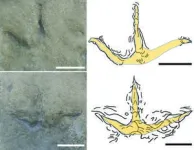
(Press-News.org) Early birds had made it to southern polar environments by 120 million years ago, according to a study published November 15, 2023 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Anthony Martin of Emory University, USA and colleagues.
Cretaceous bird fossils are abundant and diverse in northern continents, but extremely rare in southern continents, regions that were once part of the landmass of Gondwana. This presents a challenge for paleontologists trying to understand the distribution of early birds. In this study, Martin and colleagues report the discovery of a series of bird footprints from the Early Cretaceous (129-120 million years old) Wonthaggi Formation of Victoria, Australia.
The researchers described 27 individual footprints with features attributable to birds. The varying sizes and shapes of these tracks indicate the presence of several different types of birds, including some of the largest known from the Cretaceous Period. The tracks are present in multiple stratigraphic layers of an ancient polar floodplain, suggesting that these birds might have visited this area seasonally, perhaps as part of a migratory route.
Other than one bone and a few feathers, these tracks represent the oldest known evidence of birds living in Australia or any part of ancient Gondwana, and also the oldest known evidence of birds living in ancient polar environments. These findings have important implications for understanding how early birds dispersed across landmasses and biomes. It is possible that future efforts to seek early bird fossils in Gondwanan landmasses might reveal that they were more abundant in southern regions than the known fossil record has hitherto indicated.
The authors add: “We are very excited to document that a variety of birds were living in polar Australia during the Early Cretaceous Period. But we also hope our trace fossil discovery inspires other researchers to look for and find more Early Cretaceous bird tracks elsewhere in the Southern Hemisphere.”
#####
In your coverage please use this URL to provide access to the freely available article in PLOS ONE: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0293308
Citation: Martin AJ, Lowery M, Hall M, Vickers-Rich P, Rich TH, Serrano-Brañas CI, et al. (2023) Earliest known Gondwanan bird tracks: Wonthaggi Formation (Early Cretaceous), Victoria, Australia. PLoS ONE 18(11): e0293308. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0293308
Author Countries: USA, Australia
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work.
END
Australian footprints are the oldest known evidence of birds from southern regions
A diverse fauna of birds lived in southern polar regions during the Early Cretaceous
2023-11-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Treatment strategy for certain advanced prostate cancers shows promise in preclinical models
2023-11-15
Study Title: Targeting DNA methylation and B7-H3 in RB1-deficient and neuroendocrine prostate cancer
Publication: Science Translational Medicine [10.1126/scitranslmed.adf6732]
Dana-Farber Cancer Institute author: Himisha Beltran, MD
Summary: Epigenetic changes can cause prostate cancer to resist treatment by switching genes on or off. One epigenetic mechanism tags genes with DNA methylation marks. This process is mediated by molecules called DNA methyltransferases. These tags can alter gene expression in ways that promote tumors to grow and transition ...
Devil in the detail – What corporations aren’t disclosing about their C02 emissions
2023-11-15
A new study estimates most corporations are not reporting the full scope of their carbon footprint with many claiming to be ‘green’ despite a lack of reporting on Scope 3 key categories.
Though CO2 reporting is currently voluntary for most firms, corporations are under pressure from investors, regulators, politicians, non-profit organisations and other stakeholders to disclose and reduce greenhouse gas emissions (GHG).
The standard for greenhouse gas accounting, the Greenhouse Gas Protocol, is used worldwide to measure a company’s total carbon footprint with three levels of reporting.
The first measures the GHG emissions directly produced by a company ...
New ‘patch’ uses natural body motion to fix disc herniation
2023-11-15
PHILADELPHIA— A new biologic “patch” that is activated by a person’s natural motion could be the key to fixing herniated discs in people’s backs, according to researchers at the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania and the CMC VA Medical Center (CMCVAMC). Combining years of work from many different projects, the “tension-activated repair patches” (TARPs) provide controlled release of an anti-inflammatory molecule called anakinra from microcapsules over time, which helped ...
The liking gap is real for second language English speakers, new Concordia research shows
2023-11-15
A new study from Concordia’s Applied Linguistics Lab suggests that most people are usually overly harsh on themselves when speaking in a second language.
Writing in the journal Languages, PhD student Rachael Lindberg and her co-authors build on the previous understanding of individuals’ metaperception—a person’s idea of how they are perceived by others.
The idea that people frequently underestimate how likeable they are, known as the Liking Gap, ...
Study reveals link between neighborhood environmental burden and risk of cardiovascular disease
2023-11-15
BOSTON – A national study led by investigators at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC) demonstrates that neighborhood exposure to environmental hazards is significantly associated with poor cardiovascular health across the United States. The study, presented at the American Heart Association Scientific Sessions and simultaneously published in JAMA Cardiology, found that greater cumulative environmental burden (e.g., air pollution, nearby hazardous/toxic sites, poor built environment) was linked ...
