(Press-News.org) More than 150 million women worldwide use oral contraceptives. Combined OCs (COCs), made up of synthetic hormones, are the most common type. Sex hormones are known to modulate the brain network involved in fear processes.
Now a team of researchers in Canada has investigated current and lasting effects of COC use, as well as the role of body-produced and synthetic sex hormones on fear-related brain regions, the neural circuitry via which fear is processed in the brain.
“In our study, we show that healthy women currently using COCs had a thinner ventromedial prefrontal cortex than men,” said Alexandra Brouillard, a researcher at Université du Québec à Montréal and first author of the study published in Frontiers in Endocrinology. “This part of the prefrontal cortex is thought to sustain emotion regulation, such as decreasing fear signals in the context of a safe situation. Our result may represent a mechanism by which COCs could impair emotion regulation in women.”
Emotion regulation and contraceptives
“When prescribed COCs, girls and women are informed of various physical side effects, for example that the hormones they will be taking will abolish their menstrual cycle and prevent ovulation,” Brouillard explained. However, the effects of sex hormones on brain development, which continues into early adulthood, are rarely addressed. Considering how widespread COC use is, it is important to better understand its current and long-term effects on brain anatomy and emotional regulation, the researchers said.
The team recruited women who were currently using COCs; women who used COCs previously but did not at the time of the study; women who never used any form of hormonal contraception; and men. Comparing these groups allowed the researchers to see if COC use was associate with current or long-term morphologic alterations as well as to detect sex differences, since it is established that women are more susceptible to experience anxiety and stress-related disorders than men.
“As we report reduced cortical thickness of the ventromedial prefrontal cortex in COC users compared to men, our result suggests that COCs may confer a risk factor for emotion regulation deficits during their current use,” Brouillard said.
The impacts of COC use, however, may be reversible once intake is discontinued, the researchers said. Given that the vmPFC effect found in current users was not observed in past users, the findings did not support lasting anatomical effects of COC use. This, the researchers wrote, will need to be confirmed in further studies.
Much to learn
There is still much to learn when it comes to women’s brains and how they are impacted by COC use. For example, Brouillard and team are currently investigating the impact of age of onset and duration of use to delve further into the potential lasting effects of COCs. Given that many teenage girls start using COCs during adolescence, a sensitive period in brain development, user age might also impact reversibility.
Pointing to limitations in their study, the scientists said that no causal relationship can be implied between COC use and brain morphology and that generalization of their results to a general population may be limited. The researchers also cautioned that drawing conclusion from anatomical findings to behavioral and psychological impact is not possible at this point.
“The objective of our work is not to counter the use of COCs, but it is important to be aware that the pill can have an effect on the brain. Our aim is to increase scientific interest in women’s health and raise awareness about early prescription of COCs and brain development, a highly unknown topic,” concluded Brouillard.
END
Contraceptive pills might impair fear-regulating regions in women’s brains
Scientists find the use of oral contraceptives may affect fear-related brain morphology, knowledge that could deepen understanding of fear-related mechanisms that primarily affect women
2023-11-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Risk of dying in hospital from respiratory causes is higher in the summer than in the winter
2023-11-07
Global warming caused by climate change could exacerbate the burden of inpatient mortality from respiratory diseases during the warm season. This is the main conclusion of a study led by the Barcelona Institute for Global Health (ISGlobal), a centre supported by the "la Caixa" Foundation, and published in The Lancet Regional Health - Europe. The results could help health facilities adapt to climate change.
The research team analysed the association between ambient temperature and in-hospital mortality from respiratory diseases in the provinces of Madrid and Barcelona between 2006 and 2019. ...
Poetry can help people cope with loneliness or isolation
2023-11-07
Reading, writing and sharing poetry can help people cope with loneliness or isolation and reduce feelings of anxiety and depression, a new study shows.
Research by the University of Plymouth and Nottingham Trent University, funded by the Arts and Humanities Research Council, found that many people who took to sharing, discussing and writing poetry as a means to deal with the COVID-19 pandemic experienced “demonstrable positive impact on their wellbeing”.
The findings are based on a survey of 400 people which showed that poetry helped those experiencing common mental health symptoms as well as those suffering from grief.
It was carried out with registered users of the ...
French love letters confiscated by Britain finally read after 265 years
2023-11-07
UNDER STRICT EMBARGO UNTIL 19:01 (US ET) ON MONDAY 6TH NOVEMBER 2023 / 00:01AM (UK TIME) ON TUESDAY 7TH NOVEMBER 2023
Over 100 letters sent to French sailors by their fiancées, wives, parents and siblings – but never delivered – have been opened and studied for the first time since they were written in 1757-8.
The messages offer extremely rare and moving insights into the loves, lives and family quarrels of everyone from elderly peasants to wealthy officer’s wives.
The messages were seized by Britain’s Royal Navy during the Seven Years’ War, taken to the Admiralty in London ...
First in human trial of new drug raises hopes for patients with relapsed blood cancer
2023-11-06
COLUMBUS, Ohio – A new targeted drug, studied by researchers at The Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center – Arthur G. James Cancer Hospital and Richard J. Solove Research Institute (OSUCCC – James), may offer a new treatment option for patients with blood cancers, including chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and Non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) whose disease has stopped responding to standard treatments.
In the first clinical trial of this drug in humans, nemtabrutinib ...
A cutting-edge approach to tackling pollution in Houston and beyond
2023-11-06
With its notoriously hot and humid climate and robust industrial environment, Houston is one of the most ozone-polluted cities in the United States. Now, a University of Houston research team is integrating the power of machine learning (ML) with innovative analysis techniques to pinpoint the city’s air pollution sources more accurately.
