(Press-News.org) By April Toler
More than two-thirds of the world’s population is expected to live in cities by 2050, according to the United Nations. As urbanization advances around the globe, researchers at the University of Notre Dame and Stanford University said the quality of the urban physical environment will become increasingly critical to human well-being and to sustainable development initiatives.
However, measuring and tracking the quality of an urban environment, its evolution and its spatial disparities is difficult due to the amount of on-the-ground data needed to capture these patterns. To address the issue, Yong Suk Lee, assistant professor of technology, economy and global affairs in the Keough School of Global Affairs at the University of Notre Dame, and Andrea Vallebueno from Stanford University used machine learning to develop a scalable method to measure urban decay at a spatially granular level over time.
Their findings were recently published in Scientific Reports.
“As the world urbanizes, urban planners and policymakers need to make sure urban design and policies adequately address critical issues such as infrastructure and transportation improvements, poverty and the health and safety of urbanites, as well as the increasing inequality within and across cities,” Lee said. “Using machine learning to recognize patterns of neighborhood development and urban inequality, we can help urban planners and policymakers better understand the deterioration of urban space and its importance in future planning.”
Traditionally, the measurement of urban quality and quality of life in urban spaces has used sociodemographic and economic characteristics such as crime rates and income levels, survey data of urbanites’ perception and valued attributes of the urban environment, or image datasets describing the urban space and its socioeconomic qualities. The growing availability of street view images presents new prospects in identifying urban features, Lee said, but the reliability and consistency of these methods across different locations and time remains largely unexplored.
In their study, Lee and Vallebueno used the YOLOv5 model (a form of artificial intelligence that can detect objects) to detect eight object classes that indicate urban decay or contribute to an unsightly urban space — things like potholes, graffiti, garbage, tents, barred or broken windows, discolored or dilapidated façades, weeds and utility markings. They focused on three cities: San Francisco, Mexico City and South Bend, Indiana. They chose neighborhoods in these cities based on factors including urban diversity, stages of urban decay and the authors’ familiarity with the cities.
Using comparative data, they evaluated their method in three contexts: homelessness in the Tenderloin District of San Francisco between 2009 and 2021, a set of small-scale housing projects carried out in 2017 through 2019 in a subset of Mexico City neighborhoods, and the western neighborhoods of South Bend in the 2011 through 2019 period — a part of the city that had been declining for decades but also saw urban revival initiatives.
Researchers found that the trained model could adequately detect the objects it sought across different cities and neighborhoods, and did especially well where there are denser populations, such as San Francisco.
For instance, the maps allowed researchers to assess the temporal and geographic variation in homelessness in the San Francisco area, an issue that has grown over the years.
The model struggled in the more suburban area of South Bend, according to Lee, demonstrating a need to tweak the model and the types of objects identified in less dense populations. In addition, the researchers found there is still a risk for bias that should be addressed.
“Our findings indicate that trained models such as ours are capable of detecting the incidences of decay across different neighborhoods and cities, highlighting the potential of this approach to be scaled in order to track urban quality and change for urban centers across the U.S. and cities in other countries where street view imagery is available,” he said.
Lee said the model has potential to provide valuable information using data that can be collected in a more efficient way compared to using coarser, traditional economic data sources, and that it could be a valuable and timely tool for the government, nongovernmental organizations and the public.
“We found that our approach can employ machine learning to effectively track urban quality and change across multiple cities and urban areas,” Lee said. “This type of data could then be used to inform urban policy and planning and the social issues that are impacted by urbanization, including homelessness.”
Contact: Tracy DeStazio, associate director of media relations, 574-631-9958 or tdestazi@nd.edu
END
AI can alert urban planners and policymakers to cities’ decay
2023-10-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
NASA rocket to see sizzling edge of star-forming supernova
2023-10-27
A new sounding rocket mission is headed to space to understand how explosive stellar deaths lay the groundwork for new star systems. The Integral Field Ultraviolet Spectroscopic Experiment, or INFUSE, sounding rocket mission, will launch from the White Sands Missile Range in New Mexico on Oct. 29, 2023, at 9:35 p.m. MDT.
For a few months each year, the constellation Cygnus (Latin for “swan”) swoops through the northern hemisphere’s night sky. Just above its wing is a favorite target ...
IU scientists part of NIH-funded national consortium focused on improving Alzheimer’s disease diagnoses
2023-10-27
INDIANAPOLIS—Researchers at Indiana University School of Medicine will play key roles in a national consortium led by Wake Forest University School of Medicine to study the use, interpretation and implementation of biomarkers to diagnose Alzheimer’s disease.
The multi-institution effort is funded by a five-year, $9 million grant from the National Institute on Aging, part of the National Institutes of Health, that will establish the Alzheimer’s Diagnosis in Older Adults with Chronic Conditions (ADACC) Network.
