Body image, social media and gender biases associated with kids quitting sports
Survey of youth athletes pinpoints causes of sports attrition
2023-10-20
(Press-News.org) ORLANDO, Fla. (October 20, 2023) – Body image issues, social media, gender biases and coaching styles may be causing young athletes to quit sports, according to research presented by Nemours Children’s Health at the 2023 American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) National Conference & Exhibition.
Previous studies have found that 70% of children quit sports by age 13, and by age 14 girls quit at twice the rate of boys.
“Youth sports participation sets up children for a lifetime of healthy habits. Kids who participate in youth sports have improved cardiovascular fitness, muscular strength and endurance, and a healthy weight,” said lead study author Cassidy M. Foley Davelaar, DO, FAAP, CAQSM, of the Nemours Children's Health Department of Orthopedics and Sports Medicine, an associate professor at the University of Central Florida College of Medicine, and physician for the U.S. Tennis Association. “Parents need to know what drives kids to quit sports so they can support their children’s physical and mental health.”
The study surveyed 70 current or past athletes, ages 8-18, through local athletic organizations and sports medicine clinics. Its goal was to determine the various factors that motivate youth sports attrition. The reasons participants gave for abandoning sports were coaching issues, poor body image comparison from social media and the competitive pressure of the sport.
Based on these findings, the researchers note, parents need to understand coaches’ impact on youth sports participation and ensure that coaches have proper training to foster a positive environment for participation.
Results also indicated significant correlation between screen time, physical activity and body image. Many respondents say they left sports because they feel they don’t match performance or appearance expectations of athletes that they see in media and social media. Those who were less confident in their athletic abilities ranked themselves as “less fit” on the body image silhouette scale than they perceived an athlete would be. Girls were particularly prone to quitting due to competitive pressure.
“Coaches and parents need to know that their words and actions can influence kids’ participation in sports. By being mindful to not place any importance on looking a certain way, adults can encourage a more supportive, inclusive and welcome sports environment among children of all abilities." Dr. Foley Davelaar said. “We hope these findings will reveal the drivers of sports attrition so that adults can create a sports environment that brings joy and participation back to the game.”
# # #
About Nemours Children's Health
Nemours Children’s Health is one of the nation’s largest multistate pediatric health systems, which includes two free-standing children's hospitals and a network of more than 70 primary and specialty care practices. Nemours Children's seeks to transform the health of children by adopting a holistic health model that utilizes innovative, safe, and high-quality care, while also caring for the health of the whole child beyond medicine. Nemours Children's also powers the world’s most-visited website for information on the health of children and teens, Nemours KidsHealth.org.
The Nemours Foundation, established through the legacy and philanthropy of Alfred I. duPont, provides pediatric clinical care, research, education, advocacy, and prevention programs to the children, families and communities it serves. For more information, visit Nemours.org.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-10-20
JACKSONVILLE, Fla. (October 20, 2023) – Researchers from Nemours Children’s Health will present findings from a range of studies, and Nemours physician Steven Selbst, MD, will receive the Jim Seidel Distinguished Service Award for emergency medicine contributions at the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) National Conference & Exhibition, Oct. 20 – 24 in Washington, DC.
“Nemours’ vision is to go well beyond medicine – to help children everywhere stay healthy and grow into healthy adults,” ...
2023-10-20
Media contacts: Lisa Black, lblack@aap.org; or Adam Alexander, aalexander@aap.org
Toddler “formulas” that are promoted as nutritious drinks for the older infant or preschooler are generally unnecessary and nutritionally incomplete, and the marketing practices that promote them are questionable, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics.
The AAP has published a new clinical report, “Older Infant-Young Child ‘Formulas,’ ” that reviews the growing array of drinks aimed at children ages 6-36 months and observes ...
2023-10-20
Ed Sheeran convinced a jury this year that he didn’t rip off Marvin Gaye’s `Let’s Get It On.’ By way of contrast, Pharrell Williams and Robin Thicke earlier failed to establish that `Blurred Lines’ wasn’t a copy of Gaye’s `Got to Give It Up.’
