(Press-News.org) DALLAS, Nov. 2, 2023 — Medical experts note that hormone and body composition changes during the transition to menopause can increase the risk of developing heart disease after menopause.[1] The American Heart Association, a global force for healthier lives for all, offers tips to support women’s heart health during this transition.
“More women in the U.S. are living longer, and a significant portion of them will spend up to 40% of their lives postmenopausal,” said Brooke Aggarwal, Ed.D., M.S., F.A.H.A., assistant professor of medical sciences in Cardiology at Columbia University Medical Center and a volunteer for the American Heart Association’s Go Red for Women™ movement.
As women grow and change so does their risk for cardiovascular disease. Go Red for Women, the Association’s premier women’s movement, addresses awareness and clinical care gaps of women’s greatest health threat, and is a trusted source for health and well-being at every age, stage and season.
“Navigating through menopause isn’t one-size-fits-all, and neither is the journey to good heart health,” she added. “This makes it even more important to focus on heart and brain health at all stages of life.”
The best defense against menopause-related changes is working with your doctor to make sure your key health numbers are in a healthy range, and understanding which healthy habits you can fine tune to boost your heart health. These tips can help:
Health by the numbers: Blood pressure, blood sugar and body mass index should be monitored yearly. More often if your numbers are out of range. Cholesterol level is also important, and healthy numbers are more individualized based on your other risk factors. Your doctor can help you figure this one out.
The best way to eat: No single food is a miracle-worker for health. Instead, look at your overall pattern of eating. Experts at the American Heart Association rated 10 popular eating patterns and the DASH-style and Mediterranean-style way of eating rose to the top as having the most heart-healthy elements: high in vegetables, fruit, whole grains, healthy fat and lean protein; and low in salt, sugar, alcohol and processed foods.
Exercise that does double-duty: Strength and resistance training is one of the four types of exercise in a general workout routine along with endurance, balance and flexibility. Strength and resistance have the added benefit of increasing bone strength and muscle mass. As women enter menopause, bone density may take a hit and body composition tends to shift to lower muscle mass. Strength training at least twice a week can help your bones and muscles maintain strength and density.
Protect your sleep time: Healthy sleep is part of the 8 essential elements of heart health called Life’s Essential 8, but the transition to menopause comes with myriad interruptions to a good night’s rest – nightly restroom trips, night sweats, insomnia. Do whatever it takes to get your Z’s because better sleep has great health benefits: stronger immune system, better mood, more energy, clearer thinking and lower risk of chronic diseases. A few habit changes can improve sleep, like setting a notification or alarm to remind you it’s time to wind down, then shutting down electronic devices at that time. For stubborn sleep problems your doctor may be able to help.
Additional resources:
Multimedia is available in the right column of the release link.
Spanish news release will be added as available.
What is Menopause?
Menopause and Cardiovascular Risk
5 Things About Menopause Every Woman Needs to Know
Infographic - Menopause and Heart Health
Heart Health after Menopause
Life’s Essential 8
Follow AHA/ASA news on X @HeartNews
###
About the American Heart Association
The American Heart Association is a relentless force for a world of longer, healthier lives. We are dedicated to ensuring equitable health in all communities. Through collaboration with numerous organizations, and powered by millions of volunteers, we fund innovative research, advocate for the public’s health and share lifesaving resources. The Dallas-based organization has been a leading source of health information for nearly a century. Connect with us on heart.org, Facebook, X or by calling 1-800-AHA-USA1.
[1] https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/CIR.0000000000000912
END
Menopause and heart health – 4 tips for a healthy heart while your body is changing
2023-11-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Self-powered microbial fuel cell biosensor for monitoring organic freshwater pollution
2023-11-02
The discharge of organic effluents—biodegradable waste materials from plants and animals—into freshwater bodies is a significant environmental concern, affecting the health and sustainability of these aquatic ecosystems. However, the methods currently available for inspecting water quality are complex and costly.
In this regard, researchers from Ritsumeikan University, Japan, have recently developed a self-powered, inexpensive, and floating biosensor for monitoring water quality at the input of freshwater lakes and rivers. This paper was made available online on September 9, 2023, and was published in Volume 200 of the Biochemical Engineering ...
Optical-fiber based single-photon light source at room temperature for next-generation quantum processing
2023-11-02
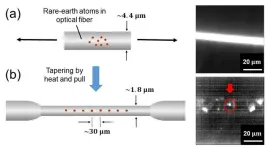
Quantum-based systems promise faster computing and stronger encryption for computation and communication systems. These systems can be built on fiber networks involving interconnected nodes which consist of qubits and single-photon generators that create entangled photon pairs.
In this regard, rare-earth (RE) atoms and ions in solid-state materials are highly promising as single-photon generators. These materials are compatible with fiber networks and emit photons across a broad range of wavelengths. Due to their wide spectral range, optical fibers ...
