H bond promoted hydride transfer
2023-11-14
(Press-News.org)
The precise catalytic conversion of chemical bonds is a paramount goal in catalysis. Enzymes, as efficient biocatalysts, are well known for their high catalytic activity, selectivity, and substrate specificity under mild reaction conditions, which can be attributed to the synergistic catalysis of multiple active sites. Inspired by the catalytic mechanism of enzymes, the rational design of catalysts with multiple active sites to stabilize TS and accelerate the rate-determining step is a promising strategy for achieving high activity and selectivity.
However, integrating multiple active sites into a single catalyst without interference during the catalytic process remains an enormous challenge because it is difficult to combine different functional groups together at will, particularly incompatible groups. Modularity is a method of decomposing complicated systems into various manageable submodules, each of which is independent of the other and works together in a certain way. Thus, it is highly desirable to construct a modularized catalytic system that mimics the synergistic catalysis of enzymes.
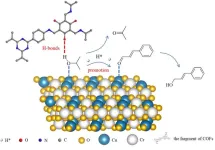
Recently, a research team led by Prof. Qihua Yang from Zhejiang Normal University, China, reported the construction of a modularized catalytic system for catalytic transfer hydrogenation (CTH) using covalent organic frameworks (COFs) and commercial Cu2Cr2O5 to simulate the function of amino acid groups and the active sites of enzymes, respectively. In the CTH of different aldehydes with isopropyl alcohol, the modularized catalytic system with both COFs and Cu2Cr2O5 demonstrates enormously enhanced activity compared to Cu2Cr2O5. Mechanistic investigations and theoretical calculations suggest that COFs can interact with the hydroxyl group of isopropyl alcohol through hydrogen bonds, facilitating the dehydrogenation of isopropyl alcohol and promoting hydrogen atom transfer between isopropanol and aldehydes, thus improving catalytic activity. In addition, the modularized catalytic system can be replaced by different submodules. The results were published in Chinese Journal of Catalysis (https://doi.org/10.1016/S1872-2067(23)64499-7).
###
About the Journal
Chinese Journal of Catalysis is co-sponsored by Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences and Chinese Chemical Society, and it is currently published by Elsevier group. This monthly journal publishes in English timely contributions of original and rigorously reviewed manuscripts covering all areas of catalysis. The journal publishes Reviews, Accounts, Communications, Articles, Highlights, Perspectives, and Viewpoints of highly scientific values that help understanding and defining of new concepts in both fundamental issues and practical applications of catalysis. Chinese Journal of Catalysis ranks at the top one journal in Applied Chemistry with a current SCI impact factor of 16.5. The Editors-in-Chief are Profs. Can Li and Tao Zhang.
At Elsevier http://www.journals.elsevier.com/chinese-journal-of-catalysis
Manuscript submission https://mc03.manuscriptcentral.com/cjcatal
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-11-14
Today marks the launch of The Transmitter, a new publication focused on helping neuroscientists stay current on the latest developments in the field and build new connections.
Created by the team that brings Spectrum to autism researchers, The Transmitter will provide essential news, insights and resources across neuroscience disciplines and career stages. Spectrum will continue to publish news and perspectives on autism research as an anchor of The Transmitter. Like Spectrum, The Transmitter is an editorially independent publication of the Simons Foundation.
“Neuroscience discoveries are rapidly shifting our understanding of ...
2023-11-14
Uncontrolled hypertension, the leading preventable risk factor for cardiovascular disease and premature deaths worldwide, disproportionately affects low-income populations.
Now, a new strategy that trains healthcare providers to deliver more comprehensive, team-based care has been found to significantly lower blood pressure in low-income patients compared to the “usual care” approach. The findings were reported by Tulane University researchers at this week’s American Heart Association Scientific Sessions in Philadelphia.
Tulane researchers conducted an 18-month clinical trial with 1,272 hypertension patients at 36 Federally Qualified Health Centers ...
