(Press-News.org) Rutgers researchers have used neuroimaging to demonstrate that cocaine addiction alters the brain’s system for evaluating how rewarding various outcomes associated with our decisions will feel. This dampens an error signal that guides learning and adaptive behavior.
The observed changes likely propagate a mysterious aspect of some addictive behavior—the tendency to keep doing harmful things that sometimes have no immediate benefit. Those changes also make it harder for long-term users of cocaine to correctly estimate how much benefit they’ll derive from other available actions.
Experts have long hypothesized that cocaine and other addictive substances can influence “reward prediction errors,” a computation the brain performs to guide learning about what is valuable in one’s environment. The substances were thought to increase reward prediction errors by interfering with the neurotransmitter dopamine’s activity, but concrete evidence for alterations in this critical brain function in people with chronic cocaine addiction has eluded researchers.
The new study, which appears in Neuron, provides strong evidence and could suggest new strategies for treating addiction in general and cocaine addiction in particular.
“The brain has sophisticated mechanisms for predicting which behaviors will bring us pleasure and pain, for updating predictions that prove incorrect and for learning how rewarding different behaviors actually are,” said lead author Anna Konova, a psychiatry professor who leads a research lab at the Rutgers University Behavioral Health Care and Brain Health Institutes.
“This sort of learning from experience is one of the most important things people do. It’s why you don’t touch a hot stove more than once. This study demonstrates that people with chronic cocaine-use disorders could struggle to learn in this way. It also shows why they struggle, and, hopefully, this understanding of the underlying mechanism will lead to better treatment options,” said Rita Goldstein, Mount Sinai Professor in Neuroimaging of Addiction at the Icahn School of Medicine who is senior co-corresponding author on the study.
The researchers studied the brain’s prediction error mechanism by recruiting people who had been using cocaine for an average of 18 years and asking them to play simple decision-making games (with small monetary rewards that could be received either for sure or by chance) — all while undergoing a functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) scan. The researchers then asked the same of another group of participants who had never used cocaine but resembled the first group in many other ways.
The group of participants that had used cocaine consistently pursued riskier playing strategies. They also had lower neural error signals when an unexpected reward was delivered or omitted as a result of those riskier decisions.
The brain’s response to mistaken predictions, the response needed to encode an error’s occurrence and avoid repeating it, was significantly lower among the cocaine-using group than among the other participants.
Such findings strongly implicate the physiological effects of chronic cocaine use on the observed differences in brain function, but the researchers note that a snapshot of brain function at a single point in time cannot prove causation. Only a study measuring brain structure and function over time, starting before the onset of cocaine use, would be able to test hypotheses about cause and effect.
That said, Konova and Goldstein believe the study results provide strong new evidence about one cause of cocaine addiction and the changes it creates in user behavior. They also hope a greater understanding of the underlying mechanisms may help develop treatment options, which remain limited.
“Although this basic science study does not have any immediate implications for public health or treatment, researchers can build on these findings to explore new treatments and prevention strategies,” Konova said. “Specifically, our findings suggest that interventions that aim to boost the impact of the outcomes of one’s decisions (the perception of received rewards) may be a valuable strategy to normalize prediction error signaling and learning from experience in addiction.”
END
Amid cocaine addiction, the brain struggles to evaluate which behaviors will be rewarding
2023-10-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study shows thyroid cancer is more common among transgender female veterans
2023-10-25
A new study by UC Davis Health endocrinology researchers has shown a high prevalence of thyroid cancer among transgender female veterans. It’s the first evidence of such a disparity in the transgender female population in the United States.
The researchers presented their findings this month at the American Thyroid Association Annual Meeting.
The study was prompted by what the doctors noticed while caring for patients.
“As a group of physicians, we observed anecdotally through clinical observation that among 50 transgender women in our clinic, two were diagnosed with thyroid ...
Study suggests marijuana use damages brain immune cells vital to adolescent development
2023-10-25
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
In a mouse study designed to explore the impact of marijuana’s major psychoactive compound, THC, on teenage brains, Johns Hopkins Medicine researchers say they found changes to the structure of microglia, which are specialized brain immune cells, that may worsen a genetic predisposition to schizophrenia. The findings, published Oct. 25 in Nature Communications, add to growing evidence of risk to brain development in adolescents who smoke or eat marijuana products.
“Recreational ...
