(Press-News.org) Researchers who are working to find alternatives to lithium-ion batteries have turned their attention to potassium-ion batteries. Potassium is an abundant resource and the technology functions in much the same way as lithium-ion batteries, but these batteries have not been developed at a large scale because the ionic radius causes problems in energy storage and substandard electrochemical performance.
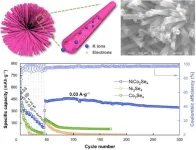
To solve this problem, researchers are considering NiCo2Se4, a bimetallic selenide, to create sphere-shaped electrodes. The spheres are constructed with NiCo2Se4 nanotubes, which improve the electrochemical reactivity for faster transfer and storage of potassium ions.
The research was presented in a paper published in Energy Materials and Devices on 14 September.
“Bimetallic selenides combine the ameliorating features of two metals, which synergize by showing rich redox reaction sites and high electrochemical activities. One bimetallic selenide, NiCo2Se4, was previously studied for sodium storage, supercapacitors, and electrocatalysts and presents considerable potential for potassium ion storage. By synthesizing NiCo2Se4 using a two-step hydrothermal process, a nanotube structure with flower-like clusters develops, creating convenient channels for potassium ion/electron transfer,” said Mingyue Wang, a researcher at the Engineering Research Center of Energy Storage Materials and Devices at Xi’an Jiaotong University in Xi’an, China.
Initially, Ni-Co precursor spheres with solid nanoneedles are prepared. These spheres have a well-defined crystalline structure that is then exposed to selenide during a process called selenization. This process introduces selenium to the Ni-Co precursor, developing the NiCo2Se4 nanotube shell. The hollow tubes form because of a phenomenon called the Kirkendall effect, which is when two metals move because of the difference in the diffusion rates of their atoms. These nanotubes are around 35 nanometers wide, giving enough space for the potassium ions and electrons to transfer.
Through a variety of tests and analysis, the researchers were able to confirm how well the NiCo2Se4 anodes could move and store potassium ions and electrons. They found that NiCo2Se4 has more active sites than other electrode materials, had uniformly distributed elements, and outperformed other electrodes that were tested during research.
“The NiCo2Se4 nanotube electrode presented a much better electrochemical performance in terms of cyclic stability and rate capability than other tested electrodes, including Ni3Se4 and Co3Se4. This is because the unique nanotube structure of NiCo2Se4 and the synergy offered by the co-presence of two metals,” said Wang. These monometallic counterparts, Ni3Se4 and Co3Se4 were not as successful as the bimetallic NiCo2Se4, simply because of the way the two metals (Ni and Co) interact together. NiCo2Se4 also had a higher capacity, which is very beneficial for maintaining cyclic stability and high-rate performance.
“This work offers new insights into the design of micro/nano-structured binary metal selenides as anodes for potassium-ion batteries with extraordinary potassium ion storage performance,” said Wang.
Other contributors include Yang Li, Shanshan Yao, Jiang Cui, Lianbo Ma, Nauman Mubarak, Hongming Zhang, and Jang-Kyo Kim from the Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering at the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology; and Shujiang Ding at the Engineering Research Center of Energy Storage Materials and Devices at Xi’an Jiaotong University.
The Research Grants Council, the Innovation and Technology Commission of Hong Kong SAR, and the National Natural Science Foundation of China supported this research.
##
About Energy Materials and Devices
Energy Materials and Devices is launched by Tsinghua University, published quarterly by Tsinghua University Press, aiming at being an international, single-blind peer-reviewed, open-access and interdisciplinary journal in the cutting-edge field of energy materials and devices. It focuses on the innovation research of the whole chain of basic research, technological innovation, achievement transformation and industrialization in the field of energy materials and devices, and publishes original, leading and forward-looking research results, including but not limited to the materials design, synthesis, integration, assembly and characterization of devices for energy storage and conversion etc.
About SciOpen
SciOpen is a professional open access resource for discovery of scientific and technical content published by the Tsinghua University Press and its publishing partners, providing the scholarly publishing community with innovative technology and market-leading capabilities. SciOpen provides end-to-end services across manuscript submission, peer review, content hosting, analytics, and identity management and expert advice to ensure each journal’s development by offering a range of options across all functions as Journal Layout, Production Services, Editorial Services, Marketing and Promotions, Online Functionality, etc. By digitalizing the publishing process, SciOpen widens the reach, deepens the impact, and accelerates the exchange of ideas.
