(Press-News.org) What if your house plant could tell you your water isn’t safe? Scientists are closer to realizing this vision, having successfully engineered a plant to turn beet red in the presence of a banned, toxic pesticide.
To achieve this, UC Riverside researchers had to solve an engineering puzzle: how to enable a plant to sense and react to a chemical in the environment without damaging its ability to function normally in all other respects.
“The biggest piece here is we’ve created an environmental sensor without modifying the plant’s native metabolism,” said Ian Wheeldon, associate professor of chemical and environmental engineering at UCR. “Previously, the biosensor component would have messed up the plant’s ability to grow toward light or stop using water when stressed. This won’t.”
A new paper detailing the chemistry behind the achievement has been published in the journal Nature Chemical Biology. The engineering process begins with a protein called abscisic acid, or ABA, that helps plants acclimate to stressful changes in the environment.
During a drought, soil dries and plants produce ABA. Additional proteins, called receptors, help the plant recognize and respond to ABA. This in turn tells the plant to close pores in its leaves and stems so less water evaporates, and the plant is less likely to wilt.
Last year the research team demonstrated that ABA receptor proteins can be trained to bind to chemicals other than ABA. Now the team has shown that once the receptors bind to this other chemical, the plant will turn beet red.
For this demonstration the team used azinphos-ethyl, a pesticide banned in many places because it is toxic to humans. “People we work with are trying to sense information about chemicals in the environment from a distance,” said Sean Cutler, UCR professor of plant cell biology. “If you had a field of these and they turned red, that would be pretty obvious, visually.”
As part of the same experiment, the research team also demonstrated the ability to turn another living organism into a sensor: yeast. The team was able to show a response in yeast to two different chemicals at the same time. However, this is not yet possible in plants.
“It would be great if we could eventually design one plant to sense 100 banned pesticides, a one-stop shop,” said Cutler. “The more you can stack, the better, especially for applications involving environmental health or defense. But there are limits to what we can engineer for these new sensing capacities at this time.”
To be clear, these plants are not being grown commercially. That would require regulatory approvals that would take many years. It is also a new technology, with a suite of issues that would need to be addressed before it could be used in farmers’ fields, or elsewhere in the real world. However, the discovery opens up possibilities.
“This paper demonstrated a visual response to one chemical in plants. We’re trying to be able to sense any chemical in an environment,” Cutler said. “Other pesticides but also drugs like birth control pills or Prozac in the water supply, things people are worried about being exposed to. These are applications within reach now.”
END
Plants transformed into detectors of dangerous chemicals
Scientists engineer plants to speak in color
2023-10-23
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
How long should kids isolate after they’ve contracted COVID-19?
2023-10-23
School policies that require students with COVID-19 to stay out of the classroom for five days are more than sufficient. That’s because children infected with the Omicron variant remained infectious for a median time of three days after testing positive for the virus, according to a study by the USC Schaeffer Center for Health Policy & Economics and Stanford University.
“We're basically saying five days is more than sufficient; public-health and education leaders may consider shorter durations,” said co-author Neeraj ...
Homeless people are 16 times more likely to die suddenly
2023-10-23
A study led by UC San Francisco has found that people who are experiencing homelessness have a 16-fold higher rate of sudden death from heart attacks, as well as other causes.
The study focused on San Francisco County, which has one of the nation’s highest concentrations of homeless people. It found that the rate of sudden cardiac death was 7 times higher than the general population.
Some of these deaths may have been prevented with defibrillators and other public policy measures to improve health in this vulnerable population, according to the authors.
The paper published ...
New study shows surprising effects of fire in North America’s boreal forests
2023-10-23
A new study, using a first-of-its-kind approach to analyze satellite imagery from boreal forests over the last three decades, found that fire may be changing the face of the region in a way researchers did not previously anticipate.
Historically, fires in North American boreal forests have led to coniferous trees being supplanted by deciduous trees, which are faster growing, take up more carbon and reflect more light, leading to cooling of the climate and decreased likelihood of fire.
The study, led by Northern Arizona University and published today in Nature Climate Change, found that, surprisingly, while forests do become more deciduous, ...
Chemists, engineers craft adjustable arrays of microscopic lenses
2023-10-23
They number in the thousands, light striking the phalanx of lenses arrayed on a face in geometric pattern, the beams refracting through transparent mounds no wider than a hair.