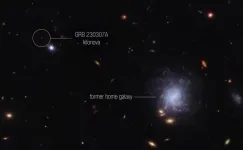
NASA's Webb makes first detection of heavy element from star merger
2023-10-25
A team of scientists has used multiple space and ground-based telescopes, including NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope, NASA’s Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope, and NASA’s Neil Gehrels Swift Observatory, to observe an exceptionally bright gamma-ray burst, GRB 230307A, and identify the neutron star merger that generated an explosion that created the burst. Webb also helped scientists detect the chemical element tellurium in the explosion’s aftermath.
Other elements near tellurium on the periodic table – like iodine, which is needed ...
A bold plan to 3D print artificial coral reef
2023-10-25
Inspired by the remarkable durability of ancient Roman construction materials in seawater, a University of Texas at Arlington civil engineering researcher is attempting to duplicate Roman concrete by developing 3D-printed materials to restore damaged or dying coral reefs.
Warda Ashraf, associate professor in the Department of Civil Engineering, will lead a multidisciplinary team, funded by a $2 million National Science Foundation (NSF) grant, that aims to build 3D-printed artificial reefs. The team’s project is titled “Carbon Sequestration and Coastal Resilience Through 3D Printed Reefs” ...
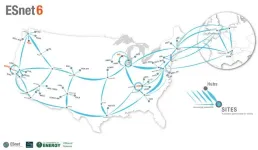
ESnet turns on 400G circuits to four DOE national labs, supercharging multi-site scientific research
2023-10-25
– By Bonnie Powell
Today’s world-changing scientific research is being conducted by collaborators at far-flung national laboratories who require high-speed, low-latency access to high performance computing facilities and specialized instruments. The Energy Sciences Network (ESnet) is proud to announce that it has supercharged the current and future bandwidth for four of the Department of Energy’s (DOE’s) national laboratories and user facilities, unleashing 400 Gigabit per second (400G) capability for Argonne National Laboratory, ...
MD Anderson Research Highlights for October 25, 2023
2023-10-25
HOUSTON ― The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center’s Research Highlights showcases the latest breakthroughs in cancer care, research and prevention. These advances are made possible through seamless collaboration between MD Anderson’s world-leading clinicians and scientists, bringing discoveries from the lab to the clinic and back.
Recent developments at MD Anderson include positive results from a Phase I trial for patients with TP53-mutant acute myeloid leukemia, a novel machine learning ...
Can AI grasp related concepts after learning only one?
2023-10-25
Humans have the ability to learn a new concept and then immediately use it to understand related uses of that concept—once children know how to “skip,” they understand what it means to “skip twice around the room” or “skip with your hands up.”
But are machines capable of this type of thinking? In the late 1980s, Jerry Fodor and Zenon Pylyshyn, philosophers and cognitive scientists, posited that artificial neural networks—the engines that drive artificial intelligence and machine learning— are not capable of making these connections, known as “compositional generalizations.” However, in the decades ...
Breakthrough T cell discovery has huge potential for engineering custom immune responses
2023-10-25
SEATTLE – T cells are soldiers on the front lines of the human immune system. They are responsible for many important roles, including attacking viral- or bacterial-infected cells and certain cancer cells, and immunological memory – remembering the specific pathogens or the cancer signatures that originally trigger T cells.
Until now, understanding how a T cell forms into a specific role, for example a cell-killing (cytotoxic) T cell or memory T cell, has eluded us. In a paper that will be published online by Cell Reports on October 25, ISB researchers made the breakthrough ...
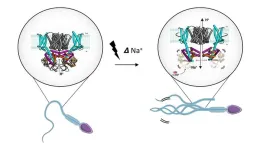
Sperm's secret voltage switch: Scientists unlock the mystery of motility
2023-10-25
Researchers at Stockholm University have unveiled the hidden intricacies of how sperm go from passive bystanders to dynamic swimmers. This transformation is a pivotal step in the journey to fertilization, and it hinges on the activation of a unique ion transporter.
Imagine sperm as tiny adventurers on a quest to reach the ultimate treasure, the egg. They don't have a map, but they make use of something even more extraordinary: chemo-attractants. These are chemical signals released by the egg that act as siren call, directing and activating the sperm. When these signals bind to receptors on the sperm's surface, it triggers a series of events, starting their movement towards ...
Simple blood test can help diagnose bipolar disorder
2023-10-25
Researchers have developed a new way of improving diagnosis of bipolar disorder that uses a simple blood test to identify biomarkers associated with the condition.
The researchers, from the University of Cambridge, used a combination of an online psychiatric assessment and a blood test to diagnose patients with bipolar disorder, many of whom had been misdiagnosed with major depressive disorder.
The researchers say the blood test on its own could diagnose up to 30% of patients with bipolar disorder, but that it is even more effective when combined with a digital mental health assessment.
Incorporating biomarker ...