(Press-News.org)
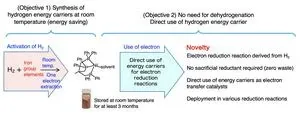
Fukuoka, Japan—In the continued effort to move humanity away from fossil fuels and towards more environmentally friendly energy sources, researchers in Japan have developed a new material capable storing hydrogen energy in a more efficient and cheaper manner. The new hydrogen energy carrier can even store said energy for up to three months at room temperature. Moreover, since the material is nickel based, its cost is relatively cheap. The results were reported in Chemistry—A European Journal.
As humanity combats the ongoing climate crisis, one avenue researchers focus on is the transition into alternative sources of energy such as hydrogen. For several decades now Kyushu University has been investigating ways to more efficiently use and store hydrogen energy in the effort to realize a carbon neutral society.
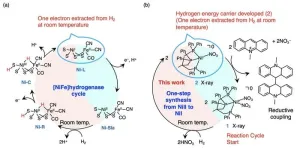
"We have been working on developing new materials that can store and transport hydrogen energy," explains Professor Seiji Ogo of Kyushu University's International Institute for Carbon-Neutral Energy Research who led the research team. "Transporting it in its gaseous state requires significant energy. An alternative way of storing and transporting it would be to 'split-up' the hydrogen atoms into its base components, electrons and protons."
Many candidates have been considered as possible hydrogen energy carries such as ammonia, formic acid, and metal hydrides. However, the final energy carrier had not yet been established.
"So, we looked to nature for hints. There are a series of enzymes called hydrogenases that catalyze hydrogen into protons and electrons and can store that energy for later use, even at room temperature," continues Ogo. "By studying these enzymes our team was able to develop a new compound that does exactly that."
Not only was their new compound able to extract and store electrons at room temperature, further investigations showed that it can be its own catalyst to extract said electron, something that had not been possible with previous hydrogen energy carriers. The team also showed that the energy could be stored for up the three months.
Ogo also highlights the fact that the compound uses an inexpensive element: nickel. Until now, similar catalysts have used expensive metals like platinum, rhodium, or iridium. Now that nickel is a viable option for hydrogen energy storage, it can potentially reduce the cost of future compounds.
The team intends to collaborate with the industrial sector to transfer their new findings into more practical applications.
"We would also like to work on improving storage time and efficiency as well as investigate the viability of cheaper metals for such compounds, " concludes Ogo. "Hopefully our findings will contribute to the goal of decarbonization so that we can build a greener and environmentally friendly future."
###
For more information about this research, see "Single-Step Synthesis of NiI from NiII with H2," Chiaki Takahashi, Takeshi Yatabe, Hidetaka Nakai, and Seiji Ogo, Chemistry—A European Journal, https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.202302297
About Kyushu University
Kyushu University is one of Japan's leading research-oriented institutes of higher education since its founding in 1911. Home to around 19,000 students and 8,000 faculty and staff, Kyushu U's world-class research centers cover a wide range of study areas and research fields, from the humanities and arts to engineering and medical sciences. Its multiple campuses—including one of the largest in Japan—are located around Fukuoka City, a coastal metropolis on the southwestern Japanese island of Kyushu that is frequently ranked among the world's most livable cities and historically known as Japan's gateway to Asia. Through its Vision 2030, Kyushu U will 'Drive Social Change with Integrative Knowledge.' Its synergistic application of knowledge will encompass all of academia and solve issues in society while innovating new systems for a better future.
END
A sweeping new guide to menopause by a UVA Health expert and collaborators highlights the profound and sometimes surprising effects the “change of life” can have on women’s lives, health, workplaces and even finances.
The paper represents a holistic review of what we know about menopause and what we still need to learn. While it is directed primarily at doctors and scientists, it offers fascinating insights into how menopause affects American women and women worldwide.
According to article co-author JoAnn V. Pinkerton, MD, UVA Health's director of midlife health, such insights represent ...
Mount Sinai Health System announced today that “Mount Sinai Fuster Heart Hospital” is the new name for its top-ranked heart service, formerly known as Mount Sinai Heart. The renaming honors Valentin Fuster, MD, PhD, Physician-in-Chief of The Mount Sinai Hospital and President of the Fuster Heart Hospital, for the immeasurable impact that he has made and will continue to make on the field of cardiology and his leadership at Mount Sinai.