A fly’s eye boasts roughly 4,000 microscopic lenses, a honeybee’s up to twice that many. These lenses, though, belong not to a compound eye but to polydimethylsiloxane — a flexible polymer long ranking as a favored playground of Nebraska’s Stephen Morin and his band of fellow chemists.
With the aid of engineers Ruiguo Yang and Grayson Minnick, Morin’s team can now arrange and ...
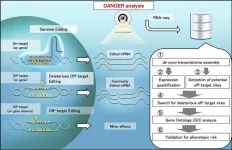
Researchers develop DANGER analysis tool for the safer design of gene editing
2023-10-23
A team of researchers has developed a software tool called DANGER (Deleterious and ANticipatable Guides Evaluated by RNA-sequencing) analysis that provides a way for the safer design of genome editing in all organisms with a transcriptome. For about a decade, researchers have used the CRISPR technology for genome editing. However, there are some challenges in the use of CRISPR. The DANGER analysis overcomes these challenges and allows researchers to perform safer on- and off-target assessments without a reference genome. It holds the potential for applications in medicine, agriculture, and biological research.
Their ...
Lung cancer outcomes significantly improved with immunotherapy-based treatment given before and after surgery
2023-10-23
HOUSTON ― A regimen of pre-surgical immunotherapy and chemotherapy followed by post-surgical immunotherapy significantly improved event-free survival (EFS) and pathologic complete response (pCR) rates compared to chemotherapy alone for patients with operable non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), according to results of a Phase III trial reported by researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center.
The findings, published today in the New England Journal of Medicine, were first presented at the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) Annual Meeting 2023.
The AEGEAN trial evaluated durvalumab given perioperatively, meaning therapy ...
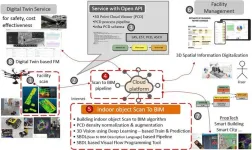
KICT develops scan to BIM for reverse engineering from 3D vision data
2023-10-23
Korea Institute of Civil Engineering and Building Technology (KICT, President Kim Byung-suk) has developed building scan to BIM (Building Information Modeling)-based reverse engineering technology required for 3D geospatial information modeling domains such as digital twin information modeling.
Scan to BIM-based reverse engineering technology was studied to prevent errors and rework caused by manual work when modeling shapes or BIM from 3D scan data. Existing reverse engineering work is either done based on a lot of manual work or semi-automatically using expensive overseas software.
KICT Research Fellow Dr. Kang Tae-wook ...
Crystals brought back by astronauts show that the Moon is 40 million years older than scientists thought
2023-10-23
More than 4 billion years ago, when the Solar System was still young and the Earth was still growing, a giant object the size of Mars crashed into the Earth. The biggest piece that broke off of the early Earth formed our Moon. But precisely when this happened has remained a mystery. In a new study in the journal Geochemical Perspectives Letters, researchers used crystals brought back from the Moon by Apollo astronauts in 1972 to help pinpoint the time of the Moon’s formation. Their discovery pushes back the age of the Moon by 40 million years, to at least 4.46 billion years old.
“These ...
Probiotics delivered in biofilm state protect the intestines and brain in NEC model
2023-10-23
(COLUMBUS, Ohio) – Necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) is a debilitating and deadly condition that affects infants who were born preterm. In NEC cases, intestinal tissues become inflamed, and in severe cases there is ischemia and death of the involved intestines. Treatment for NEC often involves surgery to remove the dying tissue.
“Even after decades of research, little has changed in terms of prognosis for infants who develop NEC,” says Gail Besner, MD, pediatric surgeon and principal investigator in the Center for Perinatal Research at Nationwide Children’s. ...
Heated yoga may reduce depression symptoms, according to recent clinical trial
2023-10-23
BOSTON – In a randomized controlled clinical trial of adults with moderate-to-severe depression, those who participated in heated yoga sessions experienced significantly greater reductions in depressive symptoms compared with a control group.
The results of the trial, which was led by investigators at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH), a founding member of Mass General Brigham (MGB), and was published in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry, indicate that heated yoga could be a viable treatment option for patients with depression.
In the eight-week trial, 80 participants ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] Plants transformed into detectors of dangerous chemicalsScientists engineer plants to speak in color