(Press-News.org) Scientists using NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope just made a breakthrough discovery in revealing how planets are made. By observing water vapor in protoplanetary disks, Webb confirmed a physical process involving the drifting of ice-coated solids from the outer regions of the disk into the rocky-planet zone.
Theories have long proposed that icy pebbles forming in the cold, outer regions of protoplanetary disks — the same area where comets originate in our solar system — should be the fundamental seeds of planet formation. The main requirement of these theories is that pebbles should drift inward toward the star due to friction in the gaseous disk, delivering both solids and water to planets.
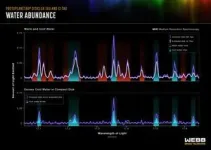
A fundamental prediction of this theory is that as icy pebbles enter into the warmer region within the “snowline” — where ice transitions to vapor — they should release large amounts of cold water vapor. This is exactly what Webb observed.
“Webb finally revealed the connection between water vapor in the inner disk and the drift of icy pebbles from the outer disk,” said principal investigator Andrea Banzatti of Texas State University, San Marcos, Texas. “This finding opens up exciting prospects for studying rocky planet formation with Webb!”
“In the past, we had this very static picture of planet formation, almost like there were these isolated zones that planets formed out of,” explained team member Colette Salyk of Vassar College in Poughkeepsie, New York. “Now we actually have evidence that these zones can interact with each other. It’s also something that is proposed to have happened in our solar system.”
Harnessing the Power of Webb
The researchers used Webb’s MIRI (the Mid-Infrared Instrument) to study four disks — two compact and two extended — around Sun-like stars. All four of these stars are estimated to be between 2 and 3 million years old, just newborns in cosmic time.
The two compact disks are expected to experience efficient pebble drift, delivering pebbles to well within a distance equivalent to Neptune’s orbit. In contrast, the extended disks are expected to have their pebbles retained in multiple rings as far out as six times the orbit of Neptune.
The Webb observations were designed to determine whether compact disks have a higher water abundance in their inner, rocky planet region, as expected if pebble drift is more efficient and is delivering lots of solid mass and water to inner planets. The team chose to use MIRI’s MRS (the Medium-Resolution Spectrometer) because it is sensitive to water vapor in disks.
The results confirmed expectations by revealing excess cool water in the compact disks, compared with the large disks.
As the pebbles drift, any time they encounter a pressure bump — an increase in pressure — they tend to collect there. These pressure traps don’t necessarily shut down pebble drift, but they do impede it. This is what appears to be happening in the large disks with rings and gaps.
Current research proposes that large planets may cause rings of increased pressure, where pebbles tend to collect. This also could have been a role of Jupiter in our solar system — inhibiting pebbles and water delivery to our small, inner, and relatively water-poor rocky planets.
Solving the Riddle
When the data first came in, the results were puzzling to the research team. “For two months, we were stuck on these preliminary results that were telling us that the compact disks had colder water, and the large disks had hotter water overall,” remembered Banzatti. “This made no sense, because we had selected a sample of stars with very similar temperatures.”
Only when Banzatti overlaid the data from the compact disks onto the data from the large disks did the answer clearly emerge: the compact disks have extra cool water just inside the snowline, at about ten times closer than the orbit of Neptune.
“Now we finally see unambiguously that it is the colder water that has an excess,” said Banzatti. “This is unprecedented and entirely due to Webb’s higher resolving power!”
The team’s results appear in the Nov. 8 edition of The Astrophysical Journal Letters.
The James Webb Space Telescope is the world’s premier space science observatory. Webb is solving mysteries in our solar system, looking beyond to distant worlds around other stars, and probing the mysterious structures and origins of our universe and our place in it. Webb is an international program led by NASA with its partners, ESA (European Space Agency) and the Canadian Space Agency.
END
NASA’s Webb findings support long-proposed process of planet formation
2023-11-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
UTIA faculty member serves as editor of the Journal of Food Distribution Research
2023-11-08
Carlos Trejo-Pech, an associate professor in the Department of Agricultural and Resource Economics at the University of Tennessee Institute of Agriculture, is a newly appointed editor of the Journal of Food Distribution Research.
“It is a great honor and big responsibility to serve as a journal editor of a publication outlet in the agricultural economics and agribusiness discipline,” said Trejo-Pech. “We, the editors, are committed to disseminating the results of high-quality research.”
The journal was established in 1969 under the auspices of the Food Distribution Research Society, the only body of scholars and practitioners in the United States dedicated ...
