(Press-News.org) People who have a higher biological age than their actual chronological age have a significantly increased risk of stroke and dementia, especially vascular dementia. These are the results of a study from Karolinska Institutet in Sweden published in the Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery and Psychiatry.
The study, which was led by Sara Hägg, associate professor, and Jonathan Mak, doctoral student at the Department of Medical Epidemiology and Biostatistics, Karolinska Institutet, shows that the increased risk persists even if other risk factors such as genetics, lifestyle and socioeconomics are taken into account.
As we age, the risk of chronic diseases such as cancer, cardiovascular disease and neurodegenerative disorders increases. Researchers have traditionally relied on chronological age – the number of years a person has been alive – as an approximate measure of biological age.
“But because people age at different rates, chronological age is a rather imprecise measure”, says Sara Hägg.
In order to measure biological age and the link to disease, the researchers used data from the UK Biobank. They studied a cohort of 325,000 people who were all between 40 and 70 years old at the time of the first measurement.
Biological age was calculated using 18 biomarkers, including blood lipids, blood sugar, blood pressure, lung function and BMI. The researchers then investigated the relationship between these biomarkers and the risk of developing neurodegenerative diseases such as dementia, stroke, ALS and Parkinson's disease within a nine-year period.
When compared to actual, chronological age, high biological age was linked to a significantly increased risk of dementia, especially vascular dementia, and ischemic stroke, (i.e. blood clot in the brain).
“If a person's biological age is five years higher than their actual age, the person has a 40 per cent higher risk of developing vascular dementia or suffering a stroke,” says Jonathan Mak.
As it is an observational study, causal relationships cannot be established. However, the results indicate that by slowing down the body's ageing processes in terms of the measured biomarkers, it may be possible to reduce or delay the onset of disease.
“Several of the values can be influenced through lifestyle and medications”, says Sara Hägg.
The results are particularly interesting because the study included such a large group of people. This makes it possible to break down the material into smaller pieces and capture less common diagnoses such as ALS.
The risk of developing ALS also increases with higher biological age. However, no such risk increase was seen for Parkinson's disease.
“We already know that Parkinson's disease is a bit unique in other contexts as well, for example, when it comes to smoking”, says Sara Hägg.
The researchers will now proceed to investigate the connection between biological age and other diseases such as cancer.
The study was funded by the Swedish Research Council, KI Foundation and the Strategic research area in epidemiology and biostatistics at KI (SFOepi). The researchers declare no conflicts of interest.
Publication: “Clinical biomarker-based biological aging and future risk of neurological disorders in the UK Biobank”, Jonathan Mak, Christopher McMurran, Sara Hägg, Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery and Psychiatry , online 6 November 2023, doi: 10.1136/jnnp-2023-331917
END
High biological age may increase the risk of dementia and stroke
2023-11-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New research shows quasars can be buried in their host galaxies
2023-11-06
-With pictures-
A new study reveals that supermassive black holes at the centres of galaxies, known as quasars, can sometimes be obscured by dense clouds of gas and dust in their host galaxies.
This challenges the prevailing idea that quasars are only obscured by donut-shaped rings of dust in the close vicinity of the black hole.
Quasars are extremely bright objects powered by black holes gorging on surrounding material.
Their powerful radiation can be blocked if thick clouds come between us and the quasar.
Astronomers have long thought this obscuring material only exists in the quasar's immediate surroundings, in a "dusty torus" (or donut) encircling it.
Now, a team of ...
EMBARGOED: Bendy X-ray detectors could revolutionize cancer treatment
2023-11-06
EMBARGOED: 0001 GMT MONDAY 6 NOVEMBER 2023
New materials developed at the University of Surrey could pave the way for a new generation of flexible X-ray detectors, with potential applications ranging from cancer treatment to better airport scanners.
Traditionally, X-ray detectors are made of heavy, rigid material such as silicon or germanium. New, flexible detectors are cheaper and can be shaped around the objects that need to be scanned, improving accuracy when screening patients and reducing risk when imaging tumours and administering radiotherapy.
Dr Prabodhi Nanayakkara, ...
Real-world analysis of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors in kidney transplant recipients
2023-11-04
Highlights
Compared with kidney transplant recipients who did not receive sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors, those treated with the medications had lower risks of experiencing kidney transplant failure, kidney transplant rejection, major adverse cardiac events, all-cause mortality, and genitourinary infections.
