(Press-News.org)
A team of scientists led by KOO Sagang from the Seoul National University and Center for Nanoparticle Research within the Institue for Basic Science Center (IBS), in collaboration with researchers from Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) and the Seoul National University, developed a new solution for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
RA is a chronic disease that, unfortunately, has no cure. The disease triggers a mix of troublesome symptoms like inflamed joints, harmful cytokines, and immune system imbalances, which work together to create a relentless cycle of worsening symptoms. While targeting some of these factors can provide short-term relief, others remain unresolved, leading to a frustrating cycle of remission and flare-ups.
One of the major hurdles in RA treatment is the inability to restore the immune system to its healthy state. This leaves the body unable to control the continuous production of harmful substances like reactive oxygen species (ROS) and inflammatory cytokines, leading to persistent inflammation and discomfort.
In essence, the ideal treatment for RA should not only provide immediate relief from inflammation and symptoms but also address the root cause by restoring the immune system to its normal, balanced state.
New nanoparticle-based system as a solution
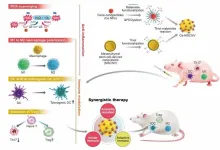
The new platform involves immobilizing ceria nanoparticles (Ce NPs) onto mesenchymal stem cell-derived nanovesicles (MSCNVs). Both of these components can hinder different pathogenic factors, allowing them to work both individually and cooperatively to achieve a comprehensive treatment.
Ce NPs - can scavenge the overproduced ROS in RA-inflicted knee joints. They also induce polarization of M1 macrophages into M2, achieving immediate relief of inflammation and symptoms.
MSCNVs - deliver immunomodulatory cytokines, which turn dendritic cells (DC) into tolerogenic dendritic cells (tDCs). This consequently generates regulatory T cells for long-term immune tolerance.
In short, this approach aims to bridge both innate and adaptive immunity to achieve both short-term pain relief, as well as convert the tissue environment into an immune-tolerant state to prevent the recurrence of symptoms.
Researchers confirmed the efficacy of this approach using a collagen-induced arthritis mouse model. The Ce-MSCNV system was able to comprehensively treat and prevent RA by simultaneously relieving the immediate and restoring T cell immunity. Supporting data suggest that improvement in conditions can be achieved after only a single-dose treatment.
The mice treated with the Ce-MSCNV combination fared far better compared to the ones only treated using the Ce NP or MSCNV group. This clearly demonstrates the synergy between anti-inflammation and immunomodulation and underlines the importance of the combined therapy for effective RA treatment. In addition, Ce-MSCNV administration prior to booster injection markedly reduced the incidence and severity of symptoms, supporting the prophylactic potential of these nanoparticles.
First author KOO Sagang stated, “One of the hardest decisions in intractable disease therapy is determining how long the treatment should be carried on. For RA, it would not be appropriate to stop treatment just because the target marker is stabilized. A safer indicator should be that the innate and adaptive components of the collapsed immune system are normalized to protect the body.”
Koo believes that the strategy adopted by Ce-MSCNVs, where different treatment mechanisms work together, provides a unique advantage in this regard. Furthermore, she predicts that a similar approach would also be applicable to other intractable, inflammatory, and autoimmune diseases for this purpose. The components within the system may also be modified. For example, other catalysts for generating ROS or other cell-derived nanovesicles could be utilized depending on the types of diseases. Overall, this study proves the potential of a hybrid nanoparticle system for the comprehensive treatment of autoimmune disease and modulation of the immune system.
END
About The Study: The results of this study of 41 large U.S. children’s hospitals suggest that bronchiolitis hospitalizations decreased transiently and then increased markedly during the COVID-19 pandemic era. Patients admitted during the pandemic era were older and were more likely to be admitted to an intensive care unit. These findings suggest that bronchiolitis seasonality has not yet returned to pre-pandemic patterns, and hospitals should prepare for the possibility of atypical timing again in 2023.
Authors: Jonathan H. Pelletier, ...
About The Study: This survey study of attitudes of 1,005 parents of children and adolescents ages 9 to 15 revealed both perceived benefits (e.g., family connectedness) and concerns (e.g., cyberbullying, addiction) of internet use. Twice as many parents reported specific concerns about internet addiction than substance addiction.
