(Press-News.org) Fatty liver diseases (FLD) have become a significant health concern worldwide, affecting millions. The two most common types of FLD are non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and alcoholic-associated liver disease (ALD). NAFLD is associated with obesity, insulin resistance, and metabolic syndrome, while ALD is caused by excessive alcohol consumption. Both NAFLD and ALD can progress to liver fibrosis, cirrhosis, and, ultimately, hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), a primary liver cancer with a poor prognosis.
Significant progress has been made in understanding the pathogenesis of FLD and HCC over the past decade. This has led to the identification of novel therapeutic targets for preventing and treating these diseases. The fifth Chinese American Liver Society (CALS)/Society of Chinese Bioscientists in America (SCBA) Hepatology Division Annual Symposium, which was held virtually on 21–22 October 2022, focused on recent insights into the pathogenesis of FLD and HCC, as well as the therapeutic targets that have emerged from these studies.
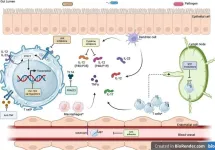
Non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) are diverse RNA molecules that do not code for proteins. NcRNAs have been shown to play essential roles in the pathogenesis of FLD and HCC. For example, microRNAs (miRNAs) are small ncRNAs that can regulate gene expression at the post-transcriptional level. miRNAs have been implicated in all aspects of FLD and HCC pathogenesis, including steatosis, inflammation, fibrosis, and carcinogenesis.
Autophagy is a cellular process that removes damaged organelles and proteins. Autophagy is essential for maintaining cellular homeostasis and preventing cell death. However, impaired autophagy has been linked to the development and progression of FLD and HCC. For example, studies have shown that hepatocyte-specific autophagy deficiency can lead to steatosis and inflammation.
Extrahepatic signalling refers to communication between the liver and other organs in the body. Extrahepatic signalling plays a vital role in regulating liver metabolism and inflammation. Disruption of extrahepatic signalling has been implicated in the pathogenesis of FLD and HCC. For example, studies have shown that obesity-related changes in adipose tissue signalling can promote the development of NAFLD.
Macrophages are a type of immune cell that plays a crucial role in inflammation. Macrophages are present in the liver and can be activated by a variety of stimuli, including steatosis, injury, and infection. The heterogeneity of macrophages in these diseases were discussed via single cell RNA sequencing. For example, studies have shown that TREM2+CD9+ NASH-associated macrophages are activated in patients with NAFLD and HCC.
In addition to the factors discussed above, other potential therapeutic targets for FLD and HCC include:
Bile acid metabolism
Oxidative stress
Apoptosis
Angiogenesis
Epigenetic regulation
The fifth CALS/SCBA Hepatology Division Annual Symposium highlighted the latest research on these and other therapeutic targets for FLD and HCC. This research can potentially lead to new and more effective treatments for these devastating diseases.
See the article:
Wen Y, Ma L, Ju C. Recent insights into the pathogenesis and therapeutic targets of chronic liver diseases. eGastroenterology 2023;1:e100020. doi:10.1136/egastro-2023-100020
About the eGastroenterology
eGastroenterology is a new, open-access, and open peer-reviewed BMJ Journal, which focuses on basic, clinical, translational, and evidence-based medicine research in all areas of gastroenterology (including hepatology, pancreatology, esophagology, and gastrointestinal surgery).
For more information, please visit: egastroenterology.bmj.com and follow us on Twitter (@eGastro_BMJ).
Sign-up to Email Alerts for eGastroenterology: https://emails.bmj.com/k/Bmj/jausu/egastroenterology
END
Ulcerative colitis (UC) and Crohn's disease (CD) are chronic inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) that affect the gastrointestinal tract. In recent decades, there have been significant advances in the understanding of IBD pathophysiology and the development of new treatments.
The International Organisation for the Study of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases (IOIBD) developed the Selecting Therapeutic Targets in Inflammatory Bowel Disease (STRIDE) programs, which recommend specific treatment goals for UC and CD in children ...
- A multicenter study of the MD Anderson, Korea University, Yonsei University, and other institutions
- Establishing subtypes of gastric cancer classification to lay the foundation of personalized treatment
Professor Sang Cheul Oh of the Division of Oncology/Hematology, Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University College of Medicine, Professor Sang‑Hee Kang of the Department of Surgery, Korea University’s Guro Hospital, and Professor Sun Young Yim of the Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University College of Medicine announced a new genetic classification system ...
