(Press-News.org) University of Cambridge media release
First of its kind AI-model can help policy-makers efficiently identify and prioritize houses for retrofitting and other decarbonizing measures.
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
Model identified ‘hard to decarbonize’ houses with 90% precision and additional data will improve this.
Model trained with open source data including from energy performance certificates, and street and aerial view images. It could be used anywhere in the world.
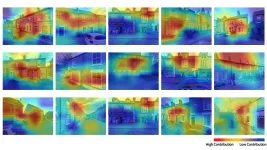
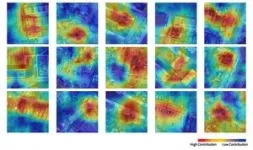
Model can even identify specific parts of houses losing most heat, including roofs and windows.
‘Hard-to-decarbonize’ (HtD) houses are responsible for over a quarter of all direct housing emissions – a major obstacle to achieving net zero – but are rarely identified or targeted for improvement.
Now a new ‘deep learning’ model trained by researchers from Cambridge University’s Department of Architecture promises to make it far easier, faster and cheaper to identify these high priority problem properties and develop strategies to improve their green credentials.
Houses can be ‘hard to decarbonize’ for various reasons including their age, structure, location, social-economic barriers and availability of data. Policymakers have tended to focus mostly on generic buildings or specific hard-to-decarbonise technologies but the study, published in the journal Sustainable Cities and Society, could help to change this.
Maoran Sun, an urban researcher and data scientist, and his PhD supervisor Dr Ronita Bardhan, who leads Cambridge’s Sustainable Design Group, show that their AI model can classify HtD houses with 90% precision and expect this to rise as they add more data, work which is already underway.
Dr Bardhan said: “This is the first time that AI has been trained to identify hard-to-decarbonize buildings using open source data to achieve this.
“Policymakers need to know how many houses they have to decarbonize, but they often lack the resources to perform detail audits on every house. Our model can direct them to high priority houses, saving them precious time and resources.”
The model also helps authorities to understand the geographical distribution of HtD houses, enabling them to efficiently target and deploy interventions efficiently.
The researchers trained their AI model using data for their home city of Cambridge, in the United Kingdom. They fed in data from Energy Performance Certificates (EPCs) as well as data from street view images, aerial view images, land surface temperature and building stock. In total, their model identified 700 HtD houses and 635 non-HtD houses. All of the data used was open source.
Maoran Sun said: “We trained our model using the limited EPC data which was available. Now the model can predict for the city’s other houses without the need for any EPC data.”
Bardhan added: “This data is available freely and our model can even be used in countries where datasets are very patchy. The framework enables users to feed in multi-source datasets for identification of HtD houses.”
Sun and Bardhan are now working on an even more advanced framework which will bring additional data layers relating to factors including energy use, poverty levels and thermal images of building facades. They expect this to increase the model’s accuracy but also to provide even more detailed information.
The model is already capable of identifying specific parts of buildings, such as roofs and windows, which are losing most heat, and whether a building is old or modern. But the researchers are confident they can significantly increase detail and accuracy.
They are already training AI models based on other UK cities using thermal images of buildings, and are collaborating with a space products-based organisation to benefit from higher resolution thermal images from new satellites. Bardhan has been part of the NSIP – UK Space Agency program where she collaborated with the Department of Astronomy and Cambridge Zero on using high resolution thermal infrared space telescopes for globally monitoring the energy efficiency of buildings.
Sun said: “Our models will increasingly help residents and authorities to target retrofitting interventions to particular building features like walls, windows and other elements.”
Bardhan explains that, until now, decarbonization policy decisions have been based on evidence derived from limited datasets, but is optimistic about AI’s power to change this.
“We can now deal with far larger datasets. Moving forward with climate change, we need adaptation strategies based on evidence of the kind provided by our model. Even very simple street view photographs can offer a wealth of information without putting anyone at risk.”
The researchers argue that by making data more visible and accessible to the public, it will become much easier to build consensus around efforts to achieve net zero.
“Empowering people with their own data makes it much easier for them to negotiate for support,” Bardhan said.
She added: “There is a lot of talk about the need for specialised skills to achieve decarbonisation but these are simple data sets and we can make this model very user friendly and accessible for the authorities and individual residents.”
Cambridge as a study site
Cambridge is an atypical city but informative site on which to base the initial model. Bardhan notes that Cambridge is relatively affluent meaning that there is a greater willingness and financial ability to decarbonize houses.
“Cambridge isn’t ‘hard to reach’ for decarbonisation in that sense,” Bardhan said. “But the city’s housing stock is quite old and building bylaws prevent retrofitting and the use of modern materials in some of the more historically important properties. So it faces interesting challenges.”
The researchers will discuss their findings with Cambridge City Council. Bardhan previously worked with the Council to assess council houses for heat loss. They will also continue to work with colleagues at Cambridge Zero and the University’s Decarbonisation Network.
Reference
M. Sun & R. Bardhan, ‘Identifying Hard-to-Decarbonize houses from multi-source data in Cambridge, UK’, Sustainable Cities and Society (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.scs.2023.105015
Media contacts
Tom Almeroth-Williams, Communications Manager (Research), University of Cambridge: researchcommunications@admin.cam.ac.uk / tel: +44 (0) 7540 139 444
Ronita Bardhan, University of Cambridge: rb867@cam.ac.uk
END
AI trained to identify least green homes by Cambridge researchers
2023-11-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
EU MiFID II unbundling rules damaged research and liquidity in London’s main stock market – new study
2023-11-02
New research from the University of Bath shows the European Union’s MiFID II financial market reforms inadvertently reduced research activity and adversely affected liquidity in London’s main stock market but that the impact on London’s less regulated Alternative Investment Market was mitigated by its special adviser rules.
