(Press-News.org) AAP media contacts: Lisa Black, 630-626-6084, lblack@aap.org
Tom McPheron, 630-626-6315, tmcpheron@aap.org
Adam Alexander, 630-626-6765, aalexander@aap.org
Washington, D.C.— A retrospective analysis of pediatric sepsis deaths at a large hospital in Arkansas found that Black children in the hospital were 2.5 times more likely to die of sepsis than white patients, according to research presented during the 2023 AAP National Conference & Exhibition at the Walter E. Washington Convention Center.
Researchers who wrote the abstract, “Racial Disparity in Pediatric Sepsis Mortality,” conducted a retrospective analysis of all patients at Arkansas Children’s Hospital (ACH) with sepsis, severe sepsis, or septic shock between January 2018 and April 2022. Researchers found 3,514 patients had sepsis during the study period with an overall mortality rate of 1.65%. Mortality was 3.13% in Black children versus 1.27% in white children, revealing that black children were far more likely to die of sepsis.
“Early recognition and resuscitation of pediatric sepsis has led to improved outcomes. Despite these advancements, Black children continue to have increased mortality rates,” said lead study author Michael Stroud, MD, FAAP, professor, Pediatric Critical Care University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, Arkansas Children’s Hospital Little Rock. “We must identify the factors contributing to this discrepancy and work to improve outcomes for all children, despite race, ethnicity, and socioeconomic status.”
Many hospitals and health centers have made advancements in how they respond to sepsis, which is a deadly emergency health risk. Today, many hospitals, like ACH, use automated, real-time, algorithm-based detection of sepsis, severe sepsis, and septic shock incorporated into the electronic medical record. This method leads to earlier recognition, resuscitation, and improved outcomes.
However, despite improvements in early recognition and resuscitation, sepsis remains a major pediatric health issue with an estimated 40,000 hospitalizations and 5,000 deaths every year in the US.
"Our research shows that mortality in black children remains higher when compared with white children, despite advances like automated recognition tools and timely administration of therapeutic interventions," Dr. Stroud said. “Further investigations are needed to identify if conscious and unconscious biases, potential socio-economic factors, and genetic predispositions are leading to racial disparities in outcomes of children with pediatric sepsis, severe sepsis, and septic shock.”
This work was internally funded by the Arkansas Children’s Hospital.
Dr. Stroud is scheduled to present his research, which is below, from 11:15 to 12:15 p.m. Saturday, Oct. 21, 2023, during session H2020. To request an interview with the authors, contact Michael Stroud, MD, at stroudmichaelh@uams.edu.
Please note: only the abstract is being presented at the meeting. In some cases, the researcher may have more data available to share with media, or may be preparing a longer article for submission to a journal.
# # #
The American Academy of Pediatrics is an organization of 67,000 primary care pediatricians, pediatric medical subspecialists and pediatric surgical specialists dedicated to the health, safety and well-being of infants, children, adolescents and young adults. For more information, visit www.aap.org. Reporters can access the meeting program and other relevant meeting information through the AAP meeting website at http://www.aapexperience.org/
ABSTRACT
Submission Type: Section on Critical Care
Abstract Title: Racial Disparity in Pediatric Sepsis Mortality
Michael Stroud
Little Rock, AR, United States
Despite improvements in early recognition and resuscitation, sepsis remains a major pediatric health issue with an estimated 40,000 hospitalizations and 5,000 deaths every year in the US. Many centers now use automated, real-time, algorithm-based detection of sepsis, severe sepsis, and septic shock incorporated into the electronic medical record (EMR). This method leads to earlier recognition, resuscitation, and improved outcomes. Recent data shows a continued discrepancy in sepsis outcomes based on race, despite improvements in outcomes among children overall. We hypothesized that mortality rates remain higher in black children with sepsis, severe sepsis, and septic shock compared to white children, despite incorporation of automated screening tools into the EMR.
