(Press-News.org) New York, NY (November 13, 2023)—Researchers at the Mount Sinai Center for Transformative Disease Modeling have released a groundbreaking study identifying 4,749 key gene clusters, termed “prognostic modules,” that significantly influence the progression of 32 different types of cancer. The study, published in Genome Research, serves as a comprehensive resource and lays the foundation for the development of next-generation cancer treatments and diagnostic markers.
Despite significant progress in cancer research, understanding the disease's genetic intricacies remains challenging. Previous research often focused on isolated gene functions in specific cancer types.
"We aimed to fill this knowledge gap by providing a comprehensive analysis of gene-gene interactions across various forms of cancer," said Bin Zhang, PhD, Willard T.C. Johnson Research Professor of Neurogenetics and Director of the Mount Sinai Center for Transformative Disease Modeling.
The team used a multi-omics approach, incorporating genomic, transcriptomic, and epigenomic data in their analysis. They employed advanced systems biology approaches to analyze more than 10,000 patient samples from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA), one of the most comprehensive public cancer databases, and used rigorous network methods to identify and validate the gene clusters that have a significant impact on cancer prognosis.
"The implications of our findings are profound. We have identified 4,749 distinct co-regulated gene modules that play a pivotal role in cancer progression," explained Dr. Zhang.
Peng Xu, PhD, Instructor of Genetics and Genomic Sciences and co-senior author, added: "Our study goes beyond merely identifying these modules. It also elucidates the multi-scale regulations that govern their functions."
In simpler terms, the study has identified critical genes and their complex relationships that either halt or promote cancer progression. This new understanding opens the door for targeted research and development of future treatments and diagnostic methods for cancers.
While this study represents a significant step forward, it is not an immediate cure for cancer. However, it serves as a crucial foundation for developing targeted therapies that could lead to improved patient outcomes. "Our findings offer fertile ground for the next wave of cancer research and treatment strategies," said Dr. Zhang.
The paper is titled “Multiscale network modeling reveals the gene regulatory landscape driving cancer prognosis in 32 cancer types.”
-####-
About the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai
The Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai is internationally renowned for its outstanding research, educational, and clinical care programs. It is the sole academic partner for the eight- member hospitals* of the Mount Sinai Health System, one of the largest academic health systems in the United States, providing care to a large and diverse patient population.
Ranked 14th nationwide in National Institutes of Health (NIH) funding and among the 99th percentile in research dollars per investigator according to the Association of American Medical Colleges, Icahn Mount Sinai has a talented, productive, and successful faculty. More than 3,000 full-time scientists, educators, and clinicians work within and across 44 academic departments and 36 multidisciplinary institutes, a structure that facilitates tremendous collaboration and synergy. Our emphasis on translational research and therapeutics is evident in such diverse areas as genomics/big data, virology, neuroscience, cardiology, geriatrics, as well as gastrointestinal and liver diseases.
Icahn Mount Sinai offers highly competitive MD, PhD, and Master’s degree programs, with current enrollment of approximately 1,300 students. It has the largest graduate medical education program in the country, with more than 2,000 clinical residents and fellows training throughout the Health System. In addition, more than 550 postdoctoral research fellows are in training within the Health System.
A culture of innovation and discovery permeates every Icahn Mount Sinai program. Mount Sinai’s technology transfer office, one of the largest in the country, partners with faculty and trainees to pursue optimal commercialization of intellectual property to ensure that Mount Sinai discoveries and innovations translate into healthcare products and services that benefit the public.
Icahn Mount Sinai’s commitment to breakthrough science and clinical care is enhanced by academic affiliations that supplement and complement the School’s programs.
Through the Mount Sinai Innovation Partners (MSIP), the Health System facilitates the real-world application and commercialization of medical breakthroughs made at Mount Sinai. Additionally, MSIP develops research partnerships with industry leaders such as Merck & Co., AstraZeneca, Novo Nordisk, and others.
The Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai is located in New York City on the border between the Upper East Side and East Harlem, and classroom teaching takes place on a campus facing Central Park. Icahn Mount Sinai’s location offers many opportunities to interact with and care for diverse communities. Learning extends well beyond the borders of our physical campus, to the eight hospitals of the Mount Sinai Health System, our academic affiliates, and globally.
-------------------------------------------------------
* Mount Sinai Health System member hospitals: The Mount Sinai Hospital; Mount Sinai Beth Israel; Mount Sinai Brooklyn; Mount Sinai Morningside; Mount Sinai Queens; Mount Sinai South Nassau; Mount Sinai West; and New York Eye and Ear Infirmary of Mount Sinai.
