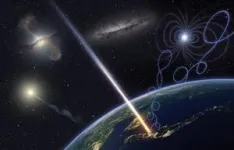
In 1991, the University of Utah Fly’s Eye experiment detected the highest-energy cosmic ray ever observed. Later dubbed the Oh-My-God particle, the cosmic ray’s energy shocked astrophysicists. Nothing in our galaxy had the power to produce it, and the particle had more energy than was theoretically possible for cosmic rays traveling to Earth from other galaxies. Simply put, the particle should not exist.
The Telescope Array has since observed more than 30 ultra-high-energy cosmic rays, though none approaching the Oh-My-God-level energy. No observations have yet revealed their origin or how they are able to travel to the Earth.
On May 27, 2021, the Telescope Array experiment detected the second-highest extreme-energy cosmic ray. At 2.4 x 1020eV, the energy of this single subatomic particle is equivalent to dropping a brick on your toe from waist height. Led by the University of Utah (the U) and the University of Tokyo, the Telescope Array consists of 507 surface detector stations arranged in a square grid that covers 700 km2 (~270 miles2) outside of Delta, Utah in the state’s West Desert. The event triggered 23 detectors at the north-west region of the Telescope Array, splashing across 48 km2 (18.5 mi2). Its arrival direction appeared to be from the Local Void, an empty area of space bordering the Milky Way galaxy.
“The particles are so high energy, they shouldn’t be affected by galactic and extra-galactic magnetic fields. You should be able to point to where they come from in the sky,” said John Matthews, Telescope Array co-spokesperson at the U and co-author of the study. “But in the case of the Oh-My-God particle and this new particle, you trace its trajectory to its source and there’s nothing high energy enough to have produced it. That’s the mystery of this—what the heck is going on?”
In their observation that published on Nov. 24, 2023, in the journal Science, an international collaboration of researchers describe the ultra-high-energy cosmic ray, evaluate its characteristics, and conclude that the rare phenomena might follow particle physics unknown to science. The researchers named it the Amaterasu particle after the sun goddess in Japanese mythology. The Oh-My-God and the Amaterasu particles were detected using different observation techniques, confirming that while rare, these ultra-high energy events are real.
“These events seem like they're coming from completely different places in the sky. It’s not like there's one mysterious source,” said John Belz, professor at the U and co-author of the study. “It could be defects in the structure of spacetime, colliding cosmic strings. I mean, I’m just spit-balling crazy ideas that people are coming up with because there's not a conventional explanation.”
Natural particle accelerators
Cosmic rays are echoes of violent celestial events that have stripped matter to its subatomic structures and hurled it through universe at nearly the speed of light. Essentially cosmic rays are charged particles with a wide range of energies consisting of positive protons, negative electrons, or entire atomic nuclei that travel through space and rain down onto Earth nearly constantly.
Cosmic rays hit Earth’s upper atmosphere and blasts apart the nucleus of oxygen and nitrogen gas, generating many secondary particles. These travel a short distance in the atmosphere and repeat the process, building a shower of billions of secondary particles that scatter to the surface. The footprint of this secondary shower is massive and requires that detectors cover an area as large as the Telescope Array. The surface detectors utilize a suite of instrumentation that gives researchers information about each cosmic ray; the timing of the signal shows its trajectory and the amount of charged particles hitting each detector reveals the primary particle’s energy.
Because particles have a charge, their flight path resembles a ball in a pinball machine as they zigzag against the electromagnetic fields through the cosmic microwave background. It’s nearly impossible to trace the trajectory of most cosmic rays, which lie on the low- to middle-end of the energy spectrum. Even high-energy cosmic rays are distorted by the microwave background. Particles with Oh-My-God and Amaterasu energy blast through intergalactic space relatively unbent. Only the most powerful of celestial events can produce them.
“Things that people think of as energetic, like supernova, are nowhere near energetic enough for this. You need huge amounts of energy, really high magnetic fields to confine the particle while it gets accelerated,” said Matthews.
Ultra-high-energy cosmic rays must exceed 5 x 1019 eV. This means that a single subatomic particle carries the same kinetic energy as a major league pitcher’s fast ball and has tens of millions of times more energy than any human-made particle accelerator can achieve. Astrophysicists calculated this theoretical limit, known as the Greisen–Zatsepin–Kuzmin (GZK) cutoff, as the maximum energy a proton can hold traveling over long distances before the effect of interactions of the microwave background radiation take their energy. Known source candidates, such as active galactic nuclei or black holes with accretion disks emitting particle jets, tend to be more than 160 million light years away from Earth. The new particle’s 2.4 x 1020 eV and the Oh-My-God particle’s 3.2 x 1020 eV easily surpass the cutoff.
Researchers also analyze cosmic ray composition for clues of its origins. A heavier particle, like iron nuclei, are heavier, have more charge and are more susceptible to bending in a magnetic field than a lighter particle made of protons from a hydrogen atom. The new particle is likely a proton. Particle physics dictates that a cosmic ray with energy beyond the GZK cutoff is too powerful for the microwave background to distort its path, but back tracing its trajectory points towards empty space.
“Maybe magnetic fields are stronger than we thought, but that disagrees with other observations that show they’re not strong enough to produce significant curvature at these ten-to-the-twentieth electron volt energies,” said Belz. “It’s a real mystery.”
Expanding the footprint
The Telescope Array is uniquely positioned to detect ultra-high-energy cosmic rays. It sits at about 1,200 m (4,000 ft), the elevation sweet-spot that allows secondary particles maximum development, but before they start to decay. Its location in Utah’s West Desert provides ideal atmospheric conditions in two ways: the dry air is crucial because humidity will absorb the ultraviolet light necessary for detection; and the region’s dark skies are essential, as light pollution will create too much noise and obscure the cosmic rays.
Astrophysicists are still baffled by the mysterious phenomena. The Telescope Array is in the middle of an expansion that that they hope will help crack the case. Once completed, 500 new scintillator detectors will expand the Telescope Array will sample cosmic ray-induced particle showers across 2,900 km2 (1,100 mi2 ), an area nearly the size of Rhode Island. The larger footprint will hopefully capture more events that will shed light on what’s going on.
END