(Press-News.org) Sunscreen usage is climbing, but so are melanoma and skin cancer rates: this, researchers say, is the sunscreen paradox.
“The problem is that people use sunscreen as a ‘permission slip’ to tan,” said Dr. Ivan Litvinov, an Associate Professor in the Department of Medicine and Chair of the Dermatology Division at McGill University and co-author with Dr. Sandra Peláez, Dr. Richie Jeremian and Dr. Pingxing Xie of two recent studies that explore the sunscreen paradox.
“People think they are protected from skin cancer because they are using a product marketed to prevent a condition.”
Most people don’t apply enough sunscreen or stay in the sun for hours after applying sunscreen in the morning. “This gives them a false sense of security,” said Litvinov.
To understand the factors between varying incidence rates of melanoma in the Atlantic provinces of Canada, a group of researchers including Litvinov and Peláez conducted 23 focus groups.
In the study, they found that Canadians living in Nova Scotia and Prince Edward Island – provinces with high melanoma incidence rates – were more likely to report using sun protection, more aware of the health risks of sun exposure, and more apt to follow the UV index. Despite this, they also received more sun exposure due to warmer temperatures and a tendency to engage in outdoor activities.
Similarly, in a second study of the United Kingdom Biobank by Jeremian, Xie and Litvinov, the researchers documented that sunscreen use was surprisingly associated with a more than twofold risk of developing skin cancer.
The sunscreen paradox
“These combined findings suggest a sunscreen paradox, whereby individuals with higher levels of sun exposure also tend to use more but not an adequate quantity of sunscreen or other sun-protection measures, providing a false sense of security,” said Litvinov.
Interventions to address knowledge and practice gaps in sun protection and skin cancer prevention must consider this sunscreen paradox and the unique norms of communities around the world, he added.
“Sunscreen is important, but it is also the least effective way to protect your skin when compared to sun protective clothing, rash guards, and sun avoidance. People can and should enjoy the outdoors, but without getting a sun burn or a suntan,” said Litvinov.
END
The sunscreen paradox: McGill University researchers warn of ‘false sense of security’
Sunscreen is important, says Dr. Ivan Litvinov, but it is also the least effective way to protect your skin when compared to sun protective clothing and sun avoidance
2023-10-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Hybrid nanomaterials promise a sustainability boost across multiple industries
2023-10-27
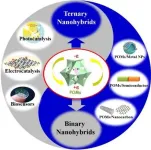
Polyoxometalate (POM)-based nanohybrids potentially offer a step-change in sustainability across a wide variety of industries, but research into the substances is in its infancy. A group of researchers has produced a comprehensive review of the sector’s progress and challenges yet to be overcome.
A new class of nanoscale hybrid materials has the potential to improve sustainability across energy systems, transport, biosensors, water purification and even 3D printing, but the field is still very young. A group of researchers has produced a detailed overview ...
Pinktober brings attention to the TMIST international breast cancer screening trial as a new site opens in Thailand
2023-10-27
A clinical trial led by the ECOG-ACRIN Cancer Research Group (ECOG-ACRIN) demonstrates how diversity among study participants is vital for reducing outcomes disparities. Among the vast group of women participating in the TMIST breast cancer screening trial--nearly 93,000 so far--21% self-identify as Black or African American. This diversity offers hope that once the trial reaches its enrollment goal of nearly 129,000 women, its results can better inform and tailor future breast cancer screening for all women.
The TMIST breast cancer study is investigating whether screening for breast cancer ...
Find-and-replace genome editing with CRISPR: A promising therapeutic Strategy
2023-10-27
Severe Combined Immunodeficiencies (SCIDs) are a group of debilitating primary immunodeficiency disorders, primarily caused by genetic mutations that disrupt T-cell development. SCID can also affect B-cell and natural killer cell function and counts. Left untreated, SCID proves fatal within the first year of life. The conventional treatment for SCID patients involves allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT), but the challenges of finding compatible donors and potential complications like graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) pose significant hurdles ...
Long COVID most prevalent in the most seriously ill
2023-10-27
A collaborative study involving researchers from Karolinska Institutet has charted the prevalence of severe physical symptom burden amongst Scandinavians for up to two years after a SARS-CoV-2 infection. Most affected were people who had a severe COVID-19 infection, while the researchers found no elevated prevalence of long COVID in those who had never been bedridden. The study is published in The Lancet Regional Health – Europe.