Results from the study will be presented at ASN Kidney Week 2023 November 1–November 5.
Philadelphia, PA (November 4, 2023) — Sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors lower blood sugar levels and have additional beneficial effects on kidney and heart health for individuals with ...
Diagnostic outcomes of concurrent DNA and RNA sequencing in individuals undergoing hereditary cancer testing
2023-11-04
About The Study: The findings of this diagnostic study including 43,000 individuals undergoing hereditary cancer testing demonstrate that the ability to perform RNA sequencing concurrently with DNA sequencing represents an important advancement in germline genetic testing by improving detection of novel variants and classification of existing variants. This expands the identification of individuals with hereditary cancer predisposition and increases opportunities for personalization of therapeutics and surveillance.
Authors: Rachid Karam, M.D., Ph.D., of Ambry Genetics ...
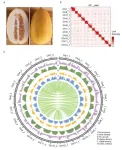
The first semi-wild-type melon T2T genome assembled by Zhengzhou Fruit Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, and China Agricultural University
2023-11-03
Melon (Cucumis melo L.) is an important vegetable crop that has an extensive history of cultivation, and has been classified into two subspecies, C. melo ssp. agrestis and C. melo ssp. melo. Previous study suggested that the two subspecies were domesticated independently [1], which may have generated different genetic mechanisms for the same trait between the two subspecies. Furthermore, the difference in their geographical distribution resulted in diverse characteristics between the two subspecies, shaping genomic imprinting in their genomes. Wild germplasm is an important genetic resource in crop breeding because of its high genetic diversity ...
Neighborhood stressors dangerously elevate pregnancy hormones
2023-11-03
Pregnant women living in blighted neighborhoods with high levels of known stressors have higher levels of testosterone – the primary sex hormone in males -- which disrupt hormone regulation and may lead to life-threatening complications during and after childbirth, according to Rutgers research.
“Previous research has shown that exposure to neighborhood stressors is associated with preterm birth, low birth weight and other complications such as preeclampsia, gestational diabetes and stillbirth,” ...
Are results from clinical trials in kidney transplant recipients applicable to the real world?
2023-11-03
Highlights
Investigators have found demographic differences between participants of kidney transplant clinical trials and transplant recipients in the United States, even in recent years.
Results from the study will be presented at ASN Kidney Week 2023 November 1–November 5.
Philadelphia, PA (November 3, 2023) — Investigators recently examined the extent to which participants in clinical trials related to kidney transplantation are similar to individuals undergoing transplantation in the United States. The ...
County-level structural racism may affect mortality rates in people with kidney failure
2023-11-03
Highlights
In a recent analysis of US data, Black patients with kidney failure experienced survival advantages compared with White patients when county-level structural racism was low, but they experienced survival disadvantages compared with White patients at higher levels of structural racism.
Results from the study will be presented at ASN Kidney Week 2023 November 1–November 5.
Philadelphia, PA (November 3, 2023) — A new analysis indicates that county-level structural racism is a significant determinant of death among individuals ...
Is high urinary albumin linked to sub-clinical cardiovascular disease in people with type 2 diabetes?
2023-11-03
Highlights
Imaging tests in individuals with type 2 diabetes without symptoms of cardiovascular disease indicated that elevated albumin in the urine may be linked with sub-clinical coronary artery pathology, including coronary artery microcalcifications.
Results from the study will be presented at ASN Kidney Week 2023 November 1–November 5.
Philadelphia, PA (November 3, 2023) — Advances in non-invasive imaging have allowed clinicians to assess both the structure and function of coronary arteries. Investigators who recently used positron emission tomography and computed tomography ...
Scientists create the most complete atlas of the human fetal kidney to date
2023-11-03
Highlights
By examining the gene expression patterns of single cells from human fetal kidneys, researchers created a map that demonstrates the trajectories of cell states in the developing kidney and that identifies characteristics associated with kidney diseases.
Results from the study will be presented at ASN Kidney Week 2023 November 1–November 5.
Philadelphia, PA (November 3, 2023) — Scientists have examined the gene expression patterns of single cells from 5 human fetal kidneys to create the most complete atlas of the ...