from UPMC Hillman Cancer Center who led an international, early-phase clinical trial report today in the journal Nature Medicine.
The findings, which involved hundreds of patients with different types of advanced solid tumors or blood cancers, point to an enticing new path for bispecific therapies that more efficiently unleash the patient’s own immune system to eliminate the cancer.
“No approved cancer drugs are like this. It is truly a novel development in the field,” said lead author Jason Luke, M.D., director of the Immunotherapy and Drug Development Center at UPMC Hillman and associate professor of hematology and oncology at the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine. “The patients in our trial had cancers that were not responding to other therapies, so to see double-digit response rates is encouraging.”
Some cancers proliferate when the patient’s immune system stops fighting them – in some cases because the cancer itself is turning off the immune response. The drug, tebotelimab, is a checkpoint inhibitor, meaning it prevents certain proteins released by tumors from binding to the surface of immune cells and telling them to stop responding to the cancer. Usually checkpoint inhibitor drugs target one immune system protein, but tebotelimab is bispecific and blocks two: PD-1 and LAG-3.
Drugs that block PD-1, such as pembrolizumab or nivolumab, have become a center point of treatment for many types of cancer. LAG-3 blocking drugs have recently been approved for advanced melanoma, but little clinical data exists to date for treatment of other types of cancer.
Luke says one drug doing the work of two may be better than two separate drugs, which might engage the immune system differently. When two drugs are used, they may not specifically bind together on the same immune cells. When one bispecific drug with two immune molecules binds to immune cells, the interactions are different and potentially generate greater immune activation.
In addition, the bispecific drug is not more toxic to the patient than one monospecific drug, whereas giving a patient two monospecific drugs typically would have added side effects.
The team enrolled 269 patients with advanced disease, including types of ovarian, breast, head and neck, cervical, and lymphoma cancers. Tumor size decreased in 34% of eligible participants.
The research team took the trial a step further and enrolled another 84 patients with advanced cancers positive for a protein called HER2 to test tebotelimab combined with an approved drug for HER2-positive cancer, called margetuximab. The response rate in those participants was 19%, which Luke said was impressive given the response rate is usually closer to 0% in these particular patients.
Luke says the next step is to develop a biomarker test that will tell doctors which patients have cancers that are expressing the proteins that tebotelimab is designed to block and then conduct another trial to see if outcomes are improved further. Additionally, future trials could test the immunotherapy in combination with chemotherapy or radiation.
“The early suggestion of response across multiple cancer types is intriguing,” said Luke. “This deserves further study, especially since this early phase trial gave us much more certainty around the safety of tebotelimab.”
This research was sponsored by MacroGenics, which is developing tebotelimab.
END
Cancer drug that targets two immune-evading tumor tactics performs well in early clinical trial
2023-10-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
International team develops novel DNA nano engine
2023-10-19
An international team of scientists has recently developed a novel type of nano engine made of DNA. It is driven by a clever mechanism and can perform pulsing movements. The researchers are now planning to fit it with a coupling and install it as a drive in complex nano machines. Their results were just published today in the journal Nature Nanotechnology.
Petr Šulc, an assistant professor at Arizona State University's School of Molecular Sciences and the Biodesign Center for Molecular Design and Biomimetics, has collaborated with professor ...
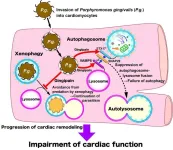
Killer smile? An oral pathogen increases heart attack damage
2023-10-19
Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University(TMDU) find that a periodontal pathogen, Porphyromonas gingivalis, inhibits autophagosome–lysosome fusion, and can therefore worsen cardiac remodeling and cause cardiac rupture after myocardial infarction
Tokyo, Japan – Brushing and flossing regularly can keep your smile shining as brightly as ever, but did you know that it could also help protect your heart? Now, researchers in Japan report that an infected mouth could lead to a broken ...
Modulation of protein stability: a new approach to studying cosolvent effects
2023-10-19
Controlling the process of destabilization is important when manipulating the unfolding and refolding of proteins in vitro (outside their native environment). To this end, urea and alcohol are used as cosolvents, substances added in small amounts along with water, to destabilize and denature proteins. Urea disturbs a native protein to produce disordered coils, and the interference by alcohol treatment yields helical structures. Research on the mechanism of cosolvents has shown that a protein’s stability between its native and denatured states is tied ...