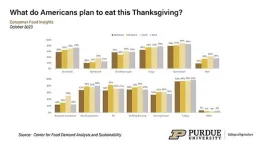
October Consumer Food Insights Report highlights thanksgiving meal plans
2023-11-08
October Consumer Food Insights Report highlights Thanksgiving meal plans
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. – Nearly eight in 10 Americans will celebrate the upcoming Thanksgiving holiday with a special meal, according to the October 2023 Consumer Food Insights Report.
The survey-based report out of Purdue University’s Center for Food Demand Analysis and Sustainabilityassesses food spending, consumer satisfaction and values, support of agricultural and food policies, and trust in information sources. Purdue ...
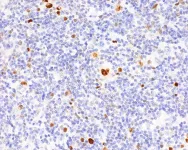
Hodgkin’s lymphoma: Small change, big effect
2023-11-08
Hodgkin’s lymphoma is one of the most common types of lymphoma in young adults. It is characterized by the presence of enlarged B lymphocytes, which are unusual in that they bear on their surface the identifying markers of many other immune cells – such as those found on phagocytes, dendritic cells, or T cells. Now, a team led by Stephan Mathas from the Experimental and Clinical Research Center (ECRC) has explained how these changes take place in the cells and what impact they have. The ECRC is a joint institution of the Max Delbrück Center and Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin.
“Many different ...
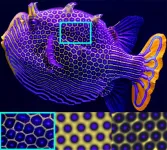
How animals get their stripes and spots
2023-11-08
Nature has no shortage of patterns, from spots on leopards to stripes on zebras and hexagons on boxfish. But a full explanation for how these patterns form has remained elusive.
Now engineers at the University of Colorado Boulder have shown that the same physical process that helps remove dirt from laundry could play a role in how tropical fish get their colorful stripes and spots. Their findings were published Nov. 8 in the journal Science Advances.
“Many biological questions are fundamentally ...
A fifth of European Red List flora and fauna species may be at risk of extinction
2023-11-08
A new analysis of 14,669 threatened species of plants and animals found in Europe reveals that about one fifth face the risk of extinction, and that agricultural land-use change poses a significant threat to these species. Axel Hochkirch of the Musée National d’Histoire Naturelle, Luxembourg, and colleagues present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on November 8, 2023.
The variety of species of living things—biodiversity—is declining around the world, as more and more species face the risk of extinction. Many efforts, including some by governments and nonprofit organizations, aim to reduce the loss ...
Head lice evolution mirrors human migration and colonization in the Americas
2023-11-08
A new analysis of lice genetic diversity suggests that lice came to the Americas twice – once during the first wave of human migration across the Bering Strait, and again during European colonization. Marina Ascunce, currently at the USDA-ARS, and colleagues, report these findings in a new study published November 8 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE.
The human louse is a wingless, blood-sucking parasite that lives its entire life on its host. It is one of the oldest known parasites to live on humans, and the two species have coevolved ...
A digital detox may not improve wellbeing: social media users who reduced their use for a week saw decreases in positive emotions as well as in negative ones
2023-11-08
A digital detox may not improve wellbeing: social media users who reduced their use for a week saw decreases in positive emotions as well as in negative ones
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0293467
Article Title: Restricting social networking site use for one week produces varied effects on mood but does not increase explicit or implicit desires to use SNSs: Findings from an ecological momentary assessment study
Author Countries: UK
Funding: This work was supported by the Economic and Social Research ...
Financial traders may seek better sleep by self-medicating with caffeine and alcohol to balance the effects of the stimulant and the sedative, per micro-longitudinal study
2023-11-08
Financial traders may seek better sleep by self-medicating with caffeine and alcohol to balance the effects of the stimulant and the sedative, per micro-longitudinal study
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0291675
Article Title: Sleep, alcohol, and caffeine in financial traders
Author Countries: USA
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work. END ...
Autism brain states hold the key to unlocking childhood memories
2023-11-08
Neuroscientists have discovered a fascinating connection between the retention of early life memories and brain developmental trajectories associated with autism [Wednesday 8th November 2023].
Most of us remember little of our experiences from before two years of age. This form of memory loss, termed “infantile amnesia” refers to the seemingly complete loss of episodic and autobiographical memories formed during early life. The research team at Trinity College Dublin investigated how infantile amnesia is affected by forms of autism.
The maternal immune response, sparked into life in response to infection during pregnancy, ...
Artificial bladders shine light on bugs that cause urinary tract infections
2023-11-08
The research, published today in Science Advances, is the first to use a sophisticated human tissue model to explore the interaction between host and pathogen for six common species that cause urinary tract infections. The findings suggest that the ‘one size fits all’ approach to diagnosis and treatment currently used in most healthcare systems is inadequate.
Urinary tract infection (UTI) is a growing problem, with around 400 million global cases per year and an estimated 250,000 UTI-related deaths associated with antimicrobial resistance ...