IU School of Medicine’s Nicole Fowler, ...
Tri-City to partner with UC San Diego Health in delivering world-class medical care
2023-10-27
After open public discussion and a unanimous board vote, Tri-City Healthcare District (“Tri-City” or “District”) announced yesterday that UC San Diego Health has been selected as the District’s future health care partner. A Joint Powers Agreement will now be co-developed that allows UC San Diego Health to provide administrative, clinical and operational management for all health care services with direct input and guidance from a diverse community board. Under the future agreement, UC San Diego ...
Physicist Tatiana Erukhimova earns national award for science outreach
2023-10-27
Texas A&M University physicist Dr. Tatiana Erukhimova has been selected as the 2023 recipient of the American Physical Society Dwight Nicholson Medal for Outreach. Established in 1994 by the Division of Plasma Physics and the Forum on Physics and Society, the Nicholson Medal is awarded annually in recognition of the humanitarian aspect of physics and physicists created through public lectures and public media, teaching, research or science-related activities. The medal is sponsored by the friends of the late plasma physicist and award namesake Dr. Dwight R. Nicholson (1947-1991), former chairman ...
Burt’s Bees® presents clinical evidence demonstrating ability of nature-based products to support barrier function and microbiome health in sensitive skin and lips
2023-10-27
DURHAM, N.C., Oct. 27, 2023 – Burt’s Bees, the #1 dermatologist recommended natural skin care brand* and a pioneer in skin care solutions, announced its latest research findings on the benefits of nature-based regimens to cleanse, nourish, and protect skin health. The studies will be presented at the hybrid Integrative Dermatology Symposium (IDS) from Oct. 27-29, 2023.
The latest research findings from Burt’s Bees highlight:
The ability of a topical treatment with a unique blend of botanicals to improve appearance of age spots in diverse skin.
The impact of a lip care product with naturally derived plant oils, butters, beeswax, ...
Possible cause of male infertility
2023-10-27
Bonn, 27. October - Mature spermatozoa are characterized by an head, midpiece and a long tail for locomotion. Now, researchers from the University Hospital Bonn (UKB) and the Transdisciplinary Research Unit "Life & Health" at the University of Bonn have found that a loss of the structural protein ACTL7B blocks spermatogenesis in male mice. The cells can no longer develop their characteristic shape and remain in a rather round form. The animals are infertile. The results of the study have now been published in the scientific journal "Development".
Male ...
Online games use dark designs to collect player data
2023-10-27
Gaming is a $193 billion industry – nearly double the size of the film and music industries combined – and there are around three billion gamers worldwide. While online gaming can improve wellbeing and foster social relations, privacy and awareness issues could potentially offset these benefits and cause real harm to gamers.
The new study, by scientists at Aalto University’s Department of Computer Science, reveals potentially questionable data collection practices in online games, along with misconceptions and concerns about privacy among players. The study also offers ...
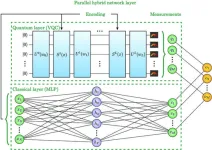
New parallel hybrid network achieves better performance through quantum-classical collaboration
2023-10-27
Building efficient quantum neural networks is a promising direction for research at the intersection of quantum computing and machine learning. A team at Terra Quantum AG designed a parallel hybrid quantum neural network and demonstrated that their model is "a powerful tool for quantum machine learning." This research was published Oct. 9 in Intelligent Computing, a Science Partner Journal.
Hybrid quantum neural networks typically consist of both a quantum layer — a variational quantum circuit — and a classical layer — a deep learning neural network called a multi-layered perceptron. This special architecture enables them to learn complicated patterns and relationships ...
Researchers at MedStar Health and Georgetown Law find success in integrating lawyers into care teams to support pregnant and postpartum patients
2023-10-27
WASHINGTON – Medical-legal partnerships (MLPs), which include a lawyer as part of a patient’s care team, can help health systems address health-harming legal needs and better support pregnant and postpartum patients, according to a new research commentary published today in Obstetrics & Gynecology. The article offers insights and expert advice from Georgetown University Health Justice Alliance’s Perinatal Legal Assistance and Wellbeing (LAW) Project at MedStar Washington Hospital Center, one of the first medical-legal partnerships ...
Hydrogel developed by Brazilian researchers improves skin wound healing in diabetics
2023-10-27
Researchers in São Paulo state, Brazil, have developed a low-cost anti-inflammatory hydrogel that in future could help treat chronic skin lesions such as those often seen in people with diabetes. They report the results of animal tests in an article published in the journal Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.
According to the International Diabetes Federation, Brazil ranks sixth among countries with the most cases of diabetes, which has reached epidemic proportions and become the fifth most frequent cause of death in the world. Some 17.7 million Brazilians suffer daily from the metabolic alterations caused ...