Cancer: Discovery of the mechanisms regulating cancer formation
2023-11-15
To form a cancer, cells need to accumulate oncogenic mutations that confer tumor-initiating properties. However, recent evidence has shown that oncogenic mutations occur at a surprisingly high frequency in normal tissues, suggesting that mutations alone are not sufficient to drive cancer formation and that other mechanisms should promote or restrain oncogene-expressing cells from progressing into invasive tumors.
In a study published in Nature, researchers led by Prof. Cédric Blanpain, MD/PhD, investigator of the WEL Research Institute, Director of the Stem Cells and Cancer Laboratory and Professor at the Université ...
Researchers halt progression in Parkinson's disease mouse model
2023-11-15
BOSTON – In a study published in Nature Communications, investigators at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC) shed new light on key cellular processes involved in the progression of Parkinson’s disease (PD). Affecting around 10 million people worldwide, Parkinson's disease is a neurodegenerative disorder caused by the progressive loss of the group of brain cells responsible for producing dopamine, a neurotransmitter that plays a critical role in regulating movement and coordination. As these neurons degenerate and dopamine levels decrease, individuals with Parkinson's disease experience a wide range of symptoms, including ...
Study: People with obesity burn less energy during day
2023-11-15
PORTLAND, Oregon – Weight influences how and when bodies burn energy, new research indicates.
An Oregon Health & Science University study published in the journal Obesity found people who have a healthy weight use more energy during the day, when most people are active and eat, while those who have obesity spend more energy during the night, when most people sleep. The study also found that during the day, those with obesity have higher levels of the hormone insulin — a sign that the body is working harder to use glucose, an energy-packed sugar.
“It was surprising to learn how dramatically the timing of when our bodies burn energy differed in ...
Female MP pioneers lost unique appeal to voters because of increasing party control over campaigning, study shows
2023-11-15
Early women parliamentary candidates found it harder to make unique appeals to represent the ‘woman’s point of view’ over time because of increasing national control over campaigning, a new study shows.
The increasing trend for men to present themselves as diligent workers for their constituents’ welfare and keen supporters for social reform also meant they challenged the idea that only female politicians could represent their sex properly in parliament, researchers have found.
The first women parliamentary candidates built on the suffrage campaigners’ argument that there was a distinctive woman’s point of ...
Can gene expression predict if a brain tumor is likely to grow back?
2023-11-15
Doctors often prescribe radiation along with surgery to treat a brain tumor called meningioma that originates in the protective membranes surrounding the brain. But side effects from radiation can be serious, including memory loss and cognitive decline, so it’s important to know which patients really need it.
Now, researchers at UC San Francisco and Northwestern Medicine, in collaboration with 10 other medical centers, have found a highly accurate way to predict the best treatment for patients based ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Carsten Bönnemann, MD, joins St. Jude to expand research on pediatric catastrophic neurological disorders
Women use professional and social networks to push past the glass ceiling
Trial finds vitamin D supplements don’t reduce covid severity but could reduce long COVID risk
Personalized support program improves smoking cessation for cervical cancer survivors
Adverse childhood experiences and treatment-resistant depression
Psilocybin trends in states that decriminalized use
New data signals high demand in aesthetic surgery in southern, rural U.S. despite access issues
$3.4 million grant to improve weight-management programs
Higher burnout rates among physicians who treat sickle cell disease
Wetlands in Brazil’s Cerrado are carbon-storage powerhouses
Brain diseases: certain neurons are especially susceptible to ALS and FTD
Father’s tobacco use may raise children’s diabetes risk
Structured exercise programs may help combat “chemo brain” according to new study in JNCCN
The ‘croak’ conundrum: Parasites complicate love signals in frogs
Global trends in the integration of traditional and modern medicine: challenges and opportunities
Medicinal plants with anti-entamoeba histolytica activity: phytochemistry, efficacy, and clinical potential
What a releaf: Tomatoes, carrots and lettuce store pharmaceutical byproducts in their leaves
Evaluating the effects of hypnotics for insomnia in obstructive sleep apnea
A new reagent makes living brains transparent for deeper, non-invasive imaging
Smaller insects more likely to escape fish mouths
Failed experiment by Cambridge scientists leads to surprise drug development breakthrough
Salad packs a healthy punch to meet a growing Vitamin B12 need
Capsule technology opens new window into individual cells
We are not alone: Our Sun escaped together with stellar “twins” from galaxy center
Scientists find new way of measuring activity of cell editors that fuel cancer
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
[Press-News.org] Australian footprints are the oldest known evidence of birds from southern regionsA diverse fauna of birds lived in southern polar regions during the Early Cretaceous