By mid-October 2023, over 771 million cases of COVID-19 had been reported to the World Health Organization (WHO). An estimated 10 to 20 per cent of the affected have persistent symptoms.
Close to 65,000 participants
In the present ...
Scientists build on artificial intelligence to create next-generation gastric acid treatment
2023-10-27
Researchers at Nagoya University in Japan created and improved artificial intelligence (AI) designs to synthesize a candidate compound for a new gastric acid inhibitor with a better binding affinity than existing drugs. Their findings, published in Communications Biology, suggest a new way to work in tandem with AI to develop pharmaceuticals.
Stomach acid is a crucial component of food digestion. However, when the balance of gastric mucosal secretion is disturbed, stomach acid can cause discomfort and, in severe cases, conditions such as gastric ulcers and reflux esophagitis. Therefore, many people turn to gastric acid suppressants, most of which target the gastric ...
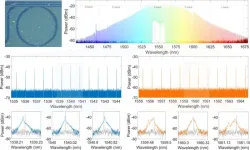
Is it possible for random bit generator to reach a rate of Peta bits/s?
2023-10-27
The optical frequency comb is an important tool in modern physics research and applications. In 2005, Theodor W. Hänsch and John L. Hall were awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics for their pioneering work on optical frequency comb technology. This sparked a great interest among researchers in the field, leading to a series of studies on optical frequency combs. Advanced nanophotonic technology has enabled integrated microresonators with ultrahigh Q factors and chip-scale microcombs. Among various comb dynamic states, a chaotic comb has high nonlinearity. In a chaotic comb, each comb tooth exhibits a chaotic dynamic ...
A new NIR-PIT biomarker paves the way for targeted cancer treatments
2023-10-27
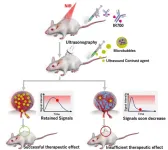
Researchers at Nagoya University in Japan and their collaborators have used a biomarker based on microbubbles to evaluate the success of near-infrared photoimmunotherapy (NIR-PIT) treatment. Using ultrasound to track the microbubbles, they were able to identify areas where cancer therapy had not been fully applied. Their findings suggest ways to improve NIR-PIT and make it a viable alternative treatment for various types of cancer.
NIR-PIT is an innovative cancer treatment that combines the use of antibodies and near-infrared light to ...
Number of dementia cases could be 42% higher than previously estimated by 2040
2023-10-27
Up to 1.7 million people could be living with dementia in England and Wales by 2040 – over 40% more than previously forecast – finds a new UCL-led study.
Previous studies, based on data up to 2010, showed that dementia incidence had declined in high-income countries. However, the new research, published in The Lancet Public Health, indicates that dementia incidence started to increase in England and Wales after 2008.
Based on this estimated upward incidence trend, researchers project that the number of people with dementia in England and Wales may be significantly higher than expected in the future.
According to previous research* in England ...
Youngest children in class with ADHD as likely to keep diagnosis in adulthood as older pupils, find scientists
2023-10-27
Lancet Psychiatry study shows for first time that younger children are no more likely to lose ADHD diagnosis over time than older classmates
Experts in charge of study examined data from more than 6,500 patients with ADHD
360 million people worldwide have been diagnosed with the condition according to WHO – with around a third under the age of 18
Children who are the youngest in their class to be identified with ADHD are just as likely to keep the diagnosis as older pupils in their year group, scientists have found.
Experts from the University of Southampton ...
Effective treatment for rare sight-threatening infection
2023-10-27
A drug candidate, based on pioneering UCL and Moorfields Eye Hospital research and currently under development by SIFI S.p.A., has been found to be highly effective in treating a rare sight-threatening eye infection in a new international clinical trial.
The findings, published in Ophthalmology, describe the efficacy and safety of the first drug candidate for the treatment of Acanthamoeba keratitis (AK), applying a novel and evidence-based treatment protocol.
AK is one type of microbial keratitis (corneal infection) – a condition ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] The sunscreen paradox: McGill University researchers warn of ‘false sense of security’Sunscreen is important, says Dr. Ivan Litvinov, but it is also the least effective way to protect your skin when compared to sun protective clothing and sun avoidance