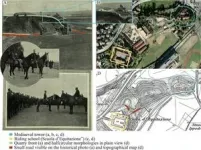
(Press-News.org) The Iron Age site of Casas del Turuñuelo was used repeatedly for ritualized animal sacrifice, according to a multidisciplinary study published November 22, 2023 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Mª Pilar Iborra Eres of the Institut Valencià de Conservació, Restauració i Investigació, Spain, Sebastián Celestino Pérez of Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas, Spain, and their colleagues.
Archaeological sites with evidence of major animal sacrifices are rarely known from the Iron Age of the Mediterranean region, and there is a gap between information offered by written sources and by the archaeological record. This makes it difficult to establish a clear understanding of the patterns and protocols of this practice. In this study, researchers examine a well-preserved example of mass animal sacrifice from an Iron Age building in southwest Spain known as Casas del Turuñuelo, associated to Tartessos and dating toward the end of the 5th Century BCE.
The authors examined and dated 6770 bones belonging to 52 sacrificed animals which were buried in three sequential phases. The identified animals were predominantly adult horses, with smaller numbers of cattle and pigs and one dog. In the first two phases, skeletons were mostly complete and unaltered, but in the third phase, skeletons (except equids) show signs of having been processed for food, suggesting that some sort of meal accompanied this ritual. These data indicate that this space was used repeatedly over several years for sacrificial rituals whose practices and purposes varied.
This case study allows researchers to establish details about ritual protocols at this site, including the intentional selection of adult animals rather than young, and the importance of fire evidenced by the presence of burned plant and animal remains. Casas del Turuñuelo also exhibits unique features compared to other sites, such as the high abundance of sacrificed horses. This study advances efforts to contextualize ritual animal sacrifices across Europe.
The authors add: “This study highlights the role of mass animal sacrifices in the context of Iron Age European societies. Zooarchaeological, taphonomic and microstratigraphic investigations shed light on animal sacrifice practices and the Tartessian ritual behavior at the Iron Age site of Casas del Turuñuelo (Badajoz, Spain).”
#####
In your coverage please use this URL to provide access to the freely available article in PLOS ONE: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0293654
Citation: Iborra Eres MP, Albizuri S, Gutiérrez Rodríguez M, Jiménez Fragoso J, Lira Garrido J, Martín Cuervo M, et al. (2023) Mass animal sacrifice at casas del Turuñuelo (Guareña, Spain): A unique Tartessian (Iron Age) site in the southwest of the Iberian Peninsula. PLoS ONE 18(11): e0293654. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0293654
Author Countries: Spain, France
Funding: The financial support and the results of this study stem from the National Project Construyendo Tarteso 2.0 I+D+I PID2019-108180GB-I00 ʽAnálisis constructivo, espacial y territorial de un modelo arquitectónico en el valle Medio del Guadianaʼ and from two projects of the Junta de Extremadura: PRI I+D+I IB18131 ‘Estudio de la hecatombe animal del yacimiento de ‘Casas del Turuñuelo’ (Guareña, Badajoz). La gestión de la cabaña equina y sus implicaciones socioeconómicas y rituales en época tartésica’ and PRI I+D+I IB18060 ‘Iberia a través de sus caballos: Estudio integral de la diversidad genética, enfermedades infecciosas y paleopatologías de los caballos extremeños de la Edad del Hierro’.
END
Casas del Turuñuelo, a site of repeated animal sacrifice in Iron Age Spain
Detailed analysis reveals rituals of mass sacrifice of horses and other animals
2023-11-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Earliest known European common hippopotamus fossil reveals their Middle Pleistocene dispersal
2023-11-22
Modern hippos first dispersed in Europe during the Middle Pleistocene, according to a study published November 22, 2023 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Beniamino Mecozzi of the Sapienza University of Rome and colleagues.
Modern hippos, Hippopotamus amphibius, arose from African ancestors during the Quaternary, a time when hippos were widespread in Europe. However, the details of the modern species’ origin and dispersal into Europe are unclear and highly debated. In this study, Mecozzi and colleagues provide new insights via analysis of a fossil hippo skull from the study area of Tor di Quinto in Rome.
The skull of Tor di Quinto, currently housed at the ...
Status threat - the concern that outsiders will undermine your group's status - is associated with increased age, conservatism, conspiracy mentality, and paranoia, in study of 300 US adults
2023-11-22
Status threat - the concern that outsiders will undermine your group's status - is associated with increased age, conservatism, conspiracy mentality, and paranoia, in study of 300 US adults
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0293930
Article Title: Conspiracy mentality, subclinical paranoia, and political conservatism are associated with perceived status threat
Author Countries: USA
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work. END ...