Over the last 25 years, Dr. Fuster has transformed Mount Sinai’s heart service into a world-leading center for cardiovascular disease, providing exceptional and compassionate care for cardiac patients, new and innovative ...
(New York, NY – October 26, 2023) – The Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai has received a $4.6 million gift from the Pershing Square Foundation to support women’s health research and advance careers for female scientists. Part of an original nearly $21 million gift that expanded a COVID-19 testing program for New York City schools and other organizations, this boost in women-focused initiatives connects the Pershing Square Foundation’s interest in supporting women in science to Mount Sinai’s leading researchers and key initiatives ...
CLEVELAND—A researcher from the Case Western Reserve University Frances Payne Bolton School of Nursing has been awarded a $3.5 million federal grant for research to improve sleep health and glucose management in young adults with type 1 diabetes.
Positive findings could lead to adding the intervention in current care protocols. The ultimate goal is to improve outcomes for a population that struggles to maintain blood-sugar (glycemic) targets, compared to other age groups.
“Young adults with type 1 diabetes are a high-risk group, and I am committed to improving their ...
AMHERST, Mass. — Last year, trucks moved 73%—11.5 billion tons—of the freight in the U.S., making trucks—and truckers—crucial to the U.S. economy. With automation in trucking projected to grow 22% over the next 10 years, a team of University of Massachusetts Amherst researchers has received a grant to explore how automation will affect the role of American long-haul truckers.
An interdisciplinary group of researchers led by Shannon Roberts, associate professor of mechanical and industrial engineering, has been awarded nearly $2 million over four years by the National Science Foundation’s (NSF) Future of Work Program.
“We know ...
COLUMBUS, Ohio – The discovery of a physical interaction between two proteins in brain cells that can be traced in mice to control of movement, anxiety and memory could one day open the door to development of new schizophrenia treatment strategies, researchers say.
The research group is the first to determine that the two proteins, both among the dozens of proteins related to risk for the development of schizophrenia, bind to each other under normal conditions in multiple regions of the brain, ...
Thirty-seven research groups will receive €395 million in total to address some of the world’s most formidable research problems spanning a range of scientific disciplines. The funding helps groups of outstanding researchers to pool different skills, knowledge and resources to push the frontiers of our knowledge. The ERC Synergy Grant scheme is part of the EU's research and innovation programme, Horizon Europe.
Iliana Ivanova, Commissioner for Innovation, Research, Culture, Education and Youth, said: “Some scientific questions are too complex to be addressed by researchers working on their own. Challenges such as climate change or ...
An international team of researchers, led by IMDEA Networks and Northeastern University in collaboration with NYU Tandon School of Engineering, Universidad Carlos III de Madrid, IMDEA Software, University of Calgary, and the International Computer Science Institute, has unveiled groundbreaking findings on the security and privacy challenges posed by the ever-growing prevalence of opaque and technically complex Internet of Things (IoT) devices in smart homes.
Smart Homes: Trusted and Secure Environments?
Smart homes are becoming increasingly interconnected, ...
PULLMAN, Wash. -- A new tool to rapidly grow cancer-killing white blood cells could advance the availability of immunotherapy, a promising therapy which harnesses the power of the body’s immune response to target cancer cells.
Washington State University researchers have developed a minifridge-sized bioreactor that is able to manufacture the cells, called T cells, at 95% of the maximum growth rate – about 30% faster than current technologies. The researchers report on their work in the journal Biotechnology Progress. They developed it using T cells from cattle, developed by co-author Bill Davis of WSU’s ...
The Institute of Science and Technology Austria (ISTA) receives its second generous ERC Synergy Grant. ISTA Professor Gašper Tkačik is one of three awarded researchers to join forces on unraveling the secrets of gene regulation during mammalian development.
Three research groups from Austria and France team up to crack open the black box of early mammalian development. Now endowed with a prestigious Synergy Grant from the European Research Council (ERC), Gašper Tkačik (ISTA), Thomas Gregor (Institut Pasteur), ...