(Press-News.org) HOUSTON ― A regimen of pre-surgical immunotherapy and chemotherapy followed by post-surgical immunotherapy significantly improved event-free survival (EFS) and pathologic complete response (pCR) rates compared to chemotherapy alone for patients with operable non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), according to results of a Phase III trial reported by researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center.
The findings, published today in the New England Journal of Medicine, were first presented at the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) Annual Meeting 2023.
The AEGEAN trial evaluated durvalumab given perioperatively, meaning therapy is given both before and after surgery. Participants on the trial received either pre-surgical (neoadjuvant) durvalumab and platinum-based chemotherapy followed by post-surgical (adjuvant) durvalumab or neoadjuvant placebo and chemotherapy followed by adjuvant placebo.
AEGEAN was the first Phase III trial investigating perioperative immunotherapy in patients with resectable NSCLC to report positive outcomes, and these data add to the growing evidence supporting the benefits of both neoadjuvant and adjuvant immunotherapy for these patients
“Our goal is to increase cures for lung cancer. Throughout decades of research with adjuvant and neoadjuvant chemotherapy, we only succeeded in increasing cures by around 5%,”
said principal investigator John Heymach, M.D., Ph.D., chair of Thoracic/Head & Neck Medical Oncology at MD Anderson. “This one study alone has the potential to increase that percentage significantly, and we look forward to many more improvements going forward.”
Of the patients receiving perioperative durvalumab, 17.2% had a pCR compared to just 4.3% of those receiving chemotherapy alone. At the first interim analysis of EFS, with a median follow-up of 11.7 months, the median EFS was 25.9 months in the placebo arm, but it had not yet been reached in the durvalumab arm.
These data correspond to a 32% lower chance of patients experiencing disease recurrence, progression events or death with the immunotherapy-based treatment when compared to chemotherapy alone. Approximately four times as many patients treated with perioperative durvalumab plus chemotherapy achieved a pCR when compared to those treated with chemotherapy alone.
Durvalumab, an immune checkpoint inhibitor targeting PD-L1, has previously been approved for treating specific patients with biliary tract cancer, liver cancer, small cell lung cancer and NSCLC. Currently, durvalumab is used for treating patients with locally advanced, unresectable NSCLC following definitive chemoradiotherapy and for patients with metastatic NSCLC in combination with tremelimumab and platinum-based chemotherapy.
For resectable NSCLC, previous studies have shown some benefit from using adjuvant or neoadjuvant immunotherapy, but Heymach explained the benefits have been modest so far. MD Anderson is engaged in longstanding multidisciplinary efforts to use neoadjuvant treatments to improve outcomes for patients. Numerous clinical studies, such as the NEOSTAR and NeoCOAST trials, are evaluating neoadjuvant immunotherapy and novel combinations to eliminate viable tumors before surgery and to reduce recurrence rates.
The Phase III AEGEAN trial is a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study to evaluate the benefits of perioperative durvalumab added to platinum-based chemotherapy in adults with untreated stage IIA-IIIB NSCLC. A total of 802 patients were randomized 1:1 into each arm. The study’s primary endpoints are pCR, assessed by a central lab, and EFS using a blinded independent central review.
Patients with EGFR/ALK mutations were excluded from the modified intent-to-treat population. A total of 740 patients were included in the efficacy analysis, including 366 on the durvalumab arm and 374 on the placebo arm. The median age of participants in each arm was 65 and 71.6% were male. Patients were 53.6% white, 41.5% Asian and 4.9% other.
Overall, the treatments were well tolerated, and side effects were consistent with previous studies. The researchers observed maximum grade 3-4 any cause adverse events in 42.4% and 43.2% of patients on the durvalumab and placebo arms, respectively.
The benefits in both pCR and EFS largely were consistent across predefined patient subgroups, and the trial continues assessment for long-term EFS as well as disease-free survival and overall survival outcomes.
“This study shows that a combination of neoadjuvant and adjuvant durvalumab offers benefit for patients and may have the potential to change standard-of-care for patients with resectable non-small cell lung cancer,” Heymach said. “Going forward, we face a series of questions about how to build more effective regimens without giving more treatment than is necessary.”
Heymach explained that future studies must determine which patients receive the most benefit from neoadjuvant therapy and may be able to avoid further treatment as well as those who remain at high risk of recurrence and may require more intensive adjuvant regimens.
The study was conducted by AstraZeneca. Heymach serves on advisory committees for Genentech, Mirati Therapeutics, Eli Lilly & Co, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Boehringer Ingelheim, Regeneron, Takeda, BerGenBio, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Curio Science, Novartis, AstraZeneca, BioAtla, Sanofi, Spectrum Pharmaceuticals, GSK, EMD Serono, Blueprint Medicines and Chugai Pharmaceutical. He receives research support from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Spectrum, Mirati Therapeutics, Bristol Myers Squibb and Takeda, as well as royalties and licensing fees from Spectrum. A full list of collaborating authors and their disclosures can be found here.
Read this press release on the MD Anderson Newsroom.
END
Lung cancer outcomes significantly improved with immunotherapy-based treatment given before and after surgery
Phase III trial finds 32% lower chance of disease recurrence, progression, or death with immunotherapy plus chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone
2023-10-23
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
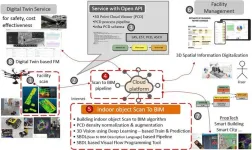
KICT develops scan to BIM for reverse engineering from 3D vision data
2023-10-23
Korea Institute of Civil Engineering and Building Technology (KICT, President Kim Byung-suk) has developed building scan to BIM (Building Information Modeling)-based reverse engineering technology required for 3D geospatial information modeling domains such as digital twin information modeling.
