(Press-News.org) Building efficient quantum neural networks is a promising direction for research at the intersection of quantum computing and machine learning. A team at Terra Quantum AG designed a parallel hybrid quantum neural network and demonstrated that their model is "a powerful tool for quantum machine learning." This research was published Oct. 9 in Intelligent Computing, a Science Partner Journal.
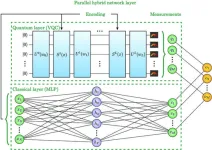
Hybrid quantum neural networks typically consist of both a quantum layer — a variational quantum circuit — and a classical layer — a deep learning neural network called a multi-layered perceptron. This special architecture enables them to learn complicated patterns and relationships from data inputs more easily than traditional machine learning methods.
In this paper, the authors focus on parallel hybrid quantum neural networks. In such networks, the quantum layer and the classical layer process the same input at the same time and then produce a joint output — a linear combination of the outputs from both layers. A parallel network could avoid the information bottleneck that often affects sequential networks, where the quantum layer and the classical layer feed data into each other and process data alternately.
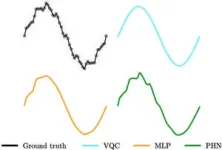
The training results demonstrate that the authors' parallel hybrid network can outperform either its quantum layer or its classical layer. Trained on two periodic datasets with high-frequency noise added, the hybrid model shows lower training loss, produces better predictions, and is found to be more adaptable to complex problems and new datasets.
The quantum and classical layers both contribute to this effective quantum-classical interplay. The quantum layer, specifically, a variational quantum circuit, maps the smooth periodical parts, while the classical multi-layered perceptron fills in the irregular additions of noise. Both variational quantum circuits and multi-layered perceptrons are considered "universal approximators." To maximize output during training, variational quantum circuits adjust the parameters of quantum gates that control the status of qubits, and multi-layered perceptrons mainly tune the strength of the connections, or so-called weights, between neurons.
At the same time, the success of a parallel hybrid network rides on the setting and tuning of the learning rate and other hyperparameters, such as the number of layers and number of neurons in each layer in the multi-layered perceptron.
Given that the quantum and classical layers learn at different speeds, the authors discussed how the contribution ratio of each layer affects the performance of the hybrid model and found that adjusting the learning rate is important in keeping a balanced contribution ratio. Therefore, they point out that building a custom learning rate scheduler is a future research direction because such a scheduler could enhance the speed and performance of the hybrid model.
END
New parallel hybrid network achieves better performance through quantum-classical collaboration
2023-10-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Researchers at MedStar Health and Georgetown Law find success in integrating lawyers into care teams to support pregnant and postpartum patients
2023-10-27
WASHINGTON – Medical-legal partnerships (MLPs), which include a lawyer as part of a patient’s care team, can help health systems address health-harming legal needs and better support pregnant and postpartum patients, according to a new research commentary published today in Obstetrics & Gynecology. The article offers insights and expert advice from Georgetown University Health Justice Alliance’s Perinatal Legal Assistance and Wellbeing (LAW) Project at MedStar Washington Hospital Center, one of the first medical-legal partnerships ...
Hydrogel developed by Brazilian researchers improves skin wound healing in diabetics
2023-10-27
Researchers in São Paulo state, Brazil, have developed a low-cost anti-inflammatory hydrogel that in future could help treat chronic skin lesions such as those often seen in people with diabetes. They report the results of animal tests in an article published in the journal Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.
According to the International Diabetes Federation, Brazil ranks sixth among countries with the most cases of diabetes, which has reached epidemic proportions and become the fifth most frequent cause of death in the world. Some 17.7 million Brazilians suffer daily from the metabolic alterations caused ...
Unlocking sugar to generate biofuels and bioproducts
2023-10-27
UPTON, NY—Plant biologists at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Brookhaven National Laboratory have engineered enzymes to modify grass plants so their biomass can be more efficiently converted into biofuels and other bioproducts. As described in a paper just published in Plant Biotechnology Journal, these enzymes modify molecules that make up plant cell walls to provide access to fuel-generating sugars normally locked within complex structures.
“The concept of biomass to biofuel seems simple, but it is technically very difficult to release the sugars,” noted Chang-Jun Liu, a senior plant biologist at Brookhaven ...
Evolutionary chance made this bat a specialist hunter
2023-10-27
Ask a biologist why predators don't exterminate all their prey, part of the answer often is that there is an ongoing arms race between predators and prey, with both parties continuously evolving new ways to cheat each other.
The hypothesis is particularly prevalent for bats and their prey; insects. 50 million years ago, the first bats evolved the ability to echolocate and thus hunt in the dark, and in response to this, some insects evolved ultrasound-sensitive ears so they could hear and evade the bats.
But if there is an ongoing arms race, bats should have responded to this, says University of Southern Denmark biologist, associate professor and bat ...
Intermittent fasting is safe, effective for those with Type 2 diabetes
2023-10-27
Time-restricted eating, also known as intermittent fasting, can help people with Type 2 diabetes lose weight and control their blood sugar levels, according to a new study published in JAMA Network Open from researchers at the University of Illinois Chicago.
Participants who ate only during an eight-hour window between noon and 8 p.m. each day actually lost more weight over six months than participants who were instructed to reduce their calorie intake by 25%. Both groups had similar reductions in long-term blood sugar levels, as measured by a test of hemoglobin A1C, which shows blood sugar levels over the past three months.
The ...
Effect of time-restricted eating on weight loss in adults with type 2 diabetes
2023-10-27
About The Study: This 6-month randomized clinical trial involving 75 adults with type 2 diabetes found that a time-restricted eating diet strategy without calorie counting was effective for weight loss and lowering of hemoglobin A1c levels compared with daily calorie counting. These findings will need to be confirmed by larger RCTs with longer follow-up.
Authors: Krista A. Varady, Ph.D., of the University of Illinois Chicago, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.39337)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article ...
Medication abortion safety and effectiveness with misoprostol alone
2023-10-27
About The Study: The findings in this study of 637 callers to safe abortion hotlines and accompaniment groups in Argentina, Nigeria, and Southeast Asia suggest that misoprostol alone is a highly effective method of pregnancy termination. Future research should explore strategies to maximize the effectiveness of misoprostol alone in clinical and nonclinical settings.
Authors: Ruvani Jayaweera, Ph.D., of Ibis Reproductive Health in Oakland, California, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.40042)
Editor’s Note: Please ...
SwRI, GTI Energy, GE celebrate mechanical completion of $155 million supercritical CO2 pilot plant
2023-10-27
SAN ANTONIO — October 27,2023 —Southwest Research Institute (SwRI®), GTI Energy, GE Vernova (GE) and the U.S. Department of Energy celebrated the ribbon-cutting of the Supercritical Transformational Electric Power (STEP) Demo pilot plant today. The $155 million, 10-megawatt supercritical carbon dioxide (sCO2) test facility at SwRI’s headquarters in San Antonio will demonstrate an innovative new method of higher-efficiency, lower-cost electric power generation.
“STEP will undoubtedly change the way we think about ...
Innovative research aims to improve wound healing and cancer therapy
2023-10-27
Jun.-Prof. Dr. Priscilla Briquez, junior professor at the Department of General and Visceral Surgery at the Freiburg University Medical Center and member of the Medical Faculty at the University of Freiburg, has received a European Research Council (ERC) Starting Grant from the European Commission. Her DRESSCODE project will receive a total of 1.5 million euros funding for five years. The project focuses on modifying proteins and developing new disease therapies.
“This support is a major opportunity for me to put together my own team and drive forward my research,” says Briquez. The focus ...
Action plan for better data on migration and health
2023-10-27
Despite rising global mobility, the state of migrant and refugee health data in European health systems is a concern, a new study shows. The analysis by an international coalition of universities, UN organizations, government representatives, and European institutions published in the journal The Lancet Regional Health Europe reveals that coverage of migrant and refugee data remains inconsistent and of suboptimal quality. According to the study this issue is not due to a lack of knowledge or technological resources ...