Transplanting gut microbes from an obesity-resistant shrew can improve microbiome diversity and decrease the weight of obese mice
2023-11-22
Transplanting gut microbes from an obesity-resistant shrew can improve microbiome diversity and decrease the weight of obese mice
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0293213
Article Title: Gut microbiota of Suncus murinus, a naturally obesity-resistant animal, improves the ecological diversity of the gut microbiota in high-fat-diet-induced obese mice
Author Countries: Japan, China
Funding: This work (PONE-D-23-21281) was supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the ...
Airborne virus infectivity can be reduced by up to 99.98% by commercially available NPBI-based air purifiers, per experiment using real-world concentrations of COVID-19 strains, flu and RSV viruses
2023-11-22
Airborne virus infectivity can be reduced by up to 99.98% by commercially available NPBI-based air purifiers, per experiment using real-world concentrations of COVID-19 strains, flu and RSV viruses
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0293504
Article Title: Bipolar ionization rapidly inactivates real-world, airborne concentrations of infective respiratory viruses
Author Countries: USA
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work. All research and 3rd party laboratory testing was funded entirely by GPS Air. Edward Sobek is an employee of GPS Air ...
7 in 8 homicide victims in South Africa are male
2023-11-22
7 in 8 homicide victims in South Africa are male, with homicide rates peaking on weekends and holidays, and firearms and sharp items being the most common murder weapons, in analysis of almost 20,000 2017 post-mortems. END ...
In Nepalese survey, 1 in 5 men who have sex with men report having attempted suicide, with over 40 percent experiencing some suicidal ideation
2023-11-22
In Nepalese survey, 1 in 5 men who have sex with men report having attempted suicide, with over 40 percent experiencing some suicidal ideation.
####
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/globalpublichealth/article?id=10.1371/journal.pgph.0002348
Article Title: Suicidal ideation, plan, and attempt among men who have sex with men in Nepal: Findings from a cross-sectional study
Author Countries: Nepal, USA
Funding: RS received funding from the National Institute on Drug Abuse (Award Number: K01DA051346). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision ...
New tool to enable exploration of human-environment interactions
2023-11-22
Spurred by the current climate crisis, there has been a heightened attention within the scientific community in recent years to how past climate variation contributed to historic human migration and other behaviors.
Now, an international group of scientists — including archaeologists, historians, climate scientists, paleo-scientists, a volcanologist and others — are calling for a strengthened commitment to transdisciplinary collaboration to study past and present human-environmental interactions, which they say will advance our understanding of these complex, entangled histories. Their recommendations were published ...
Researchers pinpoint brain area where people who are blind recognize faces identified by sound
2023-11-22
WASHINGTON – Using a specialized device that translates images into sound, Georgetown University Medical Center neuroscientists and colleagues showed that people who are blind recognized basic faces using the part of the brain known as the fusiform face area, a region that is crucial for the processing of faces in sighted people.
The findings appeared in PLOS ONE on November 22, 2023.
“It’s been known for some time that people who are blind can compensate for their loss of vision, ...
Cognitive ability mattered in the UK’s vote for Brexit, University of Bath research shows
2023-11-22
Susceptibility to misinformation and disinformation likely to have played part in Leave vote
New research from the University of Bath’s School of Management finds that higher cognitive ability was strongly linked to voting to Remain in the 2016 UK referendum on European Union Membership.
The study shows that cognitive skills including memory, verbal fluency, fluid reasoning and numerical reasoning, were correlated with how people decided to vote.
Lead author Dr Chris Dawson, from the University of Bath’s School of Management, said: “This study adds to existing academic evidence showing that low ...
Autonomous excavator constructs a 6-meter-high dry-stone wall
2023-11-22
ETH Zurich researchers deployed an autonomous excavator, called HEAP, to build a six metre-high and sixty-five-metre-long dry-stone wall. The wall is embedded in a digitally planned and autonomously excavated landscape and park.
The team of researchers included: Gramazio Kohler Research, the Robotics Systems Lab, Vision for Robotics Lab, and the Chair of Landscape Architecture. They developed this innovative design application as part of the National Centre of Competence in Research for Digital Fabrication ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
[Press-News.org] Casas del Turuñuelo, a site of repeated animal sacrifice in Iron Age SpainDetailed analysis reveals rituals of mass sacrifice of horses and other animals