The influence of media narratives on microplastics risk perception revealed
2023-11-02
In a world increasingly aware of the environmental challenges posed by microplastics, a pioneering study conducted by Ruxandra Malina Petrescu-Mag from Babes-Bolyai University, and published in PeerJ Life & Environment, sheds new light on the impact of media narratives on public perception and awareness of microplastic risks.
Microplastics - tiny plastic particles that pollute both terrestrial and marine ecosystems - have garnered significant scientific, media, and public attention in recent years. However, this study reveals a lack of consensus between the scientific community and the media, particularly when it comes to how ...
TU Delft researchers discover new ultra strong material for microchip sensors
2023-11-02
Researchers at Delft University of Technology, led by assistant professor Richard Norte, have unveiled a remarkable new material with potential to impact the world of material science: amorphous silicon carbide (a-SiC). Beyond its exceptional strength, this material demonstrates mechanical properties crucial for vibration isolation on a microchip. Amorphous silicon carbide is therefore particularly suitable for making ultra-sensitive microchip sensors.
The range of potential applications is vast. From ultra-sensitive microchip sensors and advanced solar ...
Buzz around new centralized pollination portal for better global bee data
2023-11-02
A powerful new way to fill major gaps in public bee data – including from Africa, Asia and other under-reported zones – has been addressed with a centralised tool for consolidating bee pollinator occurrences around the globe.
Called BeeBCD, the package outlined in a new Nature journal article, brings together more than 18 million bee occurrence records from multiple public and private databases to improve accuracy and accessibility of species data from around the world for future conservation, research and farming management.
The rationalised bee occurrence datasets will help support future plant and crop production ...
What a “2D” quantum superfluid feels like to the touch
2023-11-02
Researchers from Lancaster University in the UK have discovered how superfluid helium 3He would feel if you could put your hand into it.
The interface between the exotic world of quantum physics and classical physics of the human experience is one of the major open problems in modern physics.
Dr Samuli Autti is the lead author of the research published in Nature Communications.
Dr Autti said: “In practical terms, we don’t know the answer to the question ‘how does it feel to touch quantum physics?’
“These experimental conditions are extreme and the techniques complicated, but I can now tell ...
NIH grants support UCLA and Charles Drew University researchers' efforts to end HIV epidemic
2023-11-02
NIH grants support UCLA and Charles Drew University researchers' efforts to end HIV epidemic
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) has granted $2.1 million to UCLA’s Center for HIV Identification, Prevention, and Treatment Services (CHIPTS) and the UCLA-CDU Center for AIDS Research (CFAR) to support four research projects and an implementation science consultation hub. These awards will fund projects to strengthen research-community collaborations and enhance implementation strategies needed for the Ending the HIV Epidemic in the U.S. (EHE) initiative.
“These awards will support our scientists and ...
AI trained to identify least green homes by Cambridge researchers
2023-11-02
University of Cambridge media release
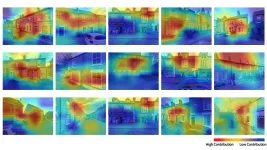
First of its kind AI-model can help policy-makers efficiently identify and prioritize houses for retrofitting and other decarbonizing measures.
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
Model identified ‘hard to decarbonize’ houses with 90% precision and additional data will improve this.
Model trained with open source data including from energy performance certificates, and street and aerial view images. It could be used anywhere in the world.
Model can even identify specific parts of houses losing most heat, including roofs and windows.
‘Hard-to-decarbonize’ (HtD) houses are responsible ...
EU MiFID II unbundling rules damaged research and liquidity in London’s main stock market – new study
2023-11-02
New research from the University of Bath shows the European Union’s MiFID II financial market reforms inadvertently reduced research activity and adversely affected liquidity in London’s main stock market but that the impact on London’s less regulated Alternative Investment Market was mitigated by its special adviser rules.
The EU’s Markets in Financial Instruments Directive II (MiFID II) from 2018 aimed to improve transparency around research costs, which were previously bundled into brokers’ overall fees to clients. The legislation demanded the fees be ‘unbundled’ to make the hidden costs more explicit ...
International study led by researchers in Singapore reveals critical insights into timely interventions for maternal depression
2023-11-02
SINGAPORE – A large-scale international study spanning three continents, led by researchers from A*STAR’s Translational Neuroscience Programme of the Singapore Institute for Clinical Sciences (SICS) in Singapore, has found that maternal depressive symptoms begin from early pregnancy and can last up to two years after childbirth.
While health professionals often emphasise the postpartum stage after childbirth as a high-risk period for the onset of depression, findings from this latest study reveal a different reality – that maternal depressive symptoms can appear from early pregnancy ...