END
COLUMBIA, Mo. -- Childhood trauma is a key risk factor for future substance use disorder, overdose, and suicide. This is particularly problematic in rural areas where children experience higher rates of adverse childhood experiences (ACEs). ACEs are commonly defined as physical and emotional abuse and neglect, sexual abuse, parental separation or divorce, intimate partner violence, and having household members with serious mental illness, substance use disorder, or a history of incarceration.
Now, a three-year, U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) grant awarded to the University of Missouri will help virtually train various members of the workforce — ...
Proteins are key to all processes in our cells and understanding their functions and regulation is of major importance.
“For many years, we have known that nearly all human proteins are modified by a specific chemical group, but its functional impact has remained undefined”, says professor Thomas Arnesen at the Department of Biomedicine, University of Bergen.
He explains:
“One of the most common protein modifications in human cells is N-terminal acetylation, which is an addition of a small chemical group (acetyl) at the starting tip (N-terminus) of a protein. The ...
Researchers have discovered a protein that seals plant roots to regulate the uptake of nutrients and water from the soil, the discovery could help develop climate proof crops that require less water and chemical fertilizers.
Researchers from the University of Nottingham identified new components of the lignin barrier in plant roots and the specific function of dirigent proteins (DPs), located in the root endodermis that control water and nutrient uptake. Their findings have been published today in Science Direct.
Plant roots function by absorbing ...
Research on the trillions of microorganisms that make up a person’s microbiome can lead to medical breakthroughs to treat diseases like inflammatory bowel syndrome and diabetes. According to Alyssa Bader, a Tsimshian Assistant Professor in the Department of Anthropology at McGill University, microbiome samples from Indigenous communities have the potential to further Western medicine, but those same communities often have been excluded from the research process and may miss out on the benefits that result from their contributions to science. ...
LOS ANGELES — An international Phase 3 clinical trial found that metastatic colorectal cancer patients with a rare genetic tumor mutation called KRAS G12C experienced superior progression-free survival rates compared to standard of care when offered a combination treatment of KRAS inhibitor sotorasib and monoclonal antibody panitumumab. City of Hope, one of the largest cancer research and treatment organizations in the United States, was a participating site and a City of Hope researcher is the lead author of the The New England Journal of Medicine study published this week.
Standard ...
A research team has synthesized a new polyoxometalate-based metal-organic complex that they then tested as a catalyst for the oxidation reactions of various sulfides. They found that the complex possesses excellent catalytic performance, good reusability, and structural stability.
The team’s work is published in the journal Polyoxometalates on October 19, 2023.
Scientists in many fields have explored the selective oxidation of sulfides to sulfoxides. Sulfoxides are organic compounds that contain sulfur and oxygen. These sulfoxides are high value-added chemicals in pharmaceuticals, agrochemistry, ...
Sunscreen usage is climbing, but so are melanoma and skin cancer rates: this, researchers say, is the sunscreen paradox.
“The problem is that people use sunscreen as a ‘permission slip’ to tan,” said Dr. Ivan Litvinov, an Associate Professor in the Department of Medicine and Chair of the Dermatology Division at McGill University and co-author with Dr. Sandra Peláez, Dr. Richie Jeremian and Dr. Pingxing Xie of two recent studies that explore the sunscreen paradox.
“People think they are protected from skin cancer ...
Polyoxometalate (POM)-based nanohybrids potentially offer a step-change in sustainability across a wide variety of industries, but research into the substances is in its infancy. A group of researchers has produced a comprehensive review of the sector’s progress and challenges yet to be overcome.
A new class of nanoscale hybrid materials has the potential to improve sustainability across energy systems, transport, biosensors, water purification and even 3D printing, but the field is still very young. A group of researchers has produced a detailed overview ...
A clinical trial led by the ECOG-ACRIN Cancer Research Group (ECOG-ACRIN) demonstrates how diversity among study participants is vital for reducing outcomes disparities. Among the vast group of women participating in the TMIST breast cancer screening trial--nearly 93,000 so far--21% self-identify as Black or African American. This diversity offers hope that once the trial reaches its enrollment goal of nearly 129,000 women, its results can better inform and tailor future breast cancer screening for all women.
The TMIST breast cancer study is investigating whether screening for breast cancer ...
Severe Combined Immunodeficiencies (SCIDs) are a group of debilitating primary immunodeficiency disorders, primarily caused by genetic mutations that disrupt T-cell development. SCID can also affect B-cell and natural killer cell function and counts. Left untreated, SCID proves fatal within the first year of life. The conventional treatment for SCID patients involves allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT), but the challenges of finding compatible donors and potential complications like graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) pose significant hurdles ...