(Press-News.org) COLUMBUS, Ohio – A $3.6 million award from the National Institutes of Health will allow neurosurgical, neurology and neuroscience researchers at The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center and College of Medicine to test a novel diagnosis and treatment combination for painful diabetic neuropathy. The approach combines spinal cord stimulation with measurement of small fiber nerve activity using a patent-pending device called Detecting Early Neuropathy (DEN).
Diabetes is a growing health concern worldwide, and rates are particularly high in the United States, with more than 37 million Americans – or about 1 in 10 – living with the disease, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Diabetes is associated with numerous health problems, including peripheral neuropathy, which can lead to severe pain.
Peripheral neuropathy is the death of the nerve endings that innervate our tissues and organs, which can worsen the control of diabetes by blunting neural communication between the brain and peripheral tissues and organs. It’s estimated that more than 30 million Americans suffer from peripheral neuropathy.
“Options to diagnose and treat peripheral neuropathy are very limited and ineffective, and thus more research is needed to develop and test new options that can reduce the pain, discomfort, high medical costs and loss of productivity for patients,” said co-principal investigator Kristy Townsend, PhD, associate professor in the Department of Neurosurgery at Ohio State. “Patients have very few options for treatment of their debilitating peripheral neuropathy, and there’s an over-reliance on addictive opioid pain medications which are only partially effective.”
With peripheral neuropathy, typically multiple nerve types – sensory, sympathetic or motor – degenerate, so the symptoms are complex and can include numbness, tingling, burning, pain, and motor loss. In severe cases, patients may undergo limb amputation.
It is estimated that up to 70% of patients with diabetes will develop neuropathy, some even in the pre-diabetes state. Other small fiber neuropathies are caused by chemotherapy, aging, and now - long COVID, said Townsend, whose research program investigates nervous system plasticity, remodeling, and regeneration in situations of metabolic disease, such as obesity, diabetes, aging, cardiometabolic disease, and peripheral neuropathy.
“Spinal cord stimulation (SCS) is a cutting-edge therapy that provides device-mediated electrical stimulation to the spinal cord and has strong prior data demonstrating its efficacy in relieving chronic pain, including in patients with painful diabetic neuropathy,” said co-principal investigator Brian Dalm, MD, a neurosurgeon and clinical assistant professor of neurological surgery at Ohio State Wexner Medical Center. Dalm specializes in neuromodulation, including deep brain stimulation, spinal cord stimulation and peripheral nerve stimulation.
The DEN is undergoing research and development by Townsend and colleagues through an academic spin-out company, Neuright Inc. The DEN was developed to more sensitively, functionally, and qualitatively measure and diagnose small fiber neuropathy so that the condition can be detected more easily, and earlier in the disease progression when therapies are likely to be more effective.
Together, this research collaboration allows synergistic clinical and translational data collection to investigate clinical outcomes and cellular mechanisms underlying the therapeutic effects of SCS for patients with painful diabetic neuropathy.
“While SCS holds great promise for patients with painful diabetic neuropathy, the mechanisms by which it works are unknown. We hypothesized that the effects include increased vascularization and release of nerve growth factors that could spur small fiber axon regeneration, and this newly funded R01 will be the first study to measure those outcomes in patients receiving SCS versus conventional medical management,” Dalm said.
DEN measurements combined with tissue analyses will, for the first time, determine if SCS increases beneficial nerve regeneration as a contributor to pain relief.
Currently, there are no effective treatments to regenerate or regrow nerve endings lost to this condition, despite the knowledge that peripheral nerves uniquely and readily regenerate after other damage, such as injury by nerve crush.
“This could be a revolutionary finding, providing evidence that a non-pharmacological approach is effective at promoting neuropathy reversal,” Townsend said.
Disclosures: Townsend is a co-founder and Chief Scientific Officer of Neuright. Dalm is a paid consultant for Medtronic, Surgical Information Sciences, Varian and Alcyone.
# # #
END
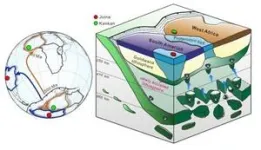
Washington, DC—Diamonds contain evidence of the mantle rocks that helped buoy and grow the ancient supercontinent Gondwana from below, according to new research from a team of scientists led by Suzette Timmerman—formerly of the University of Alberta and now at the University of Bern—and including Carnegie’s Steven Shirey, Michael Walter, and Andrew Steele. Their findings, published in Nature, demonstrate that superdeep diamonds can provide a window through space and time into the supercontinent growth and formation ...
