Is it possible for random bit generator to reach a rate of Peta bits/s?
2023-10-27
(Press-News.org)
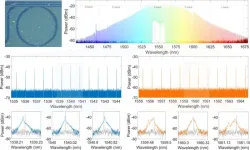
The optical frequency comb is an important tool in modern physics research and applications. In 2005, Theodor W. Hänsch and John L. Hall were awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics for their pioneering work on optical frequency comb technology. This sparked a great interest among researchers in the field, leading to a series of studies on optical frequency combs. Advanced nanophotonic technology has enabled integrated microresonators with ultrahigh Q factors and chip-scale microcombs. Among various comb dynamic states, a chaotic comb has high nonlinearity. In a chaotic comb, each comb tooth exhibits a chaotic dynamic oscillation, which is suitable for PRB generation. In 2023, Chen et al. proposed a new type of lidar for the first time using a chaotic microcomb to overcome time and frequency congestion barriers.
Researchers of Prof. Jiagui Wu Group at Southwest University (SWU), China, are interested in chaotic microcomb, which can be used to generate random bit with ultrafast rate. A microcomb contained hundreds of chaotic channels, and each comb tooth functioned as an entropy source for the PRB. The application of chaotic optical frequency combs on random number generators has the potential to significantly improve the speed of random number generation, with the possibility of rate up to Pbits/s (petabits per second). They used a Si3N4 microresonator with compactness and good scalability to generate chip-scale microcombs. It could simultaneously output hundreds of chaotic comb teeth through a wavelength division multiplexer and use them as entropy sources to generate massive random numbers. The randomness was verified with NIST statistical testing. This work could offer potential chip solutions of Pbits/s PRB with the features of low cost and a high degree of parallelism. The work entitled “Massive and parallel 10 Tbit/s physical random bit generation with chaotic microcomb” was published on Frontiers of Optoelectronics (published on Sep. 22, 2023).
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-10-27
Researchers at Nagoya University in Japan and their collaborators have used a biomarker based on microbubbles to evaluate the success of near-infrared photoimmunotherapy (NIR-PIT) treatment. Using ultrasound to track the microbubbles, they were able to identify areas where cancer therapy had not been fully applied. Their findings suggest ways to improve NIR-PIT and make it a viable alternative treatment for various types of cancer.
NIR-PIT is an innovative cancer treatment that combines the use of antibodies and near-infrared light to ...
2023-10-27
Up to 1.7 million people could be living with dementia in England and Wales by 2040 – over 40% more than previously forecast – finds a new UCL-led study.
Previous studies, based on data up to 2010, showed that dementia incidence had declined in high-income countries. However, the new research, published in The Lancet Public Health, indicates that dementia incidence started to increase in England and Wales after 2008.
Based on this estimated upward incidence trend, researchers project that the number of people with dementia in England and Wales may be significantly higher than expected in the future.
According to previous research* in England ...
2023-10-27
Lancet Psychiatry study shows for first time that younger children are no more likely to lose ADHD diagnosis over time than older classmates
Experts in charge of study examined data from more than 6,500 patients with ADHD
360 million people worldwide have been diagnosed with the condition according to WHO – with around a third under the age of 18
Children who are the youngest in their class to be identified with ADHD are just as likely to keep the diagnosis as older pupils in their year group, scientists have found.
Experts from the University of Southampton ...
2023-10-27
A drug candidate, based on pioneering UCL and Moorfields Eye Hospital research and currently under development by SIFI S.p.A., has been found to be highly effective in treating a rare sight-threatening eye infection in a new international clinical trial.
The findings, published in Ophthalmology, describe the efficacy and safety of the first drug candidate for the treatment of Acanthamoeba keratitis (AK), applying a novel and evidence-based treatment protocol.
AK is one type of microbial keratitis (corneal infection) – a condition ...
2023-10-27
Quantum physicists at Delft University of Technology have shown that it’s possible to control and manipulate spin waves on a chip using superconductors for the first time. These tiny waves in magnets may offer an alternative to electronics in the future, interesting for energy-efficient information technology or connecting pieces in a quantum computer, for example. The breakthrough, published in Science, primarily gives physicists new insight into the interaction between magnets and superconductors.
Energy-efficient substitute
"Spin waves are waves in a magnetic material that we can use to transmit information," explains ...
2023-10-27
One of the most common injuries sustained by military personnel in recent conflicts has been traumatic brain injury, or TBI. In response to this, and the fact that military operations are increasingly being conducted by small teams in far-flung areas, researchers in the University of Arizona College of Medicine – Tucson’s Department of Psychiatry are working on a portable virtual reality system to assess TBI in the field.
Psychiatry professor William “Scott” Killgore, PhD, and his team in the Social, ...
2023-10-27
Treatment with datopotamab deruxtecan (Dato-DXd), a novel Trop-2 directed antibody-drug conjugate, was found to significantly improve progression-free survival in patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer, an improvement that was primarily driven by patients with non-squamous tumors.
These results from the TROPION-Lung01 Phase III trial, which compared the standard of care in second-line docetaxel, a type of chemotherapy, with Dato-DXd, an antibody drug conjugate, in patients with pretreated metastatic non-small cell lung cancer, were presented at the European Society for Medical Oncology 2023 Congress by Dr. Aaron ...
2023-10-27
A University of Tennessee Health Science Center (UTHSC) researcher is a member of a prestigious team that has just received a highly competitive Endeavor Award totaling $3 million from The Mark Foundation for Cancer Research.
Liza Makowski, PhD professor in Hematology and Oncology at the UTHSC Center for Cancer Research, is a co-principal investigator on the award, which funds collaborative projects tackling complex challenges in the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of cancer. Entitled “Inflammatory Drivers of The Obesity-Cancer Connection”, the project is led by principal ...
2023-10-27
A new study from the University of Wisconsin–Madison suggests that chemotherapy may not be reaching its full potential, in part because researchers and doctors have long misunderstood how some of the most common cancer drugs actually ward off tumors.
For decades, researchers have believed that a class of drugs called microtubule poisons treat cancerous tumors by halting mitosis, or the division of cells. Now, a team of UW–Madison scientists has found that in patients, microtubule poisons don't actually stop cancer cells from dividing. Instead, these drugs alter ...
2023-10-26
TURKU, Finland – October 27, 2023 – The SynGAP Research Fund 501(c)(3) announced a $100,000 grant to researchers Pekka Postila and Olli Pentikäinen from the Institute of Biomedicine and InFLAMES Flagship at the University of Turku. Prof. Pentikäinen’s research focuses on molecular modeling and computer-aided drug discovery. Assoc. Prof. Postila is an expert on advanced molecular dynamics simulations of complex biomolecular systems. The dual research team was formed to study the structural effects of missense variants on the SynGAP protein, whose normal functioning ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Is it possible for random bit generator to reach a rate of Peta bits/s?