The EU’s Markets in Financial Instruments Directive II (MiFID II) from 2018 aimed to improve transparency around research costs, which were previously bundled into brokers’ overall fees to clients. The legislation demanded the fees be ‘unbundled’ to make the hidden costs more explicit ...
International study led by researchers in Singapore reveals critical insights into timely interventions for maternal depression
2023-11-02
SINGAPORE – A large-scale international study spanning three continents, led by researchers from A*STAR’s Translational Neuroscience Programme of the Singapore Institute for Clinical Sciences (SICS) in Singapore, has found that maternal depressive symptoms begin from early pregnancy and can last up to two years after childbirth.
While health professionals often emphasise the postpartum stage after childbirth as a high-risk period for the onset of depression, findings from this latest study reveal a different reality – that maternal depressive symptoms can appear from early pregnancy ...
Paper argues reducing greenhouse gas emissions is not enough to combat climate change
2023-11-02
According to a new paper in Oxford Open Climate Change, published by Oxford University Press, the strategies humanity must pursue to reduce climate change will have to include more than reducing greenhouse gases. This comes from an analysis of climate data led by researcher James Hansen.
Scientists have known since the 1800s that infrared-absorbing (greenhouse) gases warm the Earth’s surface and that the abundance of greenhouse gases changes naturally as well as from human actions. Roger Revelle, who was one of the early scientists to study global warming, wrote in 1965 that industrialization meant that human ...
Research examines why mask usage in Japan persists
2023-11-02
Osaka, Japan – When you think of Japan in the age of COVID, you might imagine a crowd of people wearing masks. But why do so many Japanese people wear masks?
In an article published this month in the International Journal of Disaster Risk Reduction, a researcher from Osaka University analyzed mask use before and after the government of Japan downgraded the legal status of COVID-19. Results showed that many people continue to wear masks for socio-psychological reasons – including reasons related to ‘relief’ and ‘norm’.
Of course, the obvious motivation for mask use is disease prevention. In the first ...
Exercise therapy based on smart data to improve patients' quality of life
2023-11-02
Regular and moderate physical activity can significantly improve the quality of life of people with internal diseases such as cancer and depression. Unfortunately, many people with internal disorders cannot sufficiently participate in exercise training for several reasons. For example, they often do not have access to appropriate exercise training programs, have a high therapeutic burden, fatigue, or simply no time to engage in physical activity. Accordingly, the Sports Medicine research group led by Professor Perikles Simon at Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU) investigates how physical activity can be promoted and integrated into patients' daily lives by applying digital tools ...
Alternative antibiotic selection can reduce the risk of healthcare-associated infections for patients with pneumonia
2023-11-02
Arlington, Va. — November 2, 2023 — A new study published today in the American Journal of Infection Control (AJIC) reveals that the use of doxycycline may help protect against Clostridioides difficile (C. diff) infection for some patients with pneumonia. Specifically, study authors found that for hospitalized patients with community-acquired pneumonia who had experienced C. diff infections in the prior year, the use of doxycycline, instead of the more commonly used azithromycin, reduced the development ...
Survey finds most Americans are unaware of many signs that someone is having a seizure
2023-11-02
Orlando, Fla - If you’ve ever seen a movie or TV show in which a character has a seizure, you probably have a fairly standard mental picture of someone falling to the ground in full body convulsions while foaming at the mouth. But that doesn’t necessarily reflect reality. A new national survey by Orlando Health finds that while most Americans recognize those classic symptoms of what’s called a generalized tonic-clonic seizure, the majority fail to recognize the subtle signs, all of which can be dangerous and have a profound ...
A “manganese bullet” targeting the top killer?
2023-11-02
Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) continue to rank as the top killer in the modern world. This deadly disorder often starts with the buildup of lipid deposits or plaques within the blood vessel, silently setting the stage for atherosclerosis. Rupture of these atherosclerotic plaques, however, could clot blood vessels and lead to life-threatening conditions including heart attack or stroke.
Dyslipidemia, meaning having too much “bad” or atherogenic lipids in the blood, represents the most common cause of CVDs and ...
New NUS study provides insights into early breast cancer development in individuals with BRCA2 mutations
2023-11-02
A pioneering study led by Professor Ashok Venkitaraman from the Cancer Science Institute of Singapore (CSI Singapore) at the National University of Singapore and Dr Mona Shehata from the University of Cambridge (UK) has uncovered vital insights into the distinct effects of BRCA2 mutations on breast tissue cells, shedding light on early breast cancer development in people with BRCA2 mutations. The research was published in the prestigious journal Nature Communications on 25 August 2023.
Breast cancer is a serious concern for individuals with BRCA2 mutations, ...
Clinical intervention directed at social risks does not increase experiences of discrimination
2023-11-02
A growing recognition of the health impact of social risks – such as food insecurity and homelessness – has prompted researchers, healthcare providers and policymakers to consider ways to address these risk factors as part of holistic clinical care. However, some healthcare providers worry the same interventions designed to help patients and families with social risks might also make them feel singled out or like they are otherwise stigmatized.
Now, new results of a rigorous study from the University of Chicago Medicine published October 2023 in JAMA Pediatrics suggest well-designed interventions that address social risks can be provided ...