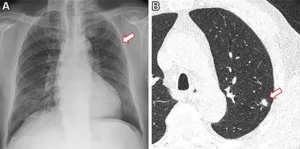
(Press-News.org) CHICAGO – Using a routine chest X-ray image, an artificial intelligence (AI) tool can identify non-smokers who are at high risk for lung cancer, according to a study being presented next week at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
Lung cancer is the most common cause of cancer death. The American Cancer Society estimates about 238,340 new cases of lung cancer in the United States this year and 127,070 lung cancer deaths. Approximately 10-20% of lung cancers occur in “never-smokers” – people who have never smoked cigarettes or smoked fewer than 100 cigarettes in their lifetime.
The United States Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) currently recommends lung cancer screening with low-dose CT for adults between the ages of 50 and 80 who have at least a 20 pack-year smoking history and currently smoke or have quit within the past 15 years. The USPSTF does not recommend screening for individuals who have never smoked or who have smoked very little. However, incidence of lung cancer among never-smokers is on the rise, and—without early detection through screening—when discovered, these cancers tend to be more advanced than those found in smokers.
“Current Medicare and USPSTF guidelines recommend lung cancer screening CT only for individuals with a substantial smoking history,” said the study’s lead author, Anika S. Walia, B.A., a medical student at Boston University School of Medicine and researcher at the Cardiovascular Imaging Research Center (CIRC) at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) and Harvard Medical School in Boston. “However, lung cancer is increasingly common in never-smokers and often presents at an advanced stage.”
One reason federal guidelines exclude never-smokers from screening recommendations is because it is difficult to predict lung cancer risk in this population. Existing lung cancer risk scores require information that is not readily available for most individuals, such as family history of lung cancer, pulmonary function testing or serum biomarkers.
For the study, CIRC researchers set out to improve lung cancer risk prediction in never-smokers by testing whether a deep learning model could identify never-smokers at high risk for lung cancer, based on their chest X-rays from the electronic medical record. Deep learning is an advanced type of AI that can be trained to search X-ray images to find patterns associated with disease.
“A major advantage to our approach is that it only requires a single chest-X-ray image, which is one of the most common tests in medicine and widely available in the electronic medical record,” Walia said.
The “CXR-Lung-Risk” model was developed using 147,497 chest X-rays of 40,643 asymptomatic smokers and never-smokers from the Prostate, Lung, Colorectal, and Ovarian (PLCO) cancer screening trial to predict lung-related mortality risk, based on a single chest X-ray image as input.
The researchers externally validated the model in a separate group of never-smokers having routine outpatient chest X-rays from 2013 to 2014. The primary outcome was six-year incident lung cancer, identified using International Classification of Disease codes. Risk scores were then converted to low, moderate and high-risk groups based on externally derived risk thresholds.
Of 17,407 patients (mean age 63 years) included in the study, 28% were deemed high risk by the deep learning model, and 2.9% of these patients later had a diagnosis of lung cancer. The high-risk group well exceeded the 1.3% six-year risk threshold where lung cancer screening CT is recommended by National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines.
After adjusting for age, sex, race, previous lower respiratory tract infection and prevalent chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, there was still a 2.1 times greater risk of developing lung cancer in the high-risk group compared to the low-risk group.
“This AI tool opens the door for opportunistic screening for never-smokers at high risk of lung cancer, using existing chest X-rays in the electronic medical record,” said senior author Michael T. Lu, M.D., M.P.H., director of artificial intelligence and co-director of CIRC at MGH. “Since cigarette smoking rates are declining, approaches to detect lung cancer early in those who do not smoke are going to be increasingly important.”
Additional co-authors are Saman Doroodgar Jorshery, M.D., Ph.D., and Vineet K. Raghu, Ph.D.
The researchers report support from the Boston University School of Medicine Student Committee on Medical School Affairs, National Academy of Medicine/Johnson & Johnson Innovation Quickfire Challenge, and the Risk Management Corporation of the Harvard Medical Institutions Incorporated.
###
Note: Copies of RSNA 2023 news releases and electronic images will be available online at RSNA.org/press23.
RSNA is an association of radiologists, radiation oncologists, medical physicists and related scientists promoting excellence in patient care and health care delivery through education, research and technologic innovation. The Society is based in Oak Brook, Illinois. (RSNA.org)
Editor’s note: The data in these releases may differ from those in the published abstract and those actually presented at the meeting, as researchers continue to update their data right up until the meeting. To ensure you are using the most up-to-date information, please call the RSNA Newsroom at 1-312-791-6610.
For patient-friendly information on lung cancer screening, visit RadiologyInfo.org.
END
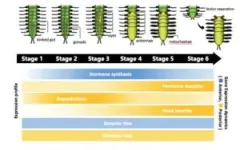
A research team, led by Professor Toru Miura from the University of Tokyo, shows how the expression of developmental genes in the Japanese green syllid worms, Megasyllis nipponica, helps form their swimming reproductive unit called stolon.