Scan to BIM-based reverse engineering technology was studied to prevent errors and rework caused by manual work when modeling shapes or BIM from 3D scan data. Existing reverse engineering work is either done based on a lot of manual work or semi-automatically using expensive overseas software.
KICT Research Fellow Dr. Kang Tae-wook ...
Crystals brought back by astronauts show that the Moon is 40 million years older than scientists thought
2023-10-23
More than 4 billion years ago, when the Solar System was still young and the Earth was still growing, a giant object the size of Mars crashed into the Earth. The biggest piece that broke off of the early Earth formed our Moon. But precisely when this happened has remained a mystery. In a new study in the journal Geochemical Perspectives Letters, researchers used crystals brought back from the Moon by Apollo astronauts in 1972 to help pinpoint the time of the Moon’s formation. Their discovery pushes back the age of the Moon by 40 million years, to at least 4.46 billion years old.
“These ...
Probiotics delivered in biofilm state protect the intestines and brain in NEC model
2023-10-23
(COLUMBUS, Ohio) – Necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) is a debilitating and deadly condition that affects infants who were born preterm. In NEC cases, intestinal tissues become inflamed, and in severe cases there is ischemia and death of the involved intestines. Treatment for NEC often involves surgery to remove the dying tissue.
“Even after decades of research, little has changed in terms of prognosis for infants who develop NEC,” says Gail Besner, MD, pediatric surgeon and principal investigator in the Center for Perinatal Research at Nationwide Children’s. ...
Heated yoga may reduce depression symptoms, according to recent clinical trial
2023-10-23
BOSTON – In a randomized controlled clinical trial of adults with moderate-to-severe depression, those who participated in heated yoga sessions experienced significantly greater reductions in depressive symptoms compared with a control group.
The results of the trial, which was led by investigators at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH), a founding member of Mass General Brigham (MGB), and was published in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry, indicate that heated yoga could be a viable treatment option for patients with depression.
In the eight-week trial, 80 participants ...
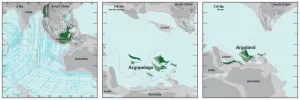
Finding Argoland: how a lost continent resurfaced
2023-10-23
Geologists have long known that around 155 million years ago, a 5000 km long piece of continent broke off western Australia and drifted away. They can see that by the ‘void’ it left behind: a basin hidden deep below the ocean known as the Argo Abyssal Plain. The underwater feature also lends its name to the newly formed continent: Argoland. The structure of the seafloor shows that this continent must have drifted off to the northwest, and must have ended up where the islands of Southeast Asia are located today. ...
Does diabetes affect the survival of individuals with colorectal cancer?
2023-10-23
Complications of diabetes can have numerous negative health effects, from impaired vision and nerve damage to kidney dysfunction and heart disease. In an analysis of information on adults with colorectal cancer, patients who also had diabetes—particularly those with diabetic complications—faced a higher risk of dying early. The results are published by Wiley online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society.
For the study, Kuo‐Liong Chien, MD, PhD, of National Taiwan University, and his colleagues ...
Better regulation of mental health ‘therapies’ urgently needed to protect the vulnerable
2023-10-23
A rise in psychological pseudoscience is putting people at risk, psychologists have warned, with social media and celebrity endorsements partly to blame.
Mental health apps, mood-boosting supplements and energy therapies are among the therapies that could do ‘more harm than good’ according to psychologists Jonathan Stea and Stephen Hupp in their new book Investigating Clinical Psychology.
“As discourse around wellness, mental health, therapy, and access to these resources increasingly enter the public domain, the potential of coming across persuasive pseudoscience has also increased,” Stea explains.
“This is the age of health misinformation. It is everywhere. ...
Do people everywhere care less about their cats than their dogs?
2023-10-23
Do canines get more care? Some studies have suggested pet owners are less emotionally attached to and less willing to finance care for cats than dogs, possibly because of cats’ behavior: cats may be perceived as caring less about humans and needing less care in return. But these studies are often conducted on non-representative samples and don’t consider possible cultural differences in attitudes to pets. A team of scientists led by Dr Peter Sandøe of the University of Copenhagen decided to investigate further.
“We and others have found that people are willing to spend much less on their cats than ...
Association for Molecular Pathology appoints Lauren S. Menser as Chief Executive Officer
2023-10-23
ROCKVILLE, Md. – Oct. 23, 2023 – The Association for Molecular Pathology (AMP), the premier global molecular diagnostic professional society, today announced the appointment of Lauren S. Menser, CAE, as its Chief Executive Officer, effective January 3, 2024. Menser will succeed Mary Steele Williams, MNA, MT(ASCP)SM, CAE, after her retirement. AMP’s national search for a new executive leader was administered by an outside consulting firm and overseen by a diverse group of member volunteers.
Menser has served AMP in various capacities for more than 17 years. Since 2016, she has served as Director of Strategic Development, ...
Predictors of opioid overdose after prescription for chronic pain
2023-10-23
A large study published in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.230459 identified 10 predictors of opioid overdose after prescription for chronic pain, which can help clinicians engage in shared decision-making with patients around opioid prescribing.
“The opioid crisis has generated interest in identifying patients at higher risk of addiction or overdose and has led to the development of several screening tools; however, these instruments have either not been validated or shown poor psychometric properties,” writes Dr. Li Wang, a researcher and methodologist at the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
[Press-News.org] Lung cancer outcomes significantly improved with immunotherapy-based treatment given before and after surgeryPhase III trial finds 32% lower chance of disease recurrence, progression, or death with immunotherapy plus chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone