(Press-News.org) Old people who follow a Mediterranean diet are at a lower risk of cognitive decline, according to a study published in the journal Molecular Nutrition and Food Research. The study provides new evidence for a better understanding of the biological mechanisms related to the impact of the diet on cognitive health in the ageing population.
The study is led by Mireia Urpí-Sardá, adjunct lecturer and member of the Biomarkers and Nutritional & Food Metabolomics research group of the Faculty of Pharmacy and Food Sciences, the Institute for Nutrition and Food Safety (INSA-UB), the Food and Nutrition Torribera Campus of the University of Barcelona, and the CIBER on Frailty and Healthy Ageing (CIBERFES).
This European study, part of the Joint Programming Initiative “A Healthy Diet for a Healthy Life” (JPI HDHL) was carried out over twelve years and it involved 840 people over 65 years of age (65% of whom were women) in the Bourdeaux and Dijon regions of France.
Healthy diet and cognitive performance
According to Cristina Andrés-Lacueva, UB professor and head of the CIBERFES group, “within the framework of the study, a dietary metabolomic index has been designed —based on biomarkers obtained from the participants’ serum— on the food groups that form part of the Mediterranean diet. Once this index is known, its association with cognitive impairment is evaluated”.
in the study, baseline levels of saturated and unsaturated fatty acids, gut microbiota-derived polyphenol metabolites and other phytochemicals in serum that reflect individual bioavailability were chosen as biomarkers. Some of these indicators have not only been recognized as marks of exposure to the main food groups of the Mediterranean diet but have also been held responsible for the health benefits of the Mediterranean dietary pattern.
The metabolome or set of metabolites — related to food and derived from gut microbiota activity — was studied through a large-scale quantitative metabolomic analysis from the serum of the participants without dementia, from the beginning of the study. Cognitive impairment was assessed by five neuropsychological tests over twelve years.
As a result, the study reveals a protective association between the score of the Mediterranean diet based on serum biomarkers and cognitive decline in older people.
Biomarkers to study the benefits of the diet
According to Mercè Pallàs, professor at the UB Neurosciences Institute (UBneuro), "the use of dietary pattern indices based on food-intake biomarkers is a step forward towards the use of more accurate and objective dietary assessment methodologies that take into account important factors such as bioavailability".
Expert Alba Tor-Roca, first author of the study and CIBERFES researcher at the UB, explains that “we found that adherence to Mediterranean diet assessed by a panel of dietary biomarkers is inversely associated with long-term cognitive decline in older people. These results support the use of these indicators in long-term follow-up assessments to observe the health benefits associated with the Mediterranean diet or other dietary patterns and therefore, guide personalized counselling at older ages”.
The study was carried out in collaboration with teams from the Department of Genetics, Microbiology and Statistics of the Faculty of Biology and the Department of Pharmacology, Toxicology and Therapeutic Chemistry of the Faculty of Pharmacy and Food Sciences of the UB. Teams from the University of Bordeaux and the INRAE centre at Clermont-Ferrand University (France), King’s College London (United Kingdom), the University of Amsterdam (the Netherlands) and the Parcelsus Medical University in Salzburg (Austria) have also participated.
Funding was obtained through the International Joint Programming Actions PCIN-2015-229, the European Regional Development Funds (ERDF) and from the former Ministry of Economy, Industry and Competitiveness (MINECO) through the Joint Programming Initiative “A Healthy Diet for a Healthy Life”.
END
Following a Mediterranean diet reduces the risk of cognitive decline in older people
Healthy diet and cognitive performance
2023-11-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
A deep-sea fish inspired researchers to develop supramolecular light-driven machinery
2023-11-17
The vision system, evolved over millions of years, is highly complex. To make vision sensitive throughout the whole range of visible wavelengths, Nature employs a supramolecular chemistry approach. The visual pigment, cis-retinal, changes its shape upon capturing a photon. This shape transformation is accompanied by changes in the supramolecular organization of the surrounding proteins, subsequently triggering a cascade of chemical signaling events that get amplified and eventually lead to visual perception in the brain.
“Some deep-sea fish have evolved antenna-like ...
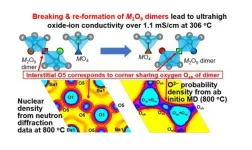
Shedding light on unique conduction mechanisms in a new type of perovskite oxide
2023-11-17
The remarkable proton and oxide-ion (dual-ion) conductivities of hexagonal perovskite-related oxide Ba7Nb3.8Mo1.2O20.1 are promising for next-generation electrochemical devices, as reported by scientists at Tokyo Tech. The unique ion-transport mechanisms they unveiled will hopefully pave the way for better dual-ion conductors, which could play an essential role in tomorrow’s clean energy technologies.
Clean energy technologies are the cornerstone of sustainable societies, and solid-oxide fuel cells (SOFCs) and proton ceramic fuel cells (PCFCs) are among the most promising types of electrochemical devices for green power generation. These devices, however, still ...
