(Press-News.org) (SACRAMENTO, Calif.) — Domestic violence went down or stayed the same during the first 10 months of the COVID-19 pandemic in five major U.S. cities. However, domestic violence involving firearms increased in three of those cities, according to a new UC Davis study published in the Journal of Family Violence.
“The increase in firearm domestic violence is concerning, as abuser firearm access is a risk factor for lethality,” said Elizabeth Tomsich, a research data analyst at the UC Davis Violence Prevention Research Center and first author of the study.
Comparing firearm domestic violence before and during pandemic
Although firearm purchasing and violence surged dramatically during the pandemic, research on firearm-involved domestic violence has been limited.
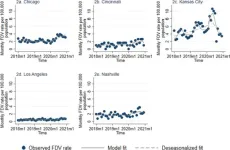
To determine the trends in domestic violence and firearm domestic violence before and during the COVID-19 pandemic, the researchers used police-reported crime data from Jan. 1, 2018 through Dec. 31, 2020. The onset of the pandemic was considered to be Mar. 20, 2020. The cities examined were Chicago, IL; Cincinnati, OH; Kansas City, MO; Los Angeles, CA; and Nashville, TN. The analysis looked at three main areas:
domestic violence incidents
firearm domestic violence incidents
firearm domestic violence as a proportion of domestic violence incidents
Findings
The researchers found variations among all five cities in the reported data.
Domestic violence: After the start of the pandemic, police reports of domestic violence decreased in Kansas City, Los Angeles and Nashville and did not change in Chicago and Cincinnati compared with trends before the pandemic.
Firearm domestic violence: There was a relative increase in reports of firearm domestic violence at the start of the pandemic in Chicago, Los Angeles and Nashville, with a relative decrease in Kansas City; there were no changes in Cincinnati.
Domestic violence as a portion of overall domestic violence: There was an increase after the start of the pandemic in Chicago, Los Angeles and Nashville, and no changes were observed in Cincinnati and Kansas City.
The researchers noted the decrease in reported domestic violence contrasted with increases in reported firearm domestic violence.
They point out that the results may reflect a decrease in reporting due to barriers from the pandemic rather than an actual decrease in domestic violence. For example, during the lockdown, it may have been harder for those experiencing domestic violence to report to law enforcement because they were confined with a perpetrator who was monitoring their communications.
By contrast, firearm domestic violence may be less sensitive to pandemic-related forces that may have affected reporting. Among violent crimes, aggravated assault is the most likely to be reported to law enforcement.
Increases in firearm purchasing during the pandemic and the reported increases in domestic firearm violence in some cities remain a concern, as firearm access is associated with a fivefold increase in the odds of intimate partner violence.
“Interventions that prohibit firearm access, such as domestic violence restraining orders and extreme risk protective orders, as well as prohibitions associated with misdemeanor domestic violence convictions, may prove valuable to address the potential increase in the risk of firearm domestic violence,” Tomsich said.
Additional authors include Julia P. Schleimer, Chris D. McCort, and Garen J. Wintemute from the UC Davis Violence Prevention Research Program.
Resources
Read the study
Download the research snapshot of the study
UC Davis Violence Prevention Research Program website
END
Domestic violence involving firearms increased during COVID-19 pandemic
Study of five major U.S. cities shows variation in domestic violence trends
2023-11-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Microbiology: River plastics may harbour potential pathogens and antimicrobial resistance genes
2023-11-01
Microbial communities growing on plastic debris in rivers may have the capacity to harbour potentially pathogenic microbes and act as reservoirs of antimicrobial resistance genes, according to a study published in Microbiome. The findings also highlight differences in the potential pathogens and antimicrobial resistance genes that new and degraded plastics may have the capacity to harbour.
Vinko Zadjelovic, Elizabeth Wellington, Joseph Christie-Oleza and colleagues characterised the microbial communities found on the surface ...
High metabolism is an early sign of Alzheimer’s disease
2023-11-01
An early phase in the process of developing Alzheimer’s disease is a metabolic increase in a part of the brain called the hippocampus, report researchers from Karolinska Institutet in a study published in Molecular Psychiatry. The discovery opens up for new potential methods of early intervention.
Alzheimer’s disease is the most common form of dementia and strikes about 20,000 people in Sweden every year. Researchers now show that a metabolic increase in the mitochondria, the cellular power ...
Trust is the most important factor for British South Asians when taking part in genetic research to tailor medications
2023-11-01
Researchers from Queen Mary University of London have gathered detailed insights from the British South Asian community that could lead to more successful implementation of genetic testing to help tailor the use of routine medications. Their findings are published today (1 November 2023) in The Pharmacogenomics Journal and indicate key issues that could affect the take up of this new type of genetic testing amongst patients.
Despite comprising 10% of the British population, individuals of South Asian heritage have historically been under-represented in ...
Cigarette style warning labels could reduce people’s meat consumption
2023-11-01
Cigarette style graphic warning labels could reduce people’s meat consumption, according to new research published today (1 November).
The study suggests the use of warning labels on meat options could improve public health and reduce the UK’s carbon footprint.
The team from Durham University tested a range of warning labels including those which warn people of the damage to climate, health, and risk of pandemics. They found that all labels were effective at discouraging people from choosing meals with meat.
All warning labels, which showed ...
New research finds that nature-based solutions are essential for Brazil to meet its 2050 net zero pledge
2023-11-01
A new study has concluded that any credible net zero pathway for Brazil must include the implementation of nature-based solutions.