A retrospective analysis of all patients at Arkansas Children’s Hospital (ACH) with sepsis, severe sepsis, or septic shock between January 2018 and April 2022 was conducted. ACH uses a best practice advisory (BPA) in the EMR for early detection in all hospital areas including the emergency department, all medical-surgical wards, all Intensive Care Units (ICU), and interfacility transport. EMR activation leads to a bedside huddle, followed by institution of clinical interventions. A sepsis episode (SE) was defined as BPA activation or a diagnosis of sepsis, severe sepsis, or septic shock in the EMR. Mortality rates, as well as demographic information and clinical outcome measures for children who died were compared between Black(B) and White(W) children. Student's t-test was used for categorical variables, chi-square for proportions, and odds ratio for overall mortality comparison.
3,514 patients had a SE during the study period; 2126(W) and 736(B). Overall mortality was 1.65% (40%(B); 47%(W)). Mortality was 3.13% (23/736) in Black children versus 1.27% in White children; OR 2.51 (1.43,4.40), p=0.001. Basic demographics including gender (Female-56.52%(B), 55.56%(W); p=0.95) and age in years (8.00+/-2.78(B), 7.87+/-2.66; p=0.97) were similar. Clinical interventions including total IV antibiotic days (23.83+/-8.36(B), 21.56+/-9.59(W); p=0.38), vasoactive infusion days (2.17+/-1.44(B), 2.63+/-0.90; p=0.18), and percent requiring Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation (26.07%(B), 18.52%(W), p=0.52) were similar. Black children who died had a longer length of hospitalization (16.70+/-6.47(B), 12.70+/-5.85(W) days; p=0.03) and longer ICU stay (7.57+/-2.57(B), 5,70+/-2.27(W) days; p=0.01). Percent over threshold for antibiotic administration (21.74%(B), 18.52%(W); p= 0.78; 1h-septic shock, 3h-sespis) and IV fluid bolus administration (8.70%(B), 14.81%(W); p=0.51; 20 minutes-septic shock, 1h-sepsis) were similar.
This single center, retrospective study shows that hospitalized Black children have a 2.5 times greater risk of death from sepsis compared to White children. Interestingly, this preliminary data suggests similar rates of timely resuscitation including antibiotic administration and IV fluid boluses. Further investigations are needed to identify biases (conscious and unconscious), potential socio-economic factors, and genetic predispositions leading to racial disparities in outcomes of children with pediatric sepsis, severe sepsis, and septic shock.
END
Research finds Black children over twice as likely to die of sepsis at one hospital
Black children 2.5 times more likely to die of sepsis compared to white children at Arkansas hospital
2023-10-20
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Electric scooter injuries increased more than 70% in youth age 18 and younger from 2020-2021
2023-10-20
Ror release: 12:01 a.m. ET Friday, Oct. 20, 2023
AAP media contacts: Lisa Black, 630-626-6084, lblack@aap.org
Tom McPheron, 630-626-6315, tmcpheron@aap.org
Adam Alexander, 630-626-6765, aalexander@aap.org
Washington, D.C.— As standing electric scooters (e-scooters) have become an increasingly popular mode of transportation, new research finds a 71% increase in injuries reported ...
Parents of toddlers are getting facts about increasingly popular nut milks and dairy substitutes from nonmedical influencers and bloggers
2023-10-20
AAP media contacts: Lisa Black, 630-626-6084, lblack@aap.org
Tom McPheron, 630-626-6315, tmcpheron@aap.org
...
Social media contributing to poor body image among teenaged athletes, associated with dropping high school sports
2023-10-20
AAP media contacts:
Lisa Black, 630-626-6084, lblack@aap.org
Tom McPheron, 630-626-6315, tmcpheron@aap.org
Adam Alexander, 630-626-6765, aalexander@aap.org
Washington, D.C.— High school sports participation sets boys and girls up with healthy habits that can lead to healthier lives, and body image issues caused by social media may be contributing to teenagers making the decision to quit, according to research presented during the 2023 AAP National Conference & Exhibition at the Walter E. Washington Convention ...
Marching band injuries strike a wrong note in emergency departments
2023-10-20
For release: 12:01 a.m. ET Friday, Oct. 20, 2023
AAP media contacts: Lisa Black, 630-626-6084, lblack@aap.org
Tom McPheron, 630-626-6315, tmcpheron@aap.org
Adam Alexander, 630-626-6765, aalexander@aap.org
Washington, D.C.—Marching band is a physically demanding task and performance art that can lead to injury similar to organized athletic activities. New research shows that 70% of marching band-related injuries reported to emergency ...