Authors: Michael Peter Milham, M.D., Ph.D., of the Child Mind Institute in New York, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.39851
Editor’s ...
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- When babies first begin to talk, their vocabulary is very limited. Often one of the first sounds they generate is “da,” which may refer to dad, a dog, a dot, or nothing at all.
How does an adult listener make sense of this limited verbal repertoire? A new study from MIT and Harvard University researchers has found that adults’ understanding of conversational context and knowledge of mispronunciations that children commonly make are critical to the ability to understand children’s early linguistic efforts.
Using ...
Nanoturbines: the heart of advancements
Flow-driven turbines lie at the heart of many revolutionary machines that have shaped our societies, from windmills to airplanes. Even life itself depends critically on turbines for fundamental processes, such as the FoF1-ATP synthase that produces fuels for biological cells and the bacterial flagella motor that propels bacteria. “Our nanoturbine has a 25-nanometer diameter rotor made from DNA material with blades configured in a right-handed or left-handed sense to control the direction of rotation. To operate, this structure is ...
The National Science Foundation has awarded $3.7 million to the University of Chicago for the first year of a grant that may provide up to $21.4 million for the final designs for a next-generation set of telescopes to map the light from the earliest moments of the universe—the Cosmic Microwave Background.
Led by the University of Chicago and Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, the collaboration seeks to build telescopes and infrastructure in both Antarctica and Chile to search for what are known as “primordial” gravitational waves—the vibrations from the Big Bang itself. It would also map the microwave light ...
The discovery of a malaria protein that helps the parasite grow inside red blood cells and plays a key regulatory role in the parasite’s immune evasion tactics could pave the way for new vaccines or therapeutics to combat the deadly infection.
The protein, known as PfAP2-P, was previously identified in a KAUST-led study that explored malarial genes and proteins displaying rhythmic 24-hour expression patterns — an adaptation that allows the parasite to synchronize its activities with those of the host during the human blood stage of its developmental cycle[1].
The expression levels of PfAP2-P seem to peak first around ...
Psoriasis — a chronic skin condition — is not caused or spread by spontaneous genetic mutations in the skin, new research suggests.
The team, from the Wellcome Sanger Institute and collaborators, sequenced skin samples from 111 people with psoriasis. They didn’t find any mutated genes in the psoriatic patches that weren’t also mutated in the individual’s unaffected skin tissue.
The study, published today (26 October) in Nature Genetics, suggests that unlike other inflammatory diseases, such as inflammatory bowel disease or chronic liver disease, somatic mutations were not responsible for the start or spread of psoriasis.
Confirming that psoriasis ...
An international team has developed the first comprehensive framework for designing networks of marine protected areas that can help vulnerable species survive as climate change drives habitat loss.
In a paper published Oct. 26 in One Earth, the researchers outlined guidelines for governments to provide long-distance larval drifters, like urchins and lobsters, as well as migratory species, like turtles and sharks, with protected stopovers along coastal corridors. Led by Stanford marine conservation scientist Nur Arafeh-Dalmau, the team included 50 scientists and practitioners ...
University of Queensland researchers have shown that endometriosis and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) share genetic risk factors, explaining why patients with one condition may also have the other.
Professor Grant Montgomery and Dr Sally Mortlock at UQ’s Institute for Molecular Bioscience found a significant relationship between the risks for endometriosis and common gastrointestinal disorders such as IBS, peptic ulcer disease (PUD) and gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD).
“This genetic finding supports the clinical observation of an increased incidence of gastrointestinal disorders in women with endometriosis,” ...
INDIANAPOLIS -- Two Regenstrief Institute and U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs researchers are key leaders of a national journal’s special supplement designed to help address the plethora of issues that can accompany a healthcare system’s transition to a new electronic health record (EHR) system.
Regenstrief Institute’s David Haggstrom, M.D., MAS, and Michael Weiner, M.D., MPH, are among four guest editors who have spent the last two years leading content development for a Journal of General Internal Medicine (JGIM) special supplement ...