Life always finds ways to surprise us. The presence of a unique reproductive mechanism of some annelid worms or segmented worms is one such surprise. In a process called stolonization, the posterior body part with gonads of the syllid worm detaches from its original body. The detached part is called the stolon, and it is full of gametes (eggs or sperms). The stolon swims around by itself and spawns when it ...
Becoming a parent is a key turning point for adopted people
Parenting is always challenging, but for adopted people becoming a mum or dad can be extra demanding, as well as extra special – according to research from the University of East Anglia.
A new study is the first in to investigate the lived experiences of adopted people in the UK as they become parents.
It finds that they are affected by issues that link back to their adoption and to difficult experiences in their past – related to loss, rejection, abuse and neglect.
Because of these ...
Anti-rheumatic drugs used for rheumatoid arthritis might prevent the development of autoimmune thyroid disease, according to a new observational study by researchers from Karolinska Institutet published in the Journal of Internal Medicine.
It is well known that patients with rheumatoid arthritis are at increased risk of autoimmune thyroid diseases such as Hashimoto's disease and Graves' disease. While patients with RA are usually treated with immunomodulatory drugs that affect the immune system, such drugs are rarely used in autoimmune thyroid diseases. Instead, such patients are treated with thyroid hormone to compensate for the changes in normal ...
During missions into space, astronauts are exposed to high levels of galactic cosmic radiation and weightlessness. Simulation experiments in male rats indicated that these aspects of spaceflight can negatively affect vascular tissues relevant to erectile dysfunction, even after a period of long-term recovery.
The research, which is published in The FASEB Journal, indicated that vascular alterations are induced by relatively low doses of galactic cosmic radiation and to a lesser extent simulated weightlessness, primarily through increases in oxidative stress. Treatment with different antioxidants could counter some of these ...
Advances in areas such as robotics and artificial intelligence enable the automation of a range of occupational tasks, leading to fundamental changes in the nature of work. New research published in The American Journal of Economics and Sociology indicates that the effects of job automation vary across race and gender, and without targeted interventions, will likely result in increasing inequality.
The research analyzes two distinct measures of automation job displacement risk for more than 1.4 million Americans across 385 occupations. The findings show that the intersection of race and gender has a significant effect on automation risks. For example, ...
Results from a study published in the American Journal of Human Biology suggest that the COVID-19 pandemic has had negative effects on bone tissue—including both bone mineral density in the forearm and total bone mineral content.
The study by investigators at Comenius University, in Slovakia, included 387 young adults whose bone health measurements were taken prior to the COVID-19 pandemic and 386 whose measurements were taken from September 2020 to November 2022 during the pandemic. Individuals participated in the study only once, either before or during the pandemic.
Certain lifestyle changes during the pandemic may have contributed ...
Cell therapy represents a potential regenerative treatment for osteoarthritis. A recent analysis of all relevant published studies indicates that stem cell transplantation from different sources is effective for treating knee osteoarthritis, the most prevalent chronic joint disease.
The review and meta-analysis, which is published in the Journal of Orthopaedic Research, included 16 studies involving 875 patients with knee osteoarthritis (441 in the stem cell transplantation group and 434 in the control group). Stem cell treatment was associated with significant reductions in patient-reported pain from the third month onwards. The most significant pain relief at different postoperative months ...
New research indicates that acoustic stimulation of the brain may ease persistent symptoms in individuals who experienced mild traumatic brain injury in the past.
The study, which is published in Annals of Clinical and Translational Neurology, included 106 military service members, veterans, or their spouses with persistent symptoms after mild traumatic brain injury 3 months to 10 years ago. Participants were randomized 1:1 to receive 10 sessions of engineered tones linked to brainwaves (intervention), or random ...
ResearchGate, the professional network for researchers, and Pensoft, an independent open access academic publisher known worldwide for its cutting-edge publishing tools and workflows, today announced a new partnership that will see a set of Pensoft’s open access journals increase their reach and visibility through ResearchGate – increasing access and engagement with its 25 million researcher members.
Pensoft is a fully open access publisher, providing high-quality end-to-end services to its own and third-party scientific journals via its in-house developed scholarly publishing platform ARPHA.
As part of this new partnership, ...
Experts have delivered a sweeping prescription to governments, civil society and industry for a globally coordinated approach to the responsible sourcing of raw materials needed to achieve a circular green economy.
In a report, the four-year EU-funded RE-SOURCING project proposes adopting the global vision of a circular economy and reduced resource consumption by 2050 and outlines a series of interim milestones and targets for three key industrial sectors: renewable energy, mobility, and electric and electronic equipment.
The report (at https://bit.ly/3uqXlqT from ...