(Press-News.org) The 11 young firefighters went through a rigorous training exercise, carrying up to 40 pounds of gear over hilly terrain during a 45-minute training exercise in the California sun. Gloves, helmets, flashlights, goggles, and more weighted them down as they sprinted through the countryside wearing fire-resistant clothing to show they were ready to serve as wildland firefighters.
When the training was over, they immediately went to the medical tent—not to rest and recover but to give samples of their blood, saliva, and urine for analysis by a team of scientists equipped with needles, test tubes, cold packs, and the gear of their own trade.
Then, the scientists from the Department of Energy’s Pacific Northwest National Laboratory (PNNL) analyzed more than 4,700 molecules—proteins, lipids, and metabolites—from each of the firefighters, looking to understand what happens when the body undergoes intense physical exercise. Measuring and interpreting the data from thousands of such measurements is a specialty of PNNL scientists who explore issues related to climate science and human health by analyzing millions of sensitive measurements using mass spectrometry each year.
For this study, the intent was to increase safety for first responders and others.
“Heat stress can be life threatening,” said Kristin Burnum-Johnson, a corresponding author of the study. “We wanted to take an in-depth look at what’s happening in the body and see if we’re able to detect danger from exhaustion in its earliest stages. Perhaps we can reduce the risk of strenuous exercise for first responders, athletes, and members of the military.”
As expected, the team detected hundreds of molecular changes in the firefighters. The differences before and after exercise underscored the body’s efforts at tissue damage and repair, maintenance of fluid balance, efforts to keep up with increased energy and oxygen demand, and the body’s attempts to repair and regenerate its proteins and other important substances.
But in the saliva, the team found some unexpected results. There was a change in the microbial mix of the mouth—the oral microbiome—showing that the body was increasingly on the lookout for bacterial invaders. Scientists also saw a decrease in signaling molecules important for inflammation and for fighting off viral infections.
A decrease in inflammation makes sense for people exercising vigorously; less inflammation allows people to breathe in air more quickly, meeting the body’s eager demand for more oxygen. Having fewer inflammatory signals in the respiratory system helps the body improve respiration and blood flow.
Less inflammation, better breathing
But less inflammation leaves the body more vulnerable to viral respiratory infection—which is exactly what other scientists have noted in elite athletes and others who exercise vigorously. Some studies have shown that a person is up to twice as likely to come down with a viral respiratory infection in the days after an especially energetic workout.
“People who are very fit might be more prone to viral respiratory infection immediately after vigorous exercise. Having less inflammatory activity to fight off an infection could be one cause,” said Ernesto Nakayasu, a corresponding author of the paper. He notes that the work provides a molecular basis for what clinicians have noticed in their patients who do strenuous workouts.
The team hopes that the findings will help explain why come people are more vulnerable to respiratory infection after a workout.
The research was published Oct. 18 in Military Medical Research.
In addition to Nakayasu and Burnum-Johnson, PNNL authors included Marina A. Gritsenko, Young-Mo Kim, Jennifer E. Kyle, Kelly G. Stratton, Carrie D. Nicora, Nathalie Munoz, Yuqian Gao, Karl K. Weitz, Vanessa L. Paurus, Kent J. Bloodsworth, Kelsey A. Allen, Lisa M. Bramer, Fernando Montes, Kathleen A. Clark, Grant Tietje, and Justin Teeguarden.
The work was funded by PNNL. Some of the mass spectrometry measurements were done at the Environmental Molecular Sciences Laboratory, a Department of Energy Office of Science user facility at PNNL.
# # #
END
The reactivation of patterns of neuronal activity based on experience is crucial for learning and memory, but these patterns and the associated brain waves vary widely and are difficult to classify. Such events, dubbed ripples, are characteristic of the hippocampus, a brain region responsible for memory. Until now, the most common way to study ripples was using frequency analysis, but a project led by the Spanish National Research Council (CSIC) has proposed a new classification strategy.
Using data science tools, a research group from the Instituto Cajal (IC-CSIC) headed by Liset M. de la Prida has managed to figure out the temporal structure of hippocampal ripples. The scientists ...
