(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON – The U.S. Naval Research Laboratory’s Melanized Microbes for Multiple Uses in Space Project, or MELSP, will use the International Space Station (ISS) to search for production of melanin variants and other useful biomaterials that can have applications both on Earth and in space. The mission is scheduled to launch in early November 2023.
Melanin is described as a group of biopolymers responsible for various biological functions, including pigmentation of skin, hair, and iris of the eyes, which helps protect body cells from solar radiation damage.
“The structure and properties of melanin are highly dependent on synthesis and polymerization conditions, therefore the production of melanin in microgravity may lead to new melanin variants with novel physico-chemical properties,” said Tiffany Hennessa, Ph.D., research biologist at NRL’s Center for Biomolecular Science and Engineering (CBMSE) and co-principal investigator of MELSP. “We will investigate how microgravity and cosmic radiation influences microbial melanin production and study the role that melanin plays in adaptation to the ISS environment.”
“Despite the significant research that has previously been conducted to understand the structure and properties of melanin, there remains considerable gaps in our knowledge that have hindered our ability to harness melanin for its full potential,” said Zheng Wang, Ph.D., principal investigator of MELSP and research biologist at CBMSE. “Assembly and polymerization of melanin in microgravity may lead to ‘more perfect’ structures with decreased heterogeneity.”
NRL scientists will analyze ISS-grown bacterial and fungal strains that lack the protective capacity of melanin to search for novel mechanisms of protection. The project will culture three microbial species on-board the ISS: bacterium Escherichia coli, along with its engineered strain synthesizing eumelanin, two melanized fungal strains: Aspergillus niger and Exophiala lecanii-corni, and their melanin-deficient mutants. Additionally, two defective DNA repair mutants of A. niger will be cultured to study the effects of space radiation on fungal DNA and melanin biosynthesis.
The MELSP project may lead to economic gain across multiple markets by providing invaluable insight into the discovery and development of novel biomaterials. It is anticipated that MELSP will generate information invaluable to the growth of this field, including key insights into melanin biosynthesis and its resulting structure-driven activity that can be harnessed for various applications on Earth.
These efforts will provide the first steps necessary to establish biomaterial production hosts for use during long-term space missions. The MELSP project will contribute to the growing body of data surrounding the influence of spaceflight on biological systems and incorporate novel perspectives on the involvement of melanin in such processes.
About the U.S. Naval Research Laboratory
NRL is a scientific and engineering command dedicated to research that drives innovative advances for the U.S. Navy and Marine Corps from the seafloor to space and in the information domain. NRL is located in Washington, D.C. with major field sites in Stennis Space Center, Mississippi; Key West, Florida; Monterey, California, and employs approximately 3,000 civilian scientists, engineers and support personnel.
For more information, contact NRL Corporate Communications at (202) 480-3746 or nrlpao@nrl.navy.mil.
END
NRL ISS Mission seeks new bioinspired materials
2023-11-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Pinpointing HIV immune response
2023-11-01
New research combining computer modeling and experiments with macaques shows the body’s immune system helps control human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infections largely by suppressing viral production in already infected cells while also killing viral infected cells, but only within a narrow time window at the start of a cell’s infection.
“To eliminate HIV, we have to understand how the immune system attempts to control the infection,” said Ruy M. Ribeiro, a theoretical biologist at Los Alamos National Laboratory who led the development of the model ...
First mice engineered to survive COVID-19 like young, healthy humans
2023-11-01
Researchers have genetically engineered the first mice that get a human-like form of COVID-19, according to a study published online November 1 in Nature.
Led by researchers from NYU Grossman School of Medicine, the new work created lab mice with human genetic material for ACE2 – a protein snagged by the pandemic virus so it can attach to human cells as part of the infection. The mice with this genetic change developed symptoms similar to young humans infected with the virus causing COVID-19, instead of dying ...
As people live longer, family caregivers face financial challenges
2023-11-01
PHILADELPHIA (November 1, 2023) – Many people overlook the short- and long-term costs of financial caregiving, a growing problem that financial advisors and employers can help address, according to a new report by the TIAA Institute and the University of Pennsylvania School of Nursing (Penn Nursing).