ABSTRACTS: 1534, 777, 1328, 1526, 1330, 545
HOUSTON ― The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center’s Research Highlights provides a glimpse into recent basic, translational, and clinical cancer research from MD Anderson experts.
This special edition features oral presentations from the Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer (SITC) 38th Annual Meeting focused on scientific advances and breakthroughs in cancer immunotherapy from MD Anderson-led studies. Highlights include fecal microbiome transplants ...
LAWRENCE — The story of Ekgmowechashala, the final primate to inhabit North America before Homo sapiens or Clovis people, reads like a spaghetti western: A grizzled and mysterious loner, against the odds, ekes out an existence on the American Plains.
Except this tale unfolded about 30 million years ago, just after the Eocene-Oligocene transition during which North America saw great cooling and drying, making the continent less hospitable to warmth-loving primates.
Today, paleontologists from the University ...
First reported in 2015, tar spot is an emerging disease on corn that has rapidly spread across the United States and Canada, causing tremendous yield loss estimated at $1.2 billion in 2021 alone. Tar spot gets its name from its iconic symptoms that resemble the splatter of “tar” on corn leaves, but these spots are in fact brown lesions formed by the fungal pathogen Phyllachora maydis. This destructive pathogen is challenging to research because it cannot survive outside its plant host; therefore, little information is currently known about the mechanisms that contribute to its disease cycle including spore formation, reproduction, and plant ...
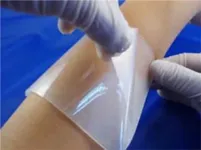
Open wounds, whether caused by accidents or from medical procedures like surgery, require proper management to speed up healing and prevent infections. While sutures and staples are common wound closure methods, they can cause secondary tissue injuries, potentially leaking fluids and gases and requiring anesthetics. Tissue adhesive glues are a more attractive alternative but often suffer from toxicity and weak adhesion.
Fortunately, tissue adhesive patches offer an innovative solution. They allow precise control of adhesion and mechanical properties through adjustable polymeric compositions. These patches can also deliver ...
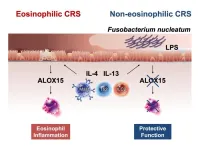
Like other countries in the world, Japan has witnessed a worrisome increase in the prevalence of chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS) over the last decade. An inflammatory disease that lasts at least 12 weeks, CRS can cause nasal congestion, nasal discharge, trouble breathing through the nose, facial pain, and even loss of sense of smell. Unfortunately, treating CRS is complex since the disease manifests in various forms. CRS can be categorized into eosinophilic (ECRS) or non-eosinophilic (non-ECRS) types. In ECRS, the nasal and sinus tissues exhibit an increased presence of eosinophils, a type of white blood cell that releases inflammatory ...
Research Highlights:
American Indian and Alaska Native adults had significantly higher death rates from premature heart attacks compared to white, Black and Asian/Pacific Islander adults in the U.S., according to an analysis of more than 370,000 heart attack deaths from 1999-2020.
In addition, despite an overall decrease in heart attack death rates among American Indian and Alaska Native adults during the last two decades, heart attack-related deaths in American Indian and Alaska Native adult men younger than 55 years old and women younger than 65 years old did not decrease.
Embargoed until 4 a.m. CT/5 a.m. ...
Research Highlights:
A child’s race, ethnicity and/or the neighborhood where they live may have an impact on their survival and recovery after a cardiac arrest.
Black children were more than four times more likely to experience a cardiac arrest compared to white or Hispanic children.
Children from neighborhoods with the highest socioeconomic status had the best odds of surviving and functioning well after a cardiac arrest.
Embargoed until 4 a.m. CT/5 a.m. ET, Monday, Nov. 6, 2023
DALLAS, Nov. 6, 2023 — Children’s ...
Research Highlights:
As more people across the U.S. use marijuana for medical and recreational reasons, two new studies suggest its regular intake may damage heart and brain health.
In one study, daily use of marijuana raised the risk of developing heart failure by about one-third, even after considering other factors, compared to people who reported never using marijuana.
In a second study, older people with any combination of Type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure and high cholesterol who used marijuana, ...