(Press-News.org) For the first time in human history, say Daniel Gervais and John Nay in a Policy Forum, nonhuman entities that are not directed by humans – such as artificial intelligence (AI)-operated corporations – should enter the legal system as a new “species” of legal subject. AI has evolved to the point where it could function as a legal subject with rights and obligations, say the authors. As such, before the issue becomes too complex and difficult to disentangle, “interspecific” legal frameworks need to be developed by which AI can be treated as legal subjects, they write. Until now, the legal system has been univocal – it allows only humans to speak to its design and use. Nonhuman legal subjects like animals have necessarily instantiated their rights through human proxies. However, their inclusion is less about defining and protecting the rights and responsibilities of these nonhuman subjects and more a vehicle for addressing human interests and obligations as it relates to them. In the United States, corporations are recognized as “artificial persons” within the legal system. However, the laws of some jurisdictions do not always explicitly require corporate entities to have human owners or managers at their helm. Thus, by law, nothing generally prevents an AI from operating a corporate entity. Here, Gervais and Nay highlight the rapidly realizing concept of AI-operated “zero-member LLCs” – or a corporate entity operating autonomously without any direct human involvement in the process. The authors discuss several pathways in which such AI-operated LLCs and their actions could be handled within the legal system. As the idea of ceasing AI development and use is highly unrealistic, Gervais and Nay discuss other options, including regulating AI by treating the machines as legally inferior to humans or engineering AI systems to be law-abiding and bringing them into the legal fold now before it becomes too complicated to do so.
END
A new “species” of legal subject: AI-led corporate entities, requiring interspecific legal frameworks
2023-10-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Special Issue: The hypothalamus
2023-10-26
While small, the hypothalamus – a complex structure located deep in the brain – plays a gargantuan role in coordinating the wide array of neuronal signals that are responsible for keeping the body in a stable state. In a Special Issue of Science, authors across four Reviews unpack this key brain region’s impact on physiological and behavioral homeostasis.
The hypothalamus consists of a complex collection of neural circuits. These circuits receive, process, and integrate sensory inputs to drive coordinated communication via a range of behavioral, ...
A safer alternative to CRISPR-Cas approaches?: Retroelement-based genome editing tools
2023-10-26
In a Perspective, Stephen Tang and Samuel Sternberg discuss retroelement-based gene editing as a safer alternative to CRISPR-Cas approaches. Precision genome editing technologies have transformed modern biology. Capabilities for programable DNA targeting have improved rapidly, largely due to the development of bacterial RNA-guided CRISPR-Cas systems, which allow precise cleavage of target DNA sequences. However, CRISPR-Cas9 systems generate a DNA double strand break (DSB), which activates cellular DNA repair pathways that can lead to unwanted and complex byproducts, ...
UCLA researcher finds first proof of menopause in wild chimpanzees
2023-10-26
Key takeaways
Female chimpanzees in Uganda’s Ngogo community experienced a menopausal transition similar to women.
Fertility among chimpanzees studied declined after age 30, and no births were observed after age 50.
The data can help researchers better understand why menopause and post-fertile survival occur in nature and how it evolved in the human species.
A team of researchers studying the Ngogo community of wild chimpanzees in western Uganda’s Kibale National Park for two decades has published a report in Science showing that females in this population can ...
Conduction electrons drive giant, nonlinear elastic response in Sr2RuO4
2023-10-26
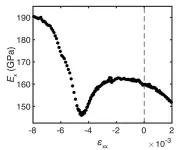
The hardness of materials is determined by the strength of the chemical bonds that are formed between the electrons of the neighbouring atoms. For example, the bonds in diamond are very strong, so it is one of the hardest materials known. The bonding is rooted in the laws of quantum mechanics, and the complex compounds that are of most interest in forefront research today are known as ‘quantum materials.’ In many quantum materials, layers of strongly bonded atoms separate layers in ...
New quantum effect demonstrated for the first time: Spinaron, a rugby in a ball pit
2023-10-26
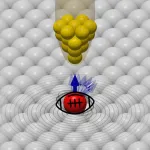
Extreme conditions prevail in the Würzburg laboratory of experimental physicists Professor Matthias Bode and Dr. Artem Odobesko. Affiliated with the Cluster of Excellence ct.qmat, a collaboration between JMU Würzburg and TU Dresden, these visionaries are setting new milestones in quantum research. Their latest endeavor is unveiling the spinaron effect. They strategically placed individual cobalt atoms onto a copper surface, brought the temperature down to 1.4 Kelvin (–271.75° Celsius), and then subjected them to a powerful external magnetic field. “The magnet we use costs half a million euros. It’s not something that’s widely available,” explains ...
Researchers identify amino acid that may play a key role for predicting and treating long COVID
2023-10-26
University of Alberta researchers have identified an amino acid that may play a key role in predicting poor clinical outcomes and the treatment of long COVID.
In research published today in Cell Reports Medicine, the team says it has developed a predictive test to determine which patients with COVID-19 will go on to develop longer-term symptoms and proposes a clinical trial of an already-approved supplement as a potential treatment.
“This research helps us understand what’s happening in the bodies of people ...
UTHealth Houston researchers awarded $3.4M NIH grant to study pharmaceutical therapies to treat acute respiratory distress syndrome
2023-10-26
A four-year, $3.4 million grant to investigate molecular mechanisms and therapeutic treatments for acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) has been awarded to UTHealth Houston researchers by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, part of the National Institutes of Health.
The study led by principal investigators Holger Eltzschig, MD, PhD, professor and chair of the Department of Anesthesiology, Critical Care and Pain Medicine at McGovern Medical School at UTHealth Houston, and Xiaoyi Yuan, PhD, assistant professor in the department, is built on many years of research in the endogenous ...
Renewed support for high power laser facilities will benefit discovery science and inertial fusion energy research at SLAC
2023-10-26
Research and technology development for plasma physics and fusion energy at the Department of Energy’s SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory just got a boost from a LaserNetUS award.
In total, the DOE’s Office of Science awarded $28.5 million to advance discovery science and inertial fusion energy, including a three-year grant for the development and operations of the Matter in Extreme Conditions (MEC) instrument at SLAC’s Linac Coherent Light Source (LCLS).
MEC has been home to high intensity laser experiments since 2012, and joined ...
TUM professor develops energy-saving AI chip
2023-10-26
The basic idea is simple: unlike previous chips, where only calculations were carried out on transistors, they are now the location of data storage as well. That saves time and energy. “As a result, the performance of the chips is also boosted,” says Hussam Amrouch, a professor of AI processor design at the Technical University of Munich (TUM). The transistors on which he performs calculations and stores data measure just 28 nanometers, with millions of them placed on each of the new AI chips. The chips of the future will have to be faster and more efficient than earlier ones. Consequently, ...
SETI Institute artist-in-residence Daniela De Paulis to receive 2023 Europlanet Prize for Public Engagement
2023-10-26
SETI Institute Artist-in-Residence Daniela De Paulis to Receive 2023 Europlanet Prize for Public Engagement
Daniela de Paulis is honored for her work bringing space and planetary science to international audiences.
October 26, 2023, Mountain View, CA -- The SETI Institute is thrilled to announce that Daniela De Paulis, a SETI Artist-in-Residence (SETI AIR), will be honored with the prestigious 2023 Europlanet Prize for Public Engagement. De Paulis’ groundbreaking project, ‘A Sign in Space,’ invited a global audience to participate in decoding a simulated message from an extraterrestrial ...