Hook-ups where one partner is drunker more likely to be seen as assault
2023-10-19
Hook-ups where one partner is drunker than the other are more likely to be seen as assault, researchers at the University of Essex revealed.
A study by Dr Veronica Lamarche, from the Department of Psychology, discovered equal consumption was more important than levels of drunkenness.
This was the case even when couples had drunk to excess and was the same across sexualities and genders.
Dr Lamarche discovered that romantic rendezvous were seen most positively when couples drank the same low level of alcohol.
And encounters where one partner was ...
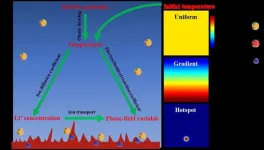
Unified picture on temperature dependence of lithium dendrite growth via phase-field simulation
2023-10-19
They published their work on Sep. 12 in Energy Material Advances.
"The great electrochemical phase-field simulation efforts devoted to exploring the dendrite growth mechanism under the temperature field recently," said paper author Shi, School of Materials Science and Engineering, Shanghai University. "The uniformity of temperature distribution inside batteries has a substantial impact on the stability of Li electrodeposition and dissolution, and the mechanism underlying the temperature-dependent Li dendrite growth remains controversial."
Shi said ...
CAR T-cell therapy effective in patients with blood cancer regardless of race
2023-10-19
(WASHINGTON, Oct. 19, 2023) – Patients with multiple myeloma treated with idecabtagene vicleucel, known as “ide-cel,” a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy, had no difference in overall survival outcomes regardless of race and ethnicity, according to a study published in Blood Advances.
“With this study, we see that Black and white patients with multiple myeloma both respond well to ide-cel,” explained Laura Peres, PhD, an epidemiologist at Moffit Cancer Center and the study’s lead author. “We hope that these findings encourage the use of ide-cel ...
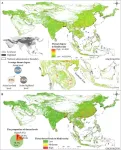
Chinese scholars show that human expansion poses widespread threat to biodiversity in Asia, especially in Southeast Asia
2023-10-19
Biodiversity is essential for sustaining food security, livelihood, ecosystem health, and economic development and for preventing future epidemics. Asia, with nearly 60% of the world's population, stands out as a priority for urgent biodiversity conservation due to its large threatened species and protected areas (PAs), and many countries globally are facing extreme biodiversity and ecological threats. Satellite observations have shown that the human activities (i.e., cropland and artificial surface creations) in Asia have rapidly expanded since the 21st century and are being expanded to highlands (hilly and mountainous regions). Obviously, the intensification of human activities ...
Pinpointing the emergence of muddy flavors in your fish
2023-10-19
Many people have experienced a muddy off-flavor in farmed fish. While the aquaculture industry has known about the problem for 20 years, it continues to impact the consumption of otherwise healthy and potentially sustainable fish. Now, University of Copenhagen researchers have been able to pinpoint exactly when the off-flavors emerge. And this can make it easier to deal with the compounds that turn people away from farmed fish.
Yuk! Musty, earthy or muddy-tasting fish is never going to go over well with the family. Perhaps you’ve tasted it in trout caught from a put-and-take pond. The off-flavor ...
Two probiotics identified as promising hypertension treatments
2023-10-19
Highlights:
High blood pressure affects a large share of the global adult population.
Previous studies suggest probiotics may help prevent hypertension.
New findings point to 2 additional probiotics as potential treatments.
Blood pressure in hypertensive mice returned to healthy levels after treatment with Bifidobacterium lactis and Lactobacillus rhamnosus.
The researchers also identified relationships between unexplored gut microbes and hypertension.
Washington, D.C. – An estimated 40% of the global adult population have high blood pressure, or hypertension, ...
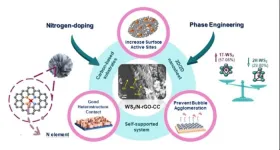
New noble-metal-free electrocatalyst decreases the energy required to generate hydrogen gas from water
2023-10-19
As a combustible fuel, the burning of hydrogen gas does not contribute to global warming. Today, the majority of hydrogen gas is generated from fossil fuels, however, and this process releases greenhouse gasses into the atmosphere. Generating hydrogen gas from clean sources, such as the splitting of water molecules with electricity through electrolysis, is important to achieving future carbon neutrality, but current methods are inefficient and limit the commercial practicality of hydrogen-based technologies. ...