The American Cancer Society has awarded the University of Cincinnati Cancer Center an Institutional Research Grant.
Cancer Center member David Plas, PhD, is primary investigator for the grant, with members Maria Czyzyk-Krzeska, MD, PhD, and Kathryn Wikenheiser-Brokamp, MD, PhD, serving as co-principal investigators.
The American Cancer Society awards Institutional Research Grants to academic and nonprofit organizations that have a track record of outstanding cancer research and a pool of experienced researchers who can mentor junior faculty. The purpose is to support early-stage ...
Washington, DC— As climate change warms the Earth, higher-latitude regions will be at greater risk for toxins produced by algal blooms, according to new research led by Carnegie’s Anna Michalak, Julian Merder, and Gang Zhao. Their findings, published in Nature Water, identify water temperatures of 20 to 25 degrees Celsius (68 to 77 degrees Fahrenheit) as being at the greatest risk for developing dangerous levels of a common algae-produced toxin called microcystin.
Harmful algal blooms result when bodies of water get overloaded with nitrogen and phosphorus ...
The Academy of Breastfeeding Medicine (ABM) has released new literature-based recommendations related to breastfeeding in the setting of substance use and substance use disorder (SUD) treatments. The new clinical protocol is published in the peer-reviewed journal Breastfeeding Medicine. Click here to read the article now.
Miriam Harris, MD and Elisha Wachman, MD, from Boston Medical Center, and coauthors, provide breastfeeding recommendations in the setting of non-prescribed opioid, stimulant, sedative-hypnotic, alcohol, nicotine, and cannabis use, and SUD treatments. They also offer guidance on the use of toxicology testing in breastfeeding ...
A new study leverages the NASA Exoplanet Archive and planetary system simulations to make narrowband SETI searches more efficient.
October 23, 2023, Mountain View, CA -- In a new study published in the Astronomical Journal, researchers used the known population of exoplanets and extrapolated to the much larger, unknown population of exoplanets to set better thresholds for planetary effects on signals from ETIs (extraterrestrial intelligences). The prior recommendation for the threshold “drift rate” contribution, caused by a planet’s motion around its host star, was 200 nHz. In this work, lead ...
Lisbon, Portugal – 23 October, 2023
The International Society of Microbiota (ISM) is proud to present the 14th International Conference on Skin Ageing & Challenges 2023. This monumental event will unfold at the Altis Grand Hotel in Lisbon, Portugal, and virtually, on November 9-10, 2023.
Skin ageing, a multifaceted issue combining both basic research, mechanistic, clinical aspects and health concerns, is gaining significant attention in the scientific community.
This year’s conference promises to be a beacon of innovation, ...
Certain gut-dwelling fungi flourish in severe cases of COVID-19, amplifying the excessive inflammation that drives this disease while also causing long-lasting changes in the immune system, according to a new study led by investigators at Weill Cornell Medicine and NewYork-Presbyterian. This discovery identifies a group of patients who may benefit from specialized, but yet-to-be determined treatments.
Utilizing patient samples and preclinical models, the research team determined that the growth of fungi in the intestinal ...
Before modern humans settled definitively in Europe, other human populations left Africa for Europe beginning approximately 60,000 years ago, albeit without settling for the long term. This was due to a major climatic crisis 40,000 years ago, combined with a super-eruption originating from the Phlegraean Fields volcanic area near current-day Naples, subsequently precipitating a decline in ancient European populations. To determine who the first modern humans to settle definitively in Europe were, a team led by CNRS scientists1 analysed the genome of two skull ...
Alem & Narayanan Advancing Infectious Disease Capabilities Through Biomedical Research Laboratory Core Support
Farhang Alem, Interim Director of the Biomedical Research Laboratory, Institute for Biohealth Innovation, and Aarthi Narayanan, Professor, Biology, received funding for the project: "Advancing Infectious Disease Capabilities through BRL Core Support."
As part of this project, Alem and Narayanan will: 1) implement a comprehensive BSL-3 facilities preventative maintenance and upgrade plan to ensure continuity of operations, compliance with federal regulations, and a safe and secure facility; 2) enhance safety ...
Ramseur To Receive Funding For APA Fellowship - APA Minority Fellowship Program (MFP)
Kevin Ramseur, II, a Mason doctoral student studying clinical psychology, is set to receive funding for: "APA Fellowship – APA Minority Fellowship Program (MFP)."
Ramseur will receive $27,144 from the American Psychological Association on a subaward from the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA). This funding will begin in Oct. 2023 and will end in late Sept. 2024.
###
About George Mason University
George Mason ...