While the ozone layer in the stratosphere protects the Earth, and us, from the harmful rays of the sun, it’s also a major pollutant that can be harmful to human health when it’s closer to the ground. Long-term exposure to surface ozone can cause difficulty breathing, worsen asthma and increase the ...
The last turn of ‘Ezekiel’s Wheel’ honors a Yale-affiliated fossil hunter
2023-11-06
New Haven, Conn. — The mystery of Ezekiel’s Wheel — the extinct sea creature, not the Biblical vision — may have taken its final turn, thanks to Yale paleontologists.
In so doing, the researchers have also finally put a scientific name to the favorite fossil of a beloved amateur fossil hunter.
Samuel J. Ciurca Jr., who died in 2021, was a curatorial affiliate of the Yale Peabody Museum for many years. He collected tens of thousands of fossils, primarily from the Silurian rocks of upstate New York and southern Ontario, Canada.
He donated more than 11,000 ...
STEM Career Days boost high school students’ career aspirations in STEM fields, MU study finds
2023-11-06
COLUMBIA, Mo. – A new study at the University of Missouri — in partnership with Harvard-Smithsonian researchers — shows that when colleges host ‘STEM Career Days,’ the students who attend are far more likely to pursue a career in a STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering and Math) related field.
The findings not only highlight the benefits of college recruiters introducing high school students to STEM-related opportunities, but they can also help increase and diversify ...
Ochsner Health and Chevron partner for a third consecutive year to offer smoking cessation and education program
2023-11-06
NEW ORLEANS, La. – Chevron and Ochsner Health continue to offer their Lung Cancer Awareness, Education and Prevention Program for a third consecutive year thanks to a $50,000 donation from Chevron. The program will be offered in Jefferson Parish for the first time and continue to reach community members in St. Tammany, East Baton Rouge, West Baton Rouge, Ascension, St. Charles, Terrebonne, and Lafourche parishes.
Ochsner Health and Chevron formed a key partnership for the Lung Cancer Awareness, Education and Prevention Program to improve lung health and overall wellness. ...
Patients more likely to lose weight if physicians offer advice using optimistic tone
2023-11-06
Embargoed for release until 5:00 p.m. ET on Monday 6 November 2023
Annals of Internal Medicine Tip Sheet
@Annalsofim
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not only on their own behalf, but also on behalf of the organization they represent.
----------------------------
1. Patients more likely to lose weight if physicians offer advice using optimistic tone
Abstract: ...
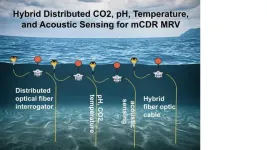
Deploying sensor nets to measure ocean CO2 and pH from the surface to the depths
2023-11-06
Researchers at the University of Pittsburgh Swanson School of Engineering, in collaboration with the National Energy Technology Laboratory, are among 11 projects in eight states selected to receive a combined $36 million to accelerate the development of marine carbon dioxide removal (mCDR) capture and storage technologies.
The funding from the U.S. Department of Energy Advanced Research Projects Agency-Energy (ARPA-E) is part of the ARPA-E Sensing Exports of Anthropogenic Carbon Through Ocean ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
300 million years of hidden genetic instructions shaping plant evolution revealed
High-fat diets cause gut bacteria to enter brain, Emory study finds
Teens and young adults with ADHD and substance use disorder face treatment gap
Instead of tracking wolves to prey, ravens remember — and revisit — common kill sites
Ravens don’t follow wolves to dinner – they remember where the food is
Mapping the lifelong behavior of killifish reveals an architecture of vertebrate aging
Designing for hard and brittle lithium needles may lead to safer batteries
Inside the brains of seals and sea lions with complex vocal behavior learning
Watching a lifetime in motion reveals the architecture of aging
Rapid evolution can ‘rescue’ species from climate change
Molecular garbage on tumors makes easy target for antibody drugs
New strategy intercepts pancreatic cancer by eliminating microscopic lesions before they become cancer
Embryogenesis in 4D: a developmental atlas for genes and cells
CNIO research links fertility with immune cells in the brain
Why do lithium-ion batteries fail? Scientists find clues in microscopic metal 'thorns'
Surface treatment of wood may keep harmful bacteria at bay
Carsten Bönnemann, MD, joins St. Jude to expand research on pediatric catastrophic neurological disorders
Women use professional and social networks to push past the glass ceiling
Trial finds vitamin D supplements don’t reduce covid severity but could reduce long COVID risk
Personalized support program improves smoking cessation for cervical cancer survivors
Adverse childhood experiences and treatment-resistant depression
Psilocybin trends in states that decriminalized use
New data signals high demand in aesthetic surgery in southern, rural U.S. despite access issues
$3.4 million grant to improve weight-management programs
Higher burnout rates among physicians who treat sickle cell disease
Wetlands in Brazil’s Cerrado are carbon-storage powerhouses
Brain diseases: certain neurons are especially susceptible to ALS and FTD
Father’s tobacco use may raise children’s diabetes risk
Structured exercise programs may help combat “chemo brain” according to new study in JNCCN
The ‘croak’ conundrum: Parasites complicate love signals in frogs
[Press-News.org] Contraceptive pills might impair fear-regulating regions in women’s brainsScientists find the use of oral contraceptives may affect fear-related brain morphology, knowledge that could deepen understanding of fear-related mechanisms that primarily affect women