New work sheds light on inner working of cells
2023-11-10
(Press-News.org)
CÚRAM researchers at University of Galway, together with colleagues at the Centre for Molecular Nanometrology at University of Strathclyde have published work unveiling the inner workings of cells.
Published recently in the German scientific journal Angewandte Chemie, the work provides a deeper understanding of the way components within cells are interconnected. This research has been on the agenda of scientists worldwide for many years, and has yielded plenty of useful information on how certain diseases behave.
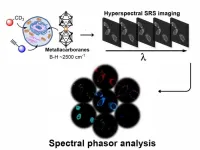
Through cellular visualisation using SRS microscopy, the team have addressed the challenge of attaining clear images of individual processes. Both time consuming and difficult to analyse due to combinations of poor image quality, previous efforts in multiplex optical detection in live cells has been limitated in how many processes can be tracked and having to physically alter the cell to get a clear image.
The presented work utilises dyes which make no adjustment to the cell itself, is completed within minutes and tracks up to 9 different aspects of the cell structure simultaneously. This represents a significant advancement in the field, improving on 7 trackable processes in previous work.
Lead author Dr Pau Farras, Associate Professor in Inorganic Chemistry in the School of Biological and Chemical Sciences, at the University of Galway and Principal Investigator at CÚRAM SFI Research Centre for Medical Devices, said: “This work will provide scientists with a tool to garner lots of information out of cells within a short space of time. This has the potential to assist in understanding how current drugs developed for a range of applications are fighting disease and even provide hints on how to improve treatments.”
The paper was published by Angewandte Chemie and can be read in full here – https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202311530
Ends
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-11-10
Actuators, which convert electrical energy into motion or force, play a pivotal role in daily life, albeit often going unnoticed. Soft material-based actuators, in particular, have gained scientific attention in recent years due to their lightweight, quiet operation, and biodegradability. A straightforward approach to creating soft actuators involves employing multi-material structures, such as "pockets" made of flexible plastic films filled with oils and coated with conductive plastics. When subjected to electrical activation, the film displaces the fluid and contracts the pocket, similar to a biological muscle. This system ...
2023-11-10
DUARTE, Calif., Nov. 10, 2023 – In a breakthrough for human milk science, researchers at City of Hope, Los Angeles, have dosed the first patient in a Phase 2a clinical trial evaluating a novel therapy for blood cancer patients undergoing allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. The investigational treatment, PBCLN-010 in combination with PBCLN-014, combines human milk sugars with a strain of bacteria found in the gut of nursing infants.
“Previous clinical trials of PBCLN-010 + PBCLN-014 have shown that it can safely and predictably control the gut microbiome ...
2023-11-10
With an eye toward a decade ahead that promises change, opportunity, and challenge, the University of Virginia on Friday launched its Futures Initiative to help plan for the next 10 years in higher education.
Over the next year, a group of thought leaders from across the University, known as the Futures Initiative Group, will examine the current drivers of change in academia, such as artificial intelligence and large language models like ChatGPT, while also looking ahead to the eventual impact of sensor technology, virtual classrooms, the Internet of Things, and myriad other technological changes.
The goal of the initiative—which was announced at Datapalooza 2023, an annual event ...
2023-11-10
INDIANAPOLIS -- Regenstrief Institute, the International Medical Informatics Association (IMIA), the International Academy of Health Sciences Informatics (IAHSI) and the American Medical Informatics Association (AMIA) are hosting a mini-summit at the AMIA 2023 Annual Symposium to address how informatics can help resolve health issues caused by climate change. The event will bring together national and international experts to form an informatics infrastructure that will highlight and bring exposure to climate change's effects on health.
The event Mini-Summit 2023 -- Climate and health: How can informatics help? was planned because of the growing awareness around ...
2023-11-10
HOUSTON ― Howard Meyers, of Dallas, Texas, a member of The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center Board of Visitors (BOV), has committed $25 million to The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center to establish the Meyers Institute for Oncology Nursing. The first of its kind, the Meyers Institute for Oncology Nursing will support and develop nurses throughout their careers by providing educational, professional and wellness-based resources tailored to cancer care nurses and nurse scientists. This ...
2023-11-10
Some individuals with anti-Ro/SSA antibodies (anti–Sjögren's-syndrome–related antigen A autoantibodies, also called anti-Ro antibodies) have autoimmune diseases such as lupus or Sjögren's syndrome, but many have no symptoms. A clinical trial published in Arthritis & Rheumatology found that high levels of these antibodies in pregnant women are associated with fetal atrioventricular block (AVB), which occurs when inflammation and subsequent scarring prevent electric signals from the heart’s atria from reaching the ventricles. The disease ...
2023-11-10
In a post hoc analysis of the phase 2 NOBILITY trial, researchers found that treatment with obinutuzumab—an antibody that targets a protein expressed on certain immune cells—was superior to placebo for preserving kidney function and preventing flares in patients with lupus nephritis, a kidney condition associated with the autoimmune disease lupus.
In the analysis, which is published in Arthritis & Rheumatology, compared with standard-of-care treatment alone, the addition of obinutuzumab to lupus nephritis treatment reduced the risk of developing a composite outcome of death, fall in kidney function, or treatment failure by 60%. Adding obinutuzumab ...
2023-11-10
Statement Highlights:
The new American Heart Association PREVENTTM risk calculator estimates the 10- and 30-year risk of total cardiovascular disease for people aged 30 years and older.
The calculator estimates the risk of heart attack, stroke and — for the first time — heart failure. The equations are sex-specific and race-free, acknowledging that race is not a biological factor, and can include an index of social determinants of health.
This is the first risk calculator that combines measures of cardiovascular, kidney ...
2023-11-10
Physical fitness since childhood is associated with cerebellar grey matter volume in adolescents. According to a recent study conducted at the University of Jyväskylä and the University of Eastern Finland, those who were stronger, faster and more agile, in other words, had better neuromuscular fitness since childhood, had larger Crus I grey matter volume in adolescence.
Despite the importance of the developing cerebellum on cognition and learning, the associations between physical fitness and cerebellar volume in adolescents have remained unclear. This study examined the associations ...
2023-11-10
When scientists examined pellets from recycled plastic collected in 13 countries they found hundreds of toxic chemicals, including pesticides and pharmaceuticals.
The results are published in a study led by scientists at the University of Gothenburg.
Because of this, the scientists judge recycled plastics unfit for most purposes and a hinder in the attempts to create a circular economy.
Delegates, scientists and health and environmental advocates from around the world are traveling to Nairobi, Kenya for next week’s meeting of the third session of the Plastics Treaty Intergovernmental Negotiating ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] New work sheds light on inner working of cells