Research finds 1 out of 4 youth screen positive for suicide risk in an emergency department; majority of those who identify as transgender, gender diverse, screen positive
2023-10-20
For release: 12:01 a.m. ET Friday, Oct. 20, 2023
AAP media contacts: Lisa Black, 630-626-6084, lblack@aap.org
Tom McPheron, 630-626-6315, tmcpheron@aap.org
Adam Alexander, 630-626-6765, aalexander@aap.org
Washington, D.C.— Nearly 80% of emergency department encounters involving transgender or gender diverse youth ages 10 and older ...
Safely removing nanoplastics from water using 'Prussian blue', a pigment used to dye jeans
2023-10-20
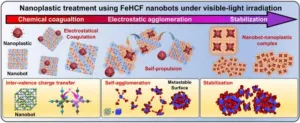
Plastic waste breaks down over time into microplastics (<0.1 μm). Microplastics smaller than 20 μm cannot be removed in currently operating water treatment plants and must be agglomerated to a larger size and then removed. Iron (Fe) or aluminum (Al) based flocculants are used for this purpose, but they are not the ultimate solution as they remain in the water and cause severe toxicity to humans, requiring a separate treatment process.
Dr. Jae-Woo Choi of the Center for Water Cycle Research at ...
Body image, social media and gender biases associated with kids quitting sports
2023-10-20
ORLANDO, Fla. (October 20, 2023) – Body image issues, social media, gender biases and coaching styles may be causing young athletes to quit sports, according to research presented by Nemours Children’s Health at the 2023 American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) National Conference & Exhibition.
Previous studies have found that 70% of children quit sports by age 13, and by age 14 girls quit at twice the rate of boys.
“Youth sports participation sets up children for a lifetime of healthy habits. Kids who participate ...
AAP 2023: Nemours Children’s presents research on body image & sports attrition, social determinants & obesity, and autism screening in primary care
2023-10-20
JACKSONVILLE, Fla. (October 20, 2023) – Researchers from Nemours Children’s Health will present findings from a range of studies, and Nemours physician Steven Selbst, MD, will receive the Jim Seidel Distinguished Service Award for emergency medicine contributions at the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) National Conference & Exhibition, Oct. 20 – 24 in Washington, DC.
“Nemours’ vision is to go well beyond medicine – to help children everywhere stay healthy and grow into healthy adults,” ...
American Academy of Pediatrics reviews toddler ‘formulas,’ questions marketing of drinks
2023-10-20
Media contacts: Lisa Black, lblack@aap.org; or Adam Alexander, aalexander@aap.org
Toddler “formulas” that are promoted as nutritious drinks for the older infant or preschooler are generally unnecessary and nutritionally incomplete, and the marketing practices that promote them are questionable, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics.
The AAP has published a new clinical report, “Older Infant-Young Child ‘Formulas,’ ” that reviews the growing array of drinks aimed at children ages 6-36 months and observes ...
Algorithm and blues: how to judge music plagiarism?
2023-10-20
Ed Sheeran convinced a jury this year that he didn’t rip off Marvin Gaye’s `Let’s Get It On.’ By way of contrast, Pharrell Williams and Robin Thicke earlier failed to establish that `Blurred Lines’ wasn’t a copy of Gaye’s `Got to Give It Up.’
Could automated algorithms bring a new objectivity to music copyright infringement decisions, limiting the number, scale and expense of court cases?
Musicologist Dr Patrick Savage of the University of Auckland researched the topic in collaboration with Yuchen Yuan of Keio University, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New knowledge on heritability paves the way for better treatment of people with chronic inflammatory bowel disease
Under the Lens: Microbiologists Nicola Holden and Gil Domingue weigh in on the raw milk debate
Science reveals why you can’t resist a snack – even when you’re full
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
[Press-News.org] Research finds Black children over twice as likely to die of sepsis at one hospitalBlack children 2.5 times more likely to die of sepsis compared to white children at Arkansas hospital