Francis Crick Institute press release
Under strict embargo: 16:00hrs GMT Thursday 9 November 2023
Peer reviewed
Experimental study
People and animals
Reducing vitamin B5 slows breast cancer growth in mice
A group of researchers led by the Francis Crick Institute, working with the National Physical Laboratory (NPL) and Imperial College London, have discovered that breast cancer cells expressing a cancer-driving gene heavily rely on vitamin B5 to grow and survive. The researchers are part of Cancer Grand Challenges team Rosetta, funded by Cancer Research UK.
In their research published today in Nature Metabolism, the team studied the metabolic effects of one of the major cancer-driving ...
About The Study: There was a favorable evolution in smell and taste function throughout the observation period of this study, with taste dysfunction showing lower frequency and faster recovery compared with smell dysfunction in this analysis that included 88 cases and 88 controls. Recovery from smell dysfunction continued over the 3-year study period. At the 3-year study endpoint, smell dysfunction was comparable between both groups. Patients with post–COVID-19 condition exhibiting chemosensory alterations should be reassured that a recovery of smell function appears to continue over three years ...
About The Study: In this study including 3.5 million patients diagnosed with cancer, a significant deficit was noted in the number of cancer treatments provided in the first year of the COVID-19 pandemic in the U.S. Data indicated that this deficit in the number of cancer treatments provided was associated with decreases in the number of cancer diagnoses, not changes in treatment strategies.
Authors: Leticia M. Nogueira, Ph.D., M.P.H., of the American Cancer Society in Kennesaw, Georgia, is the corresponding author.
To access ...
Roughly two decades ago, a community-wide reckoning emerged concerning the credibility of published literature in the social-behavioral sciences, especially psychology. Several large scale studies attempted to reproduce previously published findings to no avail or to a much lesser magnitude, sending the credibility of the findings — and future studies in social-behavioral sciences — into question.
A handful of top experts in the field, however, set out to ...
A globe-spanning scientific team has compiled the most comprehensive list of genetic variants associated with prostate cancer risk — 451 in all — through a whole-genome analysis that ranks as the largest and most diverse investigation into prostate cancer genetics yet. The research, led by the USC Center for Genetic Epidemiology, the Keck School of Medicine of USC and USC Norris Comprehensive Cancer Center, and in the United Kingdom by The Institute of Cancer Research, London, included major increases in representation ...
The gene SYNGAP1, the variants of which are top risk factors for Autism Apectrum Disorder (ASD), has previously unappreciated effects on the developing brain, according to a new study published in Nature Neuroscience. The study shows how disease-causing variants of SYNGAP1, thought primarily to affect synapses between mature neurons, could disrupt early development in a key region of the brain known as the cortex.
“Our findings reframe our understanding ...
New research finds that almost half of people who use illicit drugs in rural areas have been recently incarcerated.
Results from a survey of almost 3,000 people in eight rural areas nationwide who report using illicit drugs published today in the journal JAMA Network Open. The study found that 42% had been incarcerated, either in prison or local jails, in the preceding six months.
The study was conducted by researchers at Oregon Health & Science University and institutions across 10 states.
The findings suggest a prime ...
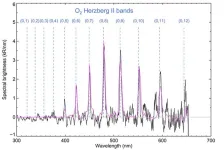
An international team led by scientists from the University of Liège has observed, for the first time in the visible range, a glow on the night side of the planet Mars. These new observations provide a better understanding of the dynamics of the upper atmosphere of the Red Planet and its variations throughout the year.
A scientific team led by researchers from the Laboratory for Planetary and Atmospheric Physics (LPAP) at the University of Liège (BE) has just observed, for the first time, lights in the night sky over Mars using the UVIS-NOMAD instrument on ...
The boom in phones, laptops and other personal devices over the last few decades has been made possible by the lithium-ion (Li-ion) battery, but as climate change demands more powerful batteries for electric vehicles and grid-scale renewable storage, lithium-ion technology might not be enough.
Lithium-metal batteries (LMBs) have theoretical capacities an order of magnitude greater than lithium-ion, but a more literal boom has stymied research for decades.
“A compounding challenge that further doomed the first wave of LMB commercialization in the late 1980s was their propensity to ...