UK’s Rural Physician Leadership Program, Anthem Medicaid announce new rural medicine scholarships
2023-11-17
MOREHEAD, Ky. (Nov. 17, 2023) — In celebration of National Rural Health Day, yesterday the University of Kentucky College of Medicine and Anthem Blue Cross and Blue Shield Medicaid in Kentucky announced new scholarship opportunities for UK’s Rural Physician Leadership Program (RPLP). The Anthem Rural Medicine Scholarships will provide $100,000 to offset the cost of medical school for students in the RPLP.
In a state that suffers from high rates for many chronic, ...
Heart repair via neuroimmune crosstalk
2023-11-17
Unlike humans, zebrafish can completely regenerate their hearts after injury. They owe this ability to the interaction between their nervous and immune systems, as researchers led by Suphansa Sawamiphak from the Max Delbrück Center now report in the journal Developmental Cell.
Each year, more than 300,000 people in Germany have a myocardial infarction – the technical term for heart attack. The number of people surviving a heart attack has increased significantly, but this severe cardiac event causes irreparable damage to their hearts. A heart attack ...
BU researchers develop new method to help with analysis of single cell data
2023-11-17
(Boston)—CITE-seq (cellular indexing of transcriptomes and epitopes) is an RNA sequencing-based method that simultaneously quantifies cell surface protein and transcriptomic data within a single cell readout. The ability to study cells concurrently offers unprecedented insights into new cell types, disease states or other conditions.
While CITE-seq solves the problem of detecting a limited number of proteins while using single-cell sequencing in an unbiased way, one of its limitations is the high levels of background noise that can hinder analysis.
To rectify ...
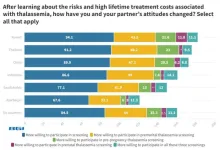
Azerbaijan women behind global average for thalassemia screening and genetic counselling | BGI Insight
2023-11-17
5.2% of the global population carry hemoglobin abnormalities, resulting in 300,000 to 400,000 children born with severe hemoglobinopathies annually. Thalassemia, a hereditary hemoglobinopathy, occurs in 4.4 out of every 10,000 live births, and is prevalent in Mediterranean coastal areas, Africa, the Middle East, Southeast Asia, and southern China.
To facilitate greater understanding of thalassemia, a hereditary hemoglobinopathy, BGI Genomics today released its State of Thalassemia Awareness Report. This report assesses the level of knowledge and attitudes related to the associated health risks, thalassemia carrier ...
Alliance and WEF sign agreement for Food Action Alliance
2023-11-17
The Alliance Bioversity International and CIAT signed an agreement with the World Economic Forum that enables the Alliance to manage initiatives under the Food Action Alliance, a movement led by the World Economic Forum for transforming sustainable food systems.
The Alliance would establish and manage initiatives in Latin America, the Caribbean, and other regions under the Food Action Alliance to boost the transformation of food systems, facilitating and scaling up multi-stakeholder flagship initiatives in specific countries mostly with multi-national companies such as Bayer, Microsoft, PepsiCo, AB InBev; among others.
The Food Action Alliance will continue to grow initiatives ...
USDA introduces a multi-year plan to strengthen U.S. genebank management of plant germplasm
2023-11-17
WASHINGTON, November 17, 2023 – The U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) released today the National Strategic Germplasm and Cultivar Collection Assessment and Utilization Plan in support of the Agricultural Research Service (ARS) U.S. National Plant Germplasm System’s (NPGS) mission.
The USDA-ARS NPGS is confident that implementing this plan will address current operational and research challenges. The collection is vital for maintaining the nation’s food supply by providing breeders and researchers the germplasm they need to furnish U. S. consumers with abundant, ...
Unravelling the secrets of neurodegenerative diseases, one protein at a time
2023-11-17
Proteins misfolding and clumping together, a process known as aggregation, is a key feature seen in several neurological conditions, including Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases.
These disorders involve the formation of small, potentially harmful structures called oligomers, which could serve as valuable indicators for early diagnosis. They are incredibly small, however, and much rarer than the healthy non-aggregated proteins. This makes it hard to detect and measure them accurately.
In collaboration with UCB Biopharma, researchers from the University of Edinburgh’s ...
A world's first in validating a UNFCCC report by a cost-efficient and transparent method to measure CO2 emission estimates using GOSAT
2023-11-17
Researchers in Japan and Mongolia have carried out the world's first instance of incorporating satellite-based CO2 emission estimates into a GHG emission report as the verification on the Second Biennial Update Report (BUR2) of Mongolia submitted to the UNFCCC on 15 November 2023, resulting in high accuracy match with actual reported values, reports a new study published online in Scientific Reports in 2023.
Countries have reported their CO2 emissions to the UNFCCC, primarily from human activities and a significant contributor to climate change. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
Researchers develop new strategy for improving inverted perovskite solar cells
Yes! The role of YAP and CTGF as potential therapeutic targets for preventing severe liver disease
Pancreatic cancer may begin hiding from the immune system earlier than we thought
[Press-News.org] Following a Mediterranean diet reduces the risk of cognitive decline in older peopleHealthy diet and cognitive performance