2023-11-14
The majority of breast cancers start in the lining of a breast milk duct and, if they remain there, are very treatable. But once these cancers become invasive – breaking through a thin matrix around the duct, called the basement membrane, and spreading to the surrounding tissue – treatment becomes more challenging.
In a recent paper, published on Nov. 13 in Nature Materials, researchers at Stanford revealed a novel physical mechanism that breast cancer cells use to break out and become invasive. They found that, in addition to established chemical methods of degrading the basement membrane, cancer ...
2023-11-14
The production of ammonia for fertilisers – which has one of the largest carbon footprints among industrial processes – will soon be possible on farms using low-cost, low-energy and environmentally friendly technology.
This is thanks to researchers at UNSW Sydney and their collaborators who have developed an innovative technique for sustainable ammonia production at scale.
Up until now, the production of ammonia has relied on high-energy processes that leave a massive global carbon footprint – temperatures of more ...
2023-11-14
American Geophysical Union
13 November 2023
AGU Release No. 23-42
For Immediate Release
This press release and accompanying multimedia are available online at: https://news.agu.org/press-release/some-of-todays-earthquakes-may-be-aftershocks-from-quakes-in-the-1800s
Some of today’s earthquakes may be aftershocks from quakes in the 1800s
Aftershocks follow large earthquakes — sometimes for weeks, other times for decades. But in the U.S., some areas may be experiencing shocks from centuries-old events.
AGU press contact:
Liza Lester, +1 (202) 777-7494, news@agu.org (UTC-5 hours)
Contact ...
2023-11-14
A few decades ago, seismologists imaging the deep planet identified a thin layer, just over a few hundred kilometers thick. The origin of this layer, known as the E prime layer, has been a mystery — until now.
An international team of researchers, including Arizona State University scientists Dan Shim, Taehyun Kim and Joseph O’Rourke of the School of Earth and Space Exploration, has revealed that water from the Earth's surface can penetrate deep into the planet, altering the composition of the outermost region of the metallic liquid core and creating a distinct, thin layer. Illustration of silica crystals coming out from the liquid metal of ...
2023-11-14
Faster warming in the Arctic will be responsible for a global 2C temperature rise being reached eight years earlier than if the region was warming at the average global rate, according to a new modelling study led by UCL researchers.
The Arctic is currently warming nearly four times faster than the global average rate. The new study, published in the journal Earth System Dynamics, aimed to estimate the impact of this faster warming on how quickly the global temperature thresholds of 1.5C and 2C, set down in the Paris Agreement, are likely to be breached.
To do this, the research team created alternative ...
2023-11-14
Surrey scientists are celebrating with colleagues around the world, after winning new funding for a ‘library of greening’ – a new database enabling towns and cities to learn from each other's success developing green spaces, waterways and other sustainability initiatives.
The RECLAIM Network Plus provides a one-stop-shop for towns and cities looking to mitigate the impacts of climate change and improve their resilience. It has over 500 members worldwide, offering information and support to implement projects such as ...
2023-11-14
Investigators from the Antiphospholipid Syndrome Alliance for Clinical Trials and International Networking (APS ACTION) presented new research findings in antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) at the American College of Rheumatology (ACR) Convergence 2023, the ACR’s annual meeting.
Hospital for Special Surgery (HSS), one of the leading centers in the United States providing care for adults and children with APS, is the lead coordinating center for APS ACTION, an international research network of 34 academic institutions dedicated to advancing the understanding and management of APS. APS ACTION conducts large, ...
2023-11-14
A University of Texas at Arlington engineering researcher has received a NASA grant to use rotating detonation rocket engines (RDREs) for in-space propulsion to make them more efficient, compact and powerful.
Liwei Zhang, an assistant professor in the Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering (MAE), will lead the $900,000 grant.
“Detonation is very fast combustion. Inside an RDRE, detonation waves spin around in a circle at supersonic speeds. Compared to conventional engines that rely on regular combustion, an RDRE has a theoretically ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] H bond promoted hydride transfer