Actions such as halting deforestation and large-scale restoration of native vegetation would have immediate impact, at a fraction of the cost of carbon-negative technologies.
However, stronger policy frameworks will be needed if nature-based solutions are to achieve their full potential in Brazil.
Without the implementation of nature-based solutions, in particular ending deforestation and restoring ...
New position statement supports permanent standard time
2023-10-31
DARIEN, IL – An updated position statement from the American Academy of Sleep Medicine supports the replacement of daylight saving time with permanent standard time.
It is the position of the AASM that the United States should eliminate seasonal time changes in favor of permanent standard time, which aligns best with human circadian biology. According to the statement, evidence supports the distinct benefits of standard time for health and safety, while also underscoring the potential harms that result from seasonal time changes to and from daylight saving time.
“By causing the human body ...
Reverse engineering Jackson Pollock
2023-10-31
Can a machine be trained to paint like Jackson Pollock? More specifically, can 3D-printing harness the Pollock's distinctive techniques to quickly and accurately print complex shapes?
“I wanted to know, can one replicate Jackson Pollock, and reverse engineer what he did,” said L. Mahadevan, the Lola England de Valpine Professor of Applied Mathematics at the Harvard John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS), and Professor of Organismic and Evolutionary Biology, and of Physics in the Faculty of Arts and Sciences (FAS).
Mahadevan and his team combined physics and machine learning to develop a new 3D-printing ...
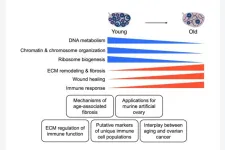
Proteomic quantification of native and ECM-enriched mouse ovaries reveals an age-dependent fibro-inflammatory signature
2023-10-31
“Overall, our study provides novel insight into how reproductive aging impacts the murine ovarian proteome and ECM.”
BUFFALO, NY- October 31, 2023 – A new priority research paper was published on the cover of Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 20, entitled, “Proteomic quantification of native and ECM-enriched mouse ovaries reveals an age-dependent fibro-inflammatory signature.”
The ovarian microenvironment becomes fibrotic and stiff with age, in part due to increased collagen and decreased hyaluronan. However, the extracellular matrix ...
Hix, Lajoie elected Fellows of the American Physical Society
2023-10-31
Physicists William Raphael “Raph” Hix of the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory and John Lajoie, who will join ORNL on Nov. 6 from Iowa State University, have been elected Fellows of the American Physical Society.
The society works to advance and spread physics knowledge via research journals, scientific meetings, education, outreach, advocacy and international activities. It represents more than 50,000 members, including physicists in government, academia and industry worldwide.
Hix, leader of the Theoretical and Computational ...
Illinois Tech researchers receive award from peoples gas for solution optimizing efficiency of legacy steam radiators
2023-10-31
CHICAGO—October 31, 2023—Researchers at Illinois Institute of Technology (Illinois Tech) have been recognized by Peoples Gas with the Innovation Strategies and Technologies Award for their Battery-Operated Radiator Control (BORC) system, a groundbreaking solution to optimize the efficiency of manually operated radiators.
The researchers, Assistant Professor of Architectural Engineering Mohammad Heidarinejad and Arthur W. Hill Endowed Chair in Sustainability Brent Stephens, had the insight that traditional steam radiators are ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Chimps’ love for crystals could help us understand our own ancestors’ fascination with these stones
Vaginal estrogen therapy not linked to cancer recurrence in survivors of endometrial cancer
How estrogen helps protect women from high blood pressure
Breaking the efficiency barrier: Researchers propose multi-stage solar system to harness the full spectrum
A new name, a new beginning: Building a green energy future together
From algorithms to atoms: How artificial intelligence is accelerating the discovery of next-generation energy materials
Loneliness linked to fear of embarrassment: teen research
New MOH–NUS Fellowship launched to strengthen everyday ethics in Singapore’s healthcare sector
Sungkyunkwan University researchers develop next-generation transparent electrode without rare metal indium
What's going on inside quantum computers?: New method simplifies process tomography
This ancient plant-eater had a twisted jaw and sideways-facing teeth
Jackdaw chicks listen to adults to learn about predators
Toxic algal bloom has taken a heavy toll on mental health
Beyond silicon: SKKU team presents Indium Selenide roadmap for ultra-low-power AI and quantum computing
Sugar comforts newborn babies during painful procedures
Pollen exposure linked to poorer exam results taken at the end of secondary school
7 hours 18 mins may be optimal sleep length for avoiding type 2 diabetes precursor
Around 6 deaths a year linked to clubbing in the UK
Children’s development set back years by Covid lockdowns, study reveals
Four decades of data give unique insight into the Sun’s inner life
Urban trees can absorb more CO₂ than cars emit during summer
Fund for Science and Technology awards $15 million to Scripps Oceanography
New NIH grant advances Lupus protein research
New farm-scale biochar system could cut agricultural emissions by 75 percent while removing carbon from the atmosphere
From herbal waste to high performance clean water material: Turning traditional medicine residues into powerful biochar
New sulfur-iron biochar shows powerful ability to lock up arsenic and cadmium in contaminated soils
AI-driven chart review accurately identifies potential rare disease trial participants in new study
Paleontologist Stephen Chester and colleagues reveal new clues about early primate evolution
UF research finds a gentler way to treat aggressive gum disease
Strong alcohol policy could reduce cancer in Canada
[Press-News.org] Domestic violence involving firearms increased during COVID-19 pandemicStudy of five major U.S. cities shows variation in domestic violence trends