One in five adults now provide uncompensated care to loved ones with health problems, and the report provides a comprehensive compilation of insights and research that underscores how the caregivers face a ...
Human mini guts reveal new insights into the process leading to Cronkhite-Canada syndrome and potential new therapies
2023-11-01
Researchers at Baylor College of Medicine and collaborating institutions working with human intestinal organoids, also called mini guts, have shed new light on the potential causes of Cronkhite-Canada syndrome, a rare condition characterized by abundant non-cancerous growths or polyps in the intestine and other symptoms such as hair and nail loss and changes in skin pigmentation. Published in The Journal of Clinical Investigation, the study is the first to show a connection between high polyp proliferation and increased levels of serotonin produced by the intestinal epithelium.
The findings suggest a potential new approach to treat this disease with serotonin ...
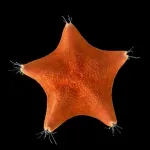
Long presumed to have no heads at all, sea stars may be nothing but
2023-11-01
For centuries, naturalists have puzzled over what might constitute the head of a sea star, commonly called a “starfish.” When looking at a worm, or a fish, it’s clear which end is the head and which is the tail. But with their five identical arms — any of which can take the lead in propelling sea stars across the seabed — it’s been anybody’s guess how to determine the front end of the organism from the back. This unusual body plan has led many to conclude that sea stars perhaps don’t have a head at all.
But ...
Starfish body is a head, say scientists
2023-11-01
EMBARGOED: Not for Release Until 01 November 2023 at 16:00 (London time)
The bodies of starfish and other echinoderms are more like heads, according to new research involving the University of Southampton.
The research, published today [1 November] in Nature, helps to answer the mystery of how these creatures evolved their distinctive star-shaped body, which has long puzzled scientists.
Echinoderms are a group of animals that includes starfish (or sea stars), sea urchins, and sand dollars. They have a unique ‘fivefold symmetric’ body plan, which means ...
Scientists reveal structures of neurotransmitter transporter
2023-11-01
(Memphis, Tenn – November 1, 2023) Neurons talk to each other using chemical signals called neurotransmitters. Scientists at St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital have drawn on structural biology expertise to determine structures of vesicular monoamine transporter 2 (VMAT2), a key component of neuronal communication. By visualizing VMAT2 in different states, scientists now better understand how it functions and how the different shapes the protein takes influence drug binding — critical information for ...
Heterogeneity of Earth’s mantle may be relics of Moon formation
2023-11-01
An interdisciplinary international research team has recently discovered that a massive anomaly deep within the Earth’s interior may be a remnant of the collision about 4.5 billion years ago that formed the Moon.
This research offers important new insights not only into Earth’s internal structure but also its long-term evolution and the formation of the inner solar system.
The study, which relied on computational fluid dynamics methods pioneered by Prof. DENG Hongping of the Shanghai Astronomical Observatory (SHAO) of ...
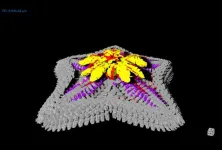
Study reveals location of starfish’s head
2023-11-01
If you put a hat on a starfish, where would you put it? On the center of the starfish? Or on the point of an arm and, if so, which one? The question is silly, but it gets at serious questions in the fields of zoology and developmental biology that have perplexed veteran scientists and schoolchildren in introductory biology classes alike: Where is the head on a starfish? And how does their body layout relate to ours?
Now, a new Stanford study that used genetic and molecular tools to map out the body regions of starfish – by creating a 3D atlas of their gene ...
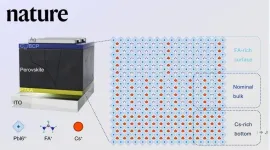
Scientists propose perovskite films homogenizing strategy to increase conversion efficiency
2023-11-01
In a study published in Nature, researchers from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences have proposed a new and promising method of fabricating homogenized perovskite films for solar cells. The process involves inhibiting phase segregation caused by internal cation inhomogeneity to increase conversion efficiency to 26.1%, thus tying the existing record.
Their work was also featured as a Nature Editor’s Pick.
For solar cells, an important alternative energy ...