Could automated algorithms bring a new objectivity to music copyright infringement decisions, limiting the number, scale and expense of court cases?
Musicologist Dr Patrick Savage of the University of Auckland researched the topic in collaboration with Yuchen Yuan of Keio University, ...
2023-10-20
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a chronic inflammatory disease of the gastrointestinal tract categorized into ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease. Currently, aminosalicylates, glucocorticoids, immunomodulating drugs, and biological agents are common strategies for the treatment of IBD. The efficacy of these therapies is limited, however, and they are frequently associated with multiple adverse effects.
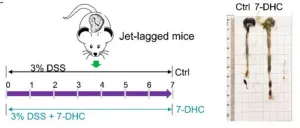
Recently, Life Metabolism published a study entitled “7-Dehydrocholesterol protects against circadian disruption and experimental colitis: potential role of RORα/γ”, which shows that gut microbiota-derived metabolite ...
2023-10-20
The cosmetics industry is turning towards natural alternatives to chemical agents used in products to pave way towards a more sustainable future. Researchers are searching for nature-derived active ingredients for skincare products through extensive bioprospecting research. In this regard, cyanobacteria, with their remarkable metabolic capacity, are a promising source of such agents. Having existed on Earth for nearly 3.5 billion years, these photosynthetic organisms have adapted to various environmental ...
2023-10-20
Consistently sleeping less than five hours a night might raise the risk of developing depressive symptoms, according to a new genetic study led by UCL (University College London) researchers.
Historically, poor sleep has been seen as a side effect of mental ill health, but this study found that the link between sleep and mental illness is more complex.
The study, published in the journal Translational Psychiatry, analysed data from people with an average age of 65 and found short sleep was associated with the onset of depressive symptoms.
Lead author Odessa S. Hamilton (UCL Institute of Epidemiology ...
2023-10-20
Dzemila Sero, now Migelien Gerritzen Fellow at the Rijksmuseum and former postdoc at the Centrum Wiskunde & Informatica, together with a team of researchers from the Rijksmuseum, Leiden and Cambridge University, examined the terracotta sculpture Study for a Hovering Putto attributed to Laurent Delvaux (1696 - 1778) and housed in the Rijksmuseum permanent collection.
The methodology and findings were published open access in Science Advances in a paper with title "Artist profiling using micro-CT scanning of a Rijksmuseum terracotta sculpture".
To acquire preserved impressions on the sculpture, researchers ...
2023-10-20
Researchers at Baylor College of Medicine and the University of Michigan conducted a phase I pilot study to assess the feasibility of using potato starch as a dietary intervention to modify the gut microbiome in bone marrow transplant patients. The study, which appears in the journal Nature Medicine, is the first part of a two-phase ongoing clinical trial evaluating the effect of modifying the microbiome on the incidence of graft-versus-host disease (GVHD), a major complication that develops in up to half ...
2023-10-20
Artificial intelligence (AI)—of ChatGPT fame—is increasingly used in medicine to improve diagnosis and treatment of diseases, and to avoid unnecessary screening for patients. But AI medical devices could also harm patients and worsen health inequities if they are not designed, tested, and used with care, according to an international task force that included a University of Rochester Medical Center bioethicist.
Jonathan Herington, PhD, was a member of the AI Task Force of the Society for Nuclear Medicine and Medical Imaging, which laid out recommendations on how to ethically develop and use AI medical devices in two papers published ...
2023-10-20
Pregnant people who gained more than the now-recommended amount of weight had a higher risk of death from heart disease or diabetes in the decades that followed, according to new analysis of 50 years of data published in The Lancet and led by researchers from the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. The group studied a large national data set that stretched from when a person gave birth through the next five decades, assessing mortality rates to show the potential long-term effects of weight gain in pregnancy. Higher risk of death was found for all weight groups studied — including those defined ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Body image, social media and gender biases associated with kids quitting sports
Survey of youth athletes pinpoints causes of sports attrition