(Press-News.org)
EMBARGOED: 0001 GMT MONDAY 6 NOVEMBER 2023
New materials developed at the University of Surrey could pave the way for a new generation of flexible X-ray detectors, with potential applications ranging from cancer treatment to better airport scanners.
Traditionally, X-ray detectors are made of heavy, rigid material such as silicon or germanium. New, flexible detectors are cheaper and can be shaped around the objects that need to be scanned, improving accuracy when screening patients and reducing risk when imaging tumours and administering radiotherapy.
Dr Prabodhi Nanayakkara, who led the research at the University of Surrey, said:
“This new material is flexible, low-cost, and sensitive. But what’s exciting is that this material is tissue equivalent. This paves the way for live dosimetry, which just isn’t possible with current technology.”
Most of the X-ray detectors on the market today are heavy, rigid, energy-consuming and expensive if a large area needs to be covered.
Substances built up of hydrogen and carbon, known as organic semiconductors, offer a more flexible solution, but until now, did not allow as detailed an X-ray image to be produced as traditional detectors.
To solve this challenge, scientists at the University of Surrey's Advanced Technology Institute created devices based on an ink by adding low quantities of high atomic number elements to an organic semiconductor.
Building on the team’s previous research in this field, their new detector behaves more like human tissue under X-rays, which could lead to new, safer techniques for administering radiotherapy, mammography and radiography. Their findings are published in the journal Advanced Science.
Professor Ravi Silva, director of Surrey's Advanced Technology Institute, said:
“This new technology could be used in a variety of settings, such as radiotherapy, scanning historical artefacts and in security scanners. The University of Surrey together with its spin out SilverRay Ltd continues to lead the way in flexible X-ray detectors – we're pleased to see the technology shows real promise for a range of uses.”
Co-author, Professor Martin Heeney, Imperial College London, commented:
“We have been developing heavy analogues of traditional organic semiconductors for some time, and we were intrigued when Dr Imalka Jayawardena suggested their application in X-ray detectors. These results are very exciting, especially considering this was the first material investigated, and there is plenty of scope for further improvements.”
END
EMBARGOED: Bendy X-ray detectors could revolutionize cancer treatment
2023-11-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Real-world analysis of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors in kidney transplant recipients
2023-11-04
Highlights
Compared with kidney transplant recipients who did not receive sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors, those treated with the medications had lower risks of experiencing kidney transplant failure, kidney transplant rejection, major adverse cardiac events, all-cause mortality, and genitourinary infections.
Results from the study will be presented at ASN Kidney Week 2023 November 1–November 5.
Philadelphia, PA (November 4, 2023) — Sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors lower blood sugar levels and have additional beneficial effects on kidney and heart health for individuals with ...
Diagnostic outcomes of concurrent DNA and RNA sequencing in individuals undergoing hereditary cancer testing
2023-11-04
About The Study: The findings of this diagnostic study including 43,000 individuals undergoing hereditary cancer testing demonstrate that the ability to perform RNA sequencing concurrently with DNA sequencing represents an important advancement in germline genetic testing by improving detection of novel variants and classification of existing variants. This expands the identification of individuals with hereditary cancer predisposition and increases opportunities for personalization of therapeutics and surveillance.
Authors: Rachid Karam, M.D., Ph.D., of Ambry Genetics ...
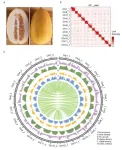
The first semi-wild-type melon T2T genome assembled by Zhengzhou Fruit Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, and China Agricultural University
2023-11-03
Melon (Cucumis melo L.) is an important vegetable crop that has an extensive history of cultivation, and has been classified into two subspecies, C. melo ssp. agrestis and C. melo ssp. melo. Previous study suggested that the two subspecies were domesticated independently [1], which may have generated different genetic mechanisms for the same trait between the two subspecies. Furthermore, the difference in their geographical distribution resulted in diverse characteristics between the two subspecies, shaping genomic imprinting in their genomes. Wild germplasm is an important genetic resource in crop breeding because of its high genetic diversity ...
Neighborhood stressors dangerously elevate pregnancy hormones
2023-11-03
Pregnant women living in blighted neighborhoods with high levels of known stressors have higher levels of testosterone – the primary sex hormone in males -- which disrupt hormone regulation and may lead to life-threatening complications during and after childbirth, according to Rutgers research.
“Previous research has shown that exposure to neighborhood stressors is associated with preterm birth, low birth weight and other complications such as preeclampsia, gestational diabetes and stillbirth,” ...
Are results from clinical trials in kidney transplant recipients applicable to the real world?
2023-11-03
Highlights
Investigators have found demographic differences between participants of kidney transplant clinical trials and transplant recipients in the United States, even in recent years.
Results from the study will be presented at ASN Kidney Week 2023 November 1–November 5.
Philadelphia, PA (November 3, 2023) — Investigators recently examined the extent to which participants in clinical trials related to kidney transplantation are similar to individuals undergoing transplantation in the United States. The ...
County-level structural racism may affect mortality rates in people with kidney failure
2023-11-03
Highlights
In a recent analysis of US data, Black patients with kidney failure experienced survival advantages compared with White patients when county-level structural racism was low, but they experienced survival disadvantages compared with White patients at higher levels of structural racism.
Results from the study will be presented at ASN Kidney Week 2023 November 1–November 5.
Philadelphia, PA (November 3, 2023) — A new analysis indicates that county-level structural racism is a significant determinant of death among individuals ...
Is high urinary albumin linked to sub-clinical cardiovascular disease in people with type 2 diabetes?
2023-11-03
Highlights
Imaging tests in individuals with type 2 diabetes without symptoms of cardiovascular disease indicated that elevated albumin in the urine may be linked with sub-clinical coronary artery pathology, including coronary artery microcalcifications.
Results from the study will be presented at ASN Kidney Week 2023 November 1–November 5.
Philadelphia, PA (November 3, 2023) — Advances in non-invasive imaging have allowed clinicians to assess both the structure and function of coronary arteries. Investigators who recently used positron emission tomography and computed tomography ...
Scientists create the most complete atlas of the human fetal kidney to date
2023-11-03
Highlights
By examining the gene expression patterns of single cells from human fetal kidneys, researchers created a map that demonstrates the trajectories of cell states in the developing kidney and that identifies characteristics associated with kidney diseases.
Results from the study will be presented at ASN Kidney Week 2023 November 1–November 5.
Philadelphia, PA (November 3, 2023) — Scientists have examined the gene expression patterns of single cells from 5 human fetal kidneys to create the most complete atlas of the ...
Sotagliflozin protects kidney and heart in patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease
2023-11-03
Highlights
Results from the phase 3 SCORED trial indicate that sotagliflozin protects kidney and heart health in individuals with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease.
Results from the study will be presented at ASN Kidney Week 2023 November 1–November 5.
Philadelphia, PA (November 3, 2023) — Sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors, which are medications that lower blood sugar levels among other effects, provide kidney- and heart-related benefits to patients with and without diabetes. An exploratory analysis ...
HAARP artificial airglow may be widely visible in Alaska
2023-11-03
Alaskans and visitors may be able to see an artificial airglow in the sky created by the High-frequency Active Auroral Research Program during a four-day research campaign that starts Saturday.
Scientists from the University of Alaska Fairbanks, Cornell University, University of Colorado Denver, University of Florida and Georgia Institute of Technology will conduct a variety of experiments at the UAF-operated research site.
The experiments will focus on the ionosphere, the region of the atmosphere between about 30 and 350 miles ...