Finding your niche: A synthetic cancer stem cell microenvironment
2023-11-09
(Press-News.org)
Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) report the construction of a synthetic polymer biomaterial that successfully recapitulates the pancreatic adenocarcinoma microenvironment and could be used to identify novel treatment targets
Tokyo, Japan – One of the biggest challenges in biomedical research is finding a way to capture the complexity of the human body in laboratory-based techniques, to enable them to be investigated accurately. Now, researchers from Japan report an approach for precisely imitating a key feature of aggressive cancers in the laboratory.
In a study published recently in Inflammation and Regeneration, researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) have revealed that a synthetic scaffold mimicking the cancer microenvironment could be a powerful tool for understanding cancer progression and treatment.
Pancreatic adenocarcinoma is a particularly deadly cancer, in part because it is difficult to detect in the early stages, and in part because of the presence of persistent cancer stem cells (CSCs), which are responsible for metastasis, resistance to treatment, and relapse. These CSCs exist within a specialized cancer microenvironment called a niche, and disrupting this CSC niche could impair cancer progression.
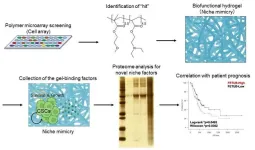
“CSCs communicate with their niche through various cues, such as biological factors, physicochemical factors, and inflammatory factors,” says lead author of the study Yoshitaka Murota. “The complexity of the CSC niche makes it challenging to identify useful treatment targets, particularly in patient samples, so we sought to design a laboratory-based artificial niche that would recapitulate this intricate microenvironment.”
To do this, the researchers applied pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells to an extensive array of synthetic biofunctional materials. They then assessed cellular growth on each of the candidate materials to select the one that most strongly supported growth of CSCs, but not non-CSCs.
“The results were unequivocal,” explains Kouichi Tabu, senior author. “When we embedded the selected polymer in hydrogel to create a niche-mimicking scaffold, it specifically supported substantial growth and proliferation of human pancreatic CSCs.”
Next, the researchers analyzed the serum proteins that were enriched on the hydrogel where the pancreatic cells were growing and compared them to factors known to promote pancreatic cancer. The analysis showed that the niche-mimicking biomaterial trapped multiple serum factors, one of which is closely associated with poor prognosis in patients with pancreatic adenocarcinoma.
“Taken together, our findings show that the polymeric hydrogel that we fabricated accurately mimics the pancreatic CSC niche and can be used to identify therapeutic targets that correlate significantly with patient survival,” says Murota.
Given that CSCs and the cancer microenvironment are virtually universal features of cancer, it is likely that the findings from this study can be applied to other cancer types. Using this type of synthetic polymer material to create artificial CSC niches may help identify important cancer biomarkers and treatment targets in the future.
###
The article, “A niche‑mimicking polymer hydrogel‑based approach to identify molecular targets for tackling human pancreatic cancer stem cells,” was published in Inflammation and Regeneration at DOI: 10.1186/s41232-023-00296-0
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-11-09
The 11 young firefighters went through a rigorous training exercise, carrying up to 40 pounds of gear over hilly terrain during a 45-minute training exercise in the California sun. Gloves, helmets, flashlights, goggles, and more weighted them down as they sprinted through the countryside wearing fire-resistant clothing to show they were ready to serve as wildland firefighters.
When the training was over, they immediately went to the medical tent—not to rest and recover but to give samples of their blood, ...
2023-11-09
The reactivation of patterns of neuronal activity based on experience is crucial for learning and memory, but these patterns and the associated brain waves vary widely and are difficult to classify. Such events, dubbed ripples, are characteristic of the hippocampus, a brain region responsible for memory. Until now, the most common way to study ripples was using frequency analysis, but a project led by the Spanish National Research Council (CSIC) has proposed a new classification strategy.
Using data science tools, a research group from the Instituto Cajal (IC-CSIC) headed by Liset M. de la Prida has managed to figure out the temporal structure of hippocampal ripples. The scientists ...
2023-11-09
Francis Crick Institute press release
Under strict embargo: 16:00hrs GMT Thursday 9 November 2023
Peer reviewed
Experimental study
People and animals
Reducing vitamin B5 slows breast cancer growth in mice
A group of researchers led by the Francis Crick Institute, working with the National Physical Laboratory (NPL) and Imperial College London, have discovered that breast cancer cells expressing a cancer-driving gene heavily rely on vitamin B5 to grow and survive. The researchers are part of Cancer Grand Challenges team Rosetta, funded by Cancer Research UK.
In their research published today in Nature Metabolism, the team studied the metabolic effects of one of the major cancer-driving ...
2023-11-09
About The Study: There was a favorable evolution in smell and taste function throughout the observation period of this study, with taste dysfunction showing lower frequency and faster recovery compared with smell dysfunction in this analysis that included 88 cases and 88 controls. Recovery from smell dysfunction continued over the 3-year study period. At the 3-year study endpoint, smell dysfunction was comparable between both groups. Patients with post–COVID-19 condition exhibiting chemosensory alterations should be reassured that a recovery of smell function appears to continue over three years ...
2023-11-09
About The Study: In this study including 3.5 million patients diagnosed with cancer, a significant deficit was noted in the number of cancer treatments provided in the first year of the COVID-19 pandemic in the U.S. Data indicated that this deficit in the number of cancer treatments provided was associated with decreases in the number of cancer diagnoses, not changes in treatment strategies.
Authors: Leticia M. Nogueira, Ph.D., M.P.H., of the American Cancer Society in Kennesaw, Georgia, is the corresponding author.
To access ...
2023-11-09
Roughly two decades ago, a community-wide reckoning emerged concerning the credibility of published literature in the social-behavioral sciences, especially psychology. Several large scale studies attempted to reproduce previously published findings to no avail or to a much lesser magnitude, sending the credibility of the findings — and future studies in social-behavioral sciences — into question.
A handful of top experts in the field, however, set out to ...
2023-11-09
A globe-spanning scientific team has compiled the most comprehensive list of genetic variants associated with prostate cancer risk — 451 in all — through a whole-genome analysis that ranks as the largest and most diverse investigation into prostate cancer genetics yet. The research, led by the USC Center for Genetic Epidemiology, the Keck School of Medicine of USC and USC Norris Comprehensive Cancer Center, and in the United Kingdom by The Institute of Cancer Research, London, included major increases in representation ...
2023-11-09
The gene SYNGAP1, the variants of which are top risk factors for Autism Apectrum Disorder (ASD), has previously unappreciated effects on the developing brain, according to a new study published in Nature Neuroscience. The study shows how disease-causing variants of SYNGAP1, thought primarily to affect synapses between mature neurons, could disrupt early development in a key region of the brain known as the cortex.
“Our findings reframe our understanding ...
2023-11-09
New research finds that almost half of people who use illicit drugs in rural areas have been recently incarcerated.
Results from a survey of almost 3,000 people in eight rural areas nationwide who report using illicit drugs published today in the journal JAMA Network Open. The study found that 42% had been incarcerated, either in prison or local jails, in the preceding six months.
The study was conducted by researchers at Oregon Health & Science University and institutions across 10 states.
The findings suggest a prime ...
2023-11-09
An international team led by scientists from the University of Liège has observed, for the first time in the visible range, a glow on the night side of the planet Mars. These new observations provide a better understanding of the dynamics of the upper atmosphere of the Red Planet and its variations throughout the year.
A scientific team led by researchers from the Laboratory for Planetary and Atmospheric Physics (LPAP) at the University of Liège (BE) has just observed, for the first time, lights in the night sky over Mars using the UVIS-NOMAD instrument on ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Finding your niche: A synthetic cancer stem cell microenvironment