END
Ammonia, a main component of many fertilizers, could play a key role in a carbon-free fuel system as a convenient way to transport and store clean hydrogen. The chemical, made of hydrogen and nitrogen (NH3), can also itself be burned as a zero-carbon fuel. However, new research led by Princeton University illustrates that even though it may not be a source of carbon pollution, ammonia’s widespread use in the energy sector could pose a grave risk to the nitrogen cycle and climate without proper engineering precautions.
Publishing their findings in PNAS, the interdisciplinary team of 12 researchers found that a well-engineered ammonia economy could help the world achieve ...
November 13, 2023-- There is no longer any question of how to prevent high-intensity, often catastrophic, wildfires that have become increasingly frequent across the Western U.S., according to a new study by researchers at Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health and Stanford University. The analysis reveals that low-intensity burning, such as controlled or prescribed fires, managed wildfires, and tribal cultural burning, can dramatically reduce the risk of devastating fires for years at a time. The findings are some of the first to rigorously quantify the value of low-intensity fire and be released while Congress is reassessing ...
Astrophysicist Jason Nordhaus is breaking cultural and disciplinary boundaries by helping to grow the number of deaf, hard-of-hearing, and Hispanic researchers. And, in doing so, he is enabling these future scientists to drive discoveries in one of his areas of expertise—neutron star astrophysics.
Nordhaus, an associate professor of physics at Rochester Institute of Technology’s National Technical Institute for the Deaf, has earned a National Science Foundation grant that connects NTID with Texas Tech University, a Hispanic Serving Institution. Through a series of unique summer research exchanges ...
Banding together to sell fishing rights could generate economic benefits for African countries, which receive far less from access to their fisheries on the global market than other countries do from theirs. By joining forces, UC Santa Barbara researchers say in a paper published in the journal Nature Communications, African fisheries would not just secure more competitive access fees, they could also protect their seas’ biodiversity.
“If African countries created a ‘fish cartel’ to sell fishing rights to foreign vessels, they could increase their fish biomass by 16% and make 23% more in profits,” ...
In patients with severe artery blockage in the lower leg, an artery-supporting device called a resorbable scaffold is superior to angioplasty, which has been the standard treatment, according to the results of a large international clinical trial co-led by researchers at Weill Cornell Medicine and NewYork-Presbyterian.
Angioplasty involves the widening of a narrowed artery with a small, balloon-like mechanism. A resorbable scaffold is a stent-like structure that props the artery open but is biodegradable and dissolves within a few years, avoiding some of the potential complications of a permanent ...
A compound—one of 27 million screened in a library of potential new drugs—reversed four types of chronic pain in animal studies, according to new research led by NYU College of Dentistry’s Pain Research Center and published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS).
The small molecule, which binds to an inner region of a calcium channel to indirectly regulate it, outperformed gabapentin without troublesome side effects, providing a promising candidate for treating pain.
Calcium channels play a central role in pain signaling, in part through the release of neurotransmitters such as glutamate and GABA— “the ...
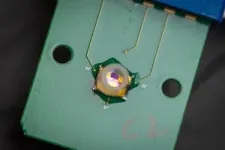
An international team of researchers has developed a handheld, non-invasive device that can detect biomarkers for Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Diseases. The biosensor can also transmit the results wirelessly to a laptop or smartphone.
The team tested the device on in vitro samples from patients and showed that it is as accurate as the state of the art. Ultimately, researchers plan to test saliva and urine samples with the biosensor. The device could be modified to detect biomarkers for other conditions as well.
Researchers present their findings ...
A research team from the University of Cologne, in collaboration with colleagues from the Leibniz Institute for Food Systems Biology in Freising, has discovered a receptor for bitter taste in twelve different cartilaginous fish (sharks and rays). The receptor belongs to the so-called taste receptors type 2 (T2R), which also make humans perceive bitter and potentially toxic foods. Until now, it was assumed that such receptors only occur in bony vertebrates. The work was published under the title ‘A singular shark bitter taste receptor provides insights into the evolution of bitter taste perception’ ...
To paraphrase Mark Twain, reports of declining phytoplankton in the North Atlantic may have been greatly exaggerated. A prominent 2019 study used ice cores in Antarctica to suggest that marine productivity in the North Atlantic had declined by 10% during the industrial era, with worrying implications that the trend might continue.
But new research led by the University of Washington shows that marine phytoplankton — on which larger organisms throughout the marine ecosystem depend — may be more stable than believed in the North Atlantic. The team’s analysis of an ice core going ...
People with arthritis who report more negative feelings about how they are aging tend to get less physical activity and perceive themselves as less healthy, according to a new study by researchers at Hospital for Special Surgery (HSS) and Weill Cornell Medicine. However, self-perception of good health explained the effect of negative thinking – providing an opportunity for clinicians to focus on a patient’s outlook on aging as well as their overall health.
“Physical activity is essential for older adults with arthritis, as it can